English HKSI Paper 3 Topic 1
This post is also available in: 繁體中文 (Chinese (Traditional)) English

HKSIP3ET1
Quiz-summary
0 of 108 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
Information
HKSIP3ET1
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 108 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Topic 1 0%
-
HKSIP3ET1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 108
1. Question
1 pointsQID835:Which of the following is not a derivative/ structural product of company A?
Correct
Answer A is not an structured product since the return of none of them is tied to the other in any way.
Incorrect
Answer A is not an structured product since the return of none of them is tied to the other in any way.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.1.1
-
Question 2 of 108
2. Question
1 pointsQID2396:Which of the following people can trade stock options directly?
Correct
People who hold rights to trade and have registered to be participants of options exchanges can trade stock options directly. Although market participants have to be type 1 licensed corporations, type 1 licensed corporations don’t necessarily hold rights to trade and are registered as market participants.
Incorrect
People who hold rights to trade and have registered to be participants of options exchanges can trade stock options directly. Although market participants have to be type 1 licensed corporations, type 1 licensed corporations don’t necessarily hold rights to trade and are registered as market participants.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.1.4
-
Question 3 of 108
3. Question
1 pointsQID2724:Which of the following is not an objective of the Securities and Futures Ordinance?
Correct
Objectives of the SFO:
I. Promoting fair, orderly and transparent markets
II. Build an advanced technological infrastructure that is flexible enough to accommodate new products and other new services
III. Regulators are highly transparent and accountable to stakeholders through a mechanism of checks and balancesPromoting cooperation among financial regulators around the world is not the goal of the SFO.
Incorrect
Objectives of the SFO:
I. Promoting fair, orderly and transparent markets
II. Build an advanced technological infrastructure that is flexible enough to accommodate new products and other new services
III. Regulators are highly transparent and accountable to stakeholders through a mechanism of checks and balancesPromoting cooperation among financial regulators around the world is not the goal of the SFO.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.1
-
Question 4 of 108
4. Question
1 pointsQID186:Which of the following descriptions about the single license regime is correct?
Correct
Although there are ten types of regulated activity, the SFC will grant to a person only one licence (or registration) which will enable the holder to undertake one or more of the ten regulated activities. This is normally referred to as the “single licence regime”.
Incorrect
Although there are ten types of regulated activity, the SFC will grant to a person only one licence (or registration) which will enable the holder to undertake one or more of the ten regulated activities. This is normally referred to as the “single licence regime”.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.15
-
Question 5 of 108
5. Question
1 pointsQID187:Although there are ten types of regulated activity, the SFC will grant to a person only one licence (or registration) which will enable the holder to undertake one or more of the ten regulated activities. This is normally referred to as the
Correct
Although there are ten types of regulated activity, the SFC will grant to a person only one licence (or registration) which will enable the holder to undertake one or more of the ten regulated activities. This is normally referred to as the “single licence regime”.
Incorrect
Although there are ten types of regulated activity, the SFC will grant to a person only one licence (or registration) which will enable the holder to undertake one or more of the ten regulated activities. This is normally referred to as the “single licence regime”.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.15
-
Question 6 of 108
6. Question
1 pointsQID228:If an AFI wishes to conduct regulated activities as defined by the SFO, which of the following entities should it approach for it to be licensed or registered?
Correct
AFIs (including banks) that are authorised and regulated by the HKMA and conduct the SFC regulated activities must be registered with the SFC as “Registered Institutions”, such status having been set up as a special category because of the special features of AFIs.
Incorrect
AFIs (including banks) that are authorised and regulated by the HKMA and conduct the SFC regulated activities must be registered with the SFC as “Registered Institutions”, such status having been set up as a special category because of the special features of AFIs.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 7 of 108
7. Question
1 pointsQID33:British Construction Bank is an AFI regulated by the HKMA. Which of the following entities is responsible for supervising the regulated activities it conducts under the SFO?
Correct
The HKMA and the SFC must work closely together in relation to any SFC-regulated activities that are carried out by registered
institutions. To this end, a memorandum of understanding (“MOU”) has been signed between the two regulators, setting out their roles and responsibilities so as to minimise overlaps under the regulatory regime.Incorrect
The HKMA and the SFC must work closely together in relation to any SFC-regulated activities that are carried out by registered
institutions. To this end, a memorandum of understanding (“MOU”) has been signed between the two regulators, setting out their roles and responsibilities so as to minimise overlaps under the regulatory regime.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 8 of 108
8. Question
1 pointsQID32:Which of the following descriptions are correct?
I. All banks in Hong Kong are supervised by the SFC.
II. Some of the activities conducted by registered institutions are regulated by the SFO.
III. A memorandum of understanding (“MOU”) has been signed between the SFC and the HKMA to minimize regulatory overlaps.
IV. The Insurance Authority is the major regulator of the insurance industry in Hong Kong.Correct
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. Clearly, the HKMA and the SFC must work closely together in relation to any SFC-regulated activities that are carried out by registered institutions. To this end, a memorandum of understanding (“MOU”) has been signed between the two regulators, setting out their roles and responsibilities so as to minimise overlaps under the regulatory regime. The Insurance Authority is the major regulator of the insurance industry in Hong Kong.
Incorrect
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. Clearly, the HKMA and the SFC must work closely together in relation to any SFC-regulated activities that are carried out by registered institutions. To this end, a memorandum of understanding (“MOU”) has been signed between the two regulators, setting out their roles and responsibilities so as to minimise overlaps under the regulatory regime. The Insurance Authority is the major regulator of the insurance industry in Hong Kong.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 9 of 108
9. Question
1 pointsQID31:Which of the following is the regulator of Authorised Financial
Institutions?Correct
As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.
Incorrect
As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 10 of 108
10. Question
1 pointsQID30:Which of the following is the regulator of Registered Institutions?
Correct
As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out
on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.Incorrect
As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out
on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 11 of 108
11. Question
1 pointsQID28:Which entity is the frontline regulator of registered institution that conducts regulated activity as defined by the SFO?
Correct
As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out on-site inspections.
Incorrect
As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out on-site inspections.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 12 of 108
12. Question
1 pointsQID341:A person engaging in any activity regulated by the SFO, which includes asset management, will need to be licensed by the
Correct
Any person that wish to conduct a regulated activity must be licensed by the SFC.
Incorrect
Any person that wish to conduct a regulated activity must be licensed by the SFC.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 13 of 108
13. Question
1 pointsQID25:British Construction Bank is an authorised financial institution (AFI). Due to the rapid development of the securities markets, the company plans to provide securities trading services to its customer. How should the company proceed?
Correct
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as
registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.Incorrect
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as
registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 14 of 108
14. Question
1 pointsQID29:Which of the following descriptions about Authorised Financial
Institutions (AFI) are true?
I. All Registered Institutions are banks.
II. If the AFIs are conducting the regulated activities as defined by the SFO, the AFIs should register with the SFC.
III. SFC is responsible for licensing AFIs for all businesses
IV. The HKMA may refer cases of suspected malpractice by registered institutions in respect of the SFC-regulated activities to the SFCCorrect
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. The HKMA may refer cases of suspected malpractice by registered institutions in respect of the SFC-regulated activities to the SFC, which may directly review those institutions.
Incorrect
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. The HKMA may refer cases of suspected malpractice by registered institutions in respect of the SFC-regulated activities to the SFC, which may directly review those institutions.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 15 of 108
15. Question
1 pointsQID24:If an AFI plans to conduct regulated activities as defined by the SFO, which of the following entities should it register with ?
Correct
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity.
Incorrect
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 16 of 108
16. Question
1 pointsQID23:British Construction Bank is an AFI regulated by the HKMA. If it plans to conduct Type 9 Regulated Activity (Asset Management) in the near future, how should it proceed?
Correct
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity.
Incorrect
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 17 of 108
17. Question
1 pointsQID232:If an Authorised Financial Institution wishes to conduct regulated activities as defined by the SFO, which of the following entities should oversee its operation?
Correct
AFIs (including banks) that are authorised and regulated by the HKMA and conduct the SFC regulated activities must be registered with the SFC as “Registered Institutions”, such status having been set up as a special category because of the special features of AFIs. They are jointly regulated by the HKMA and the SFC, with the HKMA being the front-line regulator that will apply all SFC regulatory criteria, including fitness and properness and business conduct, other than capital adequacy, the handling of client money and the audit requirements in supervising them.
Incorrect
AFIs (including banks) that are authorised and regulated by the HKMA and conduct the SFC regulated activities must be registered with the SFC as “Registered Institutions”, such status having been set up as a special category because of the special features of AFIs. They are jointly regulated by the HKMA and the SFC, with the HKMA being the front-line regulator that will apply all SFC regulatory criteria, including fitness and properness and business conduct, other than capital adequacy, the handling of client money and the audit requirements in supervising them.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 18 of 108
18. Question
1 pointsQID176:Which of the following institutions is required to become a “registered institution”?
Correct
The provisions of the SFO have different applications to the following different classes of person:
(b) “registered institution”, which refers to authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”) directly supervised by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (“HKMA”) and registered with the SFC.Incorrect
The provisions of the SFO have different applications to the following different classes of person:
(b) “registered institution”, which refers to authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”) directly supervised by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (“HKMA”) and registered with the SFC.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 19 of 108
19. Question
1 pointsQID26:British Construction Bank is an authorised financial institution. Amid the downfall of the Hong Kong banking sector, it would like to sell fund products of other companies to clients to generate revenue. Where should British Construction Bank apply for a license?
Correct
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out
on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.Incorrect
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out
on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 20 of 108
20. Question
1 pointsQID27:Which of the following descriptions about intermediaries are correct?
I. Licensed Corporations are licensed by and supervised by the SFC.
II. Authorised Financial Institutions must register with the SFC in order to conduct regulated activities.
III. Registered Institutions need to comply with some of the codes and guidelines issued by the SFC.
IV. Registered Institutions need to be registered with the company registry.Correct
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out
on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.Incorrect
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out
on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.18
-
Question 21 of 108
21. Question
1 pointsQID742:Which of the following is the objective of creating the SFO?
Correct
The objectives of the SFO are to provide a regulatory framework which:
(a) promotes a fair, orderly and transparent market;
(b) is flexible enough to cope with new products and other innovations, and further advances in technological infrastructure;
(c) is administered by a regulator with sufficient powers and discretion whose operations are transparent and who is accountable to the stakeholders through a system of adequate
checks and balances; and
(d) is on a par with international standards and compatible with international practices, but tailored to meet local needs and circumstances.Incorrect
The objectives of the SFO are to provide a regulatory framework which:
(a) promotes a fair, orderly and transparent market;
(b) is flexible enough to cope with new products and other innovations, and further advances in technological infrastructure;
(c) is administered by a regulator with sufficient powers and discretion whose operations are transparent and who is accountable to the stakeholders through a system of adequate
checks and balances; and
(d) is on a par with international standards and compatible with international practices, but tailored to meet local needs and circumstances.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.2
-
Question 22 of 108
22. Question
1 pointsQID258:Which of the following is the purpose of establishing a capital requirement?
Correct
The regulator must ensure that a licensed corporation has enough capital within the corporation (or available to it from external sources):
(a) to support the level of its business activities.Incorrect
The regulator must ensure that a licensed corporation has enough capital within the corporation (or available to it from external sources):
(a) to support the level of its business activities.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.22
-
Question 23 of 108
23. Question
1 pointsQID190:The SFO has provided powers for the SFC to make detailed rules relating to which of the following?
I. Financial Resources
II. Handling of client money and other client assets
III. The keeping of accounts and records
IV. Auditing mattersCorrect
The SFO grants the SFC powers to make detailed
rules relating to:
(a) their financial resources;
(b) the handling of client money and other client assets;
© the keeping of accounts and records; and
(d) auditing matters.Incorrect
The SFO grants the SFC powers to make detailed
rules relating to:
(a) their financial resources;
(b) the handling of client money and other client assets;
© the keeping of accounts and records; and
(d) auditing matters.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.23
-
Question 24 of 108
24. Question
1 pointsQID744:Which of the following individuals or entities should adhere to Securities and Futures (Accounts and Audit) Rules?
Correct
The SFC has made the Accounts and Audit Rules specifying the form and contents of financial statements and other documents that licensed corporations and associated entities of intermediaries (both licensed corporations and registered institutions) should prepare and the content of auditors’ reports.
Incorrect
The SFC has made the Accounts and Audit Rules specifying the form and contents of financial statements and other documents that licensed corporations and associated entities of intermediaries (both licensed corporations and registered institutions) should prepare and the content of auditors’ reports.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.23
-
Question 25 of 108
25. Question
1 pointsQID2754:For which of the following areas has the SFC not enacted subsidiary legislation?
Correct
The SFC mainly makes subsidiary legislation for the following areas:
1. Financial resources
2. Client Money
3. Client Securities
4. Accounts and Audit
5. Keeping records
6. Professional investors
7. Contract NotesIncorrect
The SFC mainly makes subsidiary legislation for the following areas:
1. Financial resources
2. Client Money
3. Client Securities
4. Accounts and Audit
5. Keeping records
6. Professional investors
7. Contract NotesHint
Reference Chapter:1.2.26
-
Question 26 of 108
26. Question
1 pointsQID758:The Fit and proper guidelines of the SFO are more likely to apply to which of the following individuals or entities?
I. Company that’s applying for a license or registration.
II. Representative of company that’s applying for a license or registration.
III. Executive Director of company that’s applying for a license or registration.
IV. Professional InvestorCorrect
The corporate (including its officers e.g. directors, managers, etc.) and individual applicants for licensing or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements stated in the Fit and Proper Guidelines. These requirements apply to applicants and to licensed and registered persons on an ongoing basis. Compliance with the requirements will be monitored by the HKMA in the case of AFIs and their executive officers and staff, and by the SFC in the case of others.
Incorrect
The corporate (including its officers e.g. directors, managers, etc.) and individual applicants for licensing or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements stated in the Fit and Proper Guidelines. These requirements apply to applicants and to licensed and registered persons on an ongoing basis. Compliance with the requirements will be monitored by the HKMA in the case of AFIs and their executive officers and staff, and by the SFC in the case of others.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.28
-
Question 27 of 108
27. Question
1 pointsQID81:What kind of sanctions can the SFC impose on individuals who violate or breach the code and guidelines of the SFC?
I. Reprimand
II. Imprisonment
III. Suspension of licence
IV. Revocation of licenceCorrect
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines:
(d) Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable. However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.
€ The SFC has the power to reprimand (privately or publicly), to fine and to suspend or revoke a licence or registration in relation to all or any part of the regulated activities specified on the licence or certificate of registration.Incorrect
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines:
(d) Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable. However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.
€ The SFC has the power to reprimand (privately or publicly), to fine and to suspend or revoke a licence or registration in relation to all or any part of the regulated activities specified on the licence or certificate of registration.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.29
-
Question 28 of 108
28. Question
1 pointsQID80:What are the legal status of the Codes and Guidelines set by the
SFC?
I. They posses the force of law and is enforceable.
II. They do not posses the force of law and is not enforceable.
III. Breach of these codes and guidelines may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.
IV. Breach of these codes and guidelines are violations of the Securities and futures ordinance and can lead to imprisonment.Correct
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines:
(d) Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable. However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.Incorrect
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines:
(d) Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable. However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.29
-
Question 29 of 108
29. Question
1 pointsQID773:The SFC-issued codes, guidelines and guidance notes
Correct
Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable. However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.
Incorrect
Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable. However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.29
-
Question 30 of 108
30. Question
1 pointsQID82:Which of the following correctly describe the power of the SFC?
I. Breaches of the subsidiary legislations of the SFO are not criminal offences
II. Breaches of the subsidiary legislations of the SFO are criminal offences
III. The SFC may refer serious cases to law enforcement agencies such as the Commercial Crimes Bureau (“CCB”) of the Hong Kong Police Force or the Independent Commission Against Corruption (“ICAC”) for investigation and action.
IV. The SFC may also apply to the courts for an injunction to restrain a person from dealing with his assets, or from carrying on all or a part of his business, if the SFC can make a case to show that it is in the public interest to issue such an order.Correct
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines:
(a) Breaches of the SFO and subsidiary legislation are legal offences and will be investigated by the SFC and enforcement action taken; the SFC may refer serious cases to law enforcement agencies such as the Commercial Crimes Bureau (“CCB”) of the Hong Kong Police Force or the Independent Commission Against Corruption (“ICAC”) for investigation and action.
(b) The SFC may also apply to the courts for an injunction to restrain a person from dealing with his assets, or from carrying on all or a part of his business, if it can make a case to show that it is in the public interest to issue such an order.Incorrect
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines:
(a) Breaches of the SFO and subsidiary legislation are legal offences and will be investigated by the SFC and enforcement action taken; the SFC may refer serious cases to law enforcement agencies such as the Commercial Crimes Bureau (“CCB”) of the Hong Kong Police Force or the Independent Commission Against Corruption (“ICAC”) for investigation and action.
(b) The SFC may also apply to the courts for an injunction to restrain a person from dealing with his assets, or from carrying on all or a part of his business, if it can make a case to show that it is in the public interest to issue such an order.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.29
-
Question 31 of 108
31. Question
1 pointsQID83:Which of the following correctly describes the status of SFC’s code of conducts and guidelines?
Correct
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines:
(d) Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable.
However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.Incorrect
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines:
(d) Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable.
However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.29
-
Question 32 of 108
32. Question
1 pointsQID85:What is the legal status of codes and guidelines issued by the SFC?
I. Codes of conduct are subsidiary legislation and have the force of law.
II. Guidelines are subsidiary legislation and have the force of law.
III. Codes of conduct do not have the force of law, a breach does not by itself render a person liable to any judicial or other proceedings.
IV. Guidelines do not have the force of law, a breach does not by itself render a person liable to any judicial or other proceedings.Correct
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines: (d) Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable.
However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.Incorrect
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines: (d) Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable.
However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.29
-
Question 33 of 108
33. Question
1 pointsQID86:Which of the following correctly describes the legal status of the Securities and Futures Commission’s codes and guidelines?
Correct
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines: (d) Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable.
However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.Incorrect
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines: (d) Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable.
However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.29
-
Question 34 of 108
34. Question
1 pointsQID87:Under the provisions of the Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO), which of the following statements relating to rules and codes of conduct are correct?
I. Failure by a licensed person to comply with a material provision of a code of conduct will of itself make the person liable to judicial proceedings.
II. A code of conduct violation shall be admissible as evidence in court proceedings.
III. The Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) is empowered under the SFO to make rules or codes of conduct.
IV. A breach of a provision in a code of conduct by a licensed person may cast doubts on his fitness and properness to hold the licence.Correct
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines:
(c) Persons prejudiced by the perpetration of market misconduct may take civil action against the wrongdoer through the courts to obtain redress. The SFO has provisions for the findings of the Market Misconduct Tribunal to be admissible in evidence in private civil actions.
(d) Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable. However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.Incorrect
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines:
(c) Persons prejudiced by the perpetration of market misconduct may take civil action against the wrongdoer through the courts to obtain redress. The SFO has provisions for the findings of the Market Misconduct Tribunal to be admissible in evidence in private civil actions.
(d) Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable. However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.29
-
Question 35 of 108
35. Question
1 pointsQID819:If an intermediary has been convicted of violation of the SFO. How can the SFC sanction such intermediary?
I. Revoke or suspend approval as a responsible officer
II. Fines
III. Reprimand, publicly or privately
IV. Jail sentenceCorrect
Section 194, SFO provides that if a “regulated person” is guilty of “misconduct”, or is not a fit and proper person, the SFC may:
(a) in the case of a licensed corporation or representative, revoke or suspend the licence in respect of all or part of the licensed regulated activity;
(b) in the case of a responsible officer (see section 1.3 of Topic 4 for the definition of this term), revoke or suspend approval as a responsible officer;
(c) publicly or privately reprimand the regulated person;
(d) prohibit the regulated person from applying for a licence, registration, approval as a responsible officer or entry in the HKMA register, or to act as an executive officer; and
(e) separately or in addition order the regulated person to pay a penalty up to the greater of HK$10 million or three times any profit gained or loss avoided as a result of his misconduct.Incorrect
Section 194, SFO provides that if a “regulated person” is guilty of “misconduct”, or is not a fit and proper person, the SFC may:
(a) in the case of a licensed corporation or representative, revoke or suspend the licence in respect of all or part of the licensed regulated activity;
(b) in the case of a responsible officer (see section 1.3 of Topic 4 for the definition of this term), revoke or suspend approval as a responsible officer;
(c) publicly or privately reprimand the regulated person;
(d) prohibit the regulated person from applying for a licence, registration, approval as a responsible officer or entry in the HKMA register, or to act as an executive officer; and
(e) separately or in addition order the regulated person to pay a penalty up to the greater of HK$10 million or three times any profit gained or loss avoided as a result of his misconduct.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.29
-
Question 36 of 108
36. Question
1 pointsQID204:How does the court take into account the codes and guidelines issued by the SFC?
Correct
A failure on the part of an intermediary or its representative to comply with a code of conduct is not a breach of law and does not by itself constitute an offence under the law.
However, it should be noted that breaches of codes of conduct may be taken into account in two important respects:
(b) a court hearing legal proceedings under the SFO shall consider the provisions of the codes if the court considers it relevant to the determination of any question arising in
the proceedings. This gives the codes a degree of legal recognition.Incorrect
A failure on the part of an intermediary or its representative to comply with a code of conduct is not a breach of law and does not by itself constitute an offence under the law.
However, it should be noted that breaches of codes of conduct may be taken into account in two important respects:
(b) a court hearing legal proceedings under the SFO shall consider the provisions of the codes if the court considers it relevant to the determination of any question arising in
the proceedings. This gives the codes a degree of legal recognition.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.29
-
Question 37 of 108
37. Question
1 pointsQID123:Which of the following descriptions about subsidiary legislations are correct?
I. Subsidiary legislations are enacted by the Chief Executive of Hong Kong after consulting the advice of the Legco
II. Subsidiary legislations are some laws made by a process of delegation from LegCo to other bodies.
III. Subsidiary legislations do not possess the force of law and are not enforceable.
IV. Subsidiary legislations possess the force of law and are enforceable.Correct
The laws passed by the Legislative Council of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (“LegCo”) are called ordinances. They are enacted by the Chief Executive of the
Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (“HKSAR”) with the advice of LegCo. Some laws are made by a process of delegation from LegCo to other bodies, such delegation usually being done under an ordinance. For example, the Securities and Futures Commission (“SFC”) has extensive powers to make rules under the Securities and Futures Ordinance (“SFO”). This process is, in the case of the SFC, generally required to be completed by a process of tabling in LegCo, which gives LegCo an opportunity to review the subsidiary legislation before it becomes law.Incorrect
The laws passed by the Legislative Council of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (“LegCo”) are called ordinances. They are enacted by the Chief Executive of the
Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (“HKSAR”) with the advice of LegCo. Some laws are made by a process of delegation from LegCo to other bodies, such delegation usually being done under an ordinance. For example, the Securities and Futures Commission (“SFC”) has extensive powers to make rules under the Securities and Futures Ordinance (“SFO”). This process is, in the case of the SFC, generally required to be completed by a process of tabling in LegCo, which gives LegCo an opportunity to review the subsidiary legislation before it becomes law.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.3
-
Question 38 of 108
38. Question
1 pointsQID847:The rules issued by the SFC, such as Client Securities Rules, are
Correct
These are some of the Major Subsidiary Legislation:
1.1 Securities and Futures (Financial Resources) Rules
1.2 Securities and Futures (Client Securities) Rules
1.3 Securities and Futures (Client Money) Rules
1.4 Securities and Futures (Keeping of Records) Rules
1.5 Securities and Futures (Contract Notes, Statements of Account and Receipts) Rules
1.6 Securities and Futures (Accounts and Audit) Rules,
plus many others.Incorrect
These are some of the Major Subsidiary Legislation:
1.1 Securities and Futures (Financial Resources) Rules
1.2 Securities and Futures (Client Securities) Rules
1.3 Securities and Futures (Client Money) Rules
1.4 Securities and Futures (Keeping of Records) Rules
1.5 Securities and Futures (Contract Notes, Statements of Account and Receipts) Rules
1.6 Securities and Futures (Accounts and Audit) Rules,
plus many others.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.3
-
Question 39 of 108
39. Question
1 pointsQID542:In Hong Kong, which of the following short selling operations are legitimate?
I. Secured short selling stock.
II. Non-secured short selling stock.
III. Short stock futures.
IV. Short stock options.Correct
Regulated short selling is defined in Schedule 1, SFO and in the Eleventh Schedule of the Rules of the Exchange to mean the sale of a security in respect of which the seller, or a person for whose benefit or on whose behalf the sale is made, has a currently exercisable and unconditional right to vest the security in the purchaser by virtue of:
(a) having under an securities borrowing and lending (“SBL”) agreement.
(b) a title to other security which is convertible into or exchangeable for the security to which the sale relates;
© an option to acquire the security to which the sale relates;
(d) rights or warrants to subscribe for and receive the security to which the sale relates; or
€ having entered into with another person an agreement or an arrangement of a description prescribed by rules made under s. 397, SFO.Incorrect
Regulated short selling is defined in Schedule 1, SFO and in the Eleventh Schedule of the Rules of the Exchange to mean the sale of a security in respect of which the seller, or a person for whose benefit or on whose behalf the sale is made, has a currently exercisable and unconditional right to vest the security in the purchaser by virtue of:
(a) having under an securities borrowing and lending (“SBL”) agreement.
(b) a title to other security which is convertible into or exchangeable for the security to which the sale relates;
© an option to acquire the security to which the sale relates;
(d) rights or warrants to subscribe for and receive the security to which the sale relates; or
€ having entered into with another person an agreement or an arrangement of a description prescribed by rules made under s. 397, SFO.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.32
-
Question 40 of 108
40. Question
1 pointsQID543:Which of the following short selling is NOT allowed?
Correct
Regulated short selling is defined in Schedule 1, SFO and in the Eleventh Schedule of the Rules of the Exchange to mean the sale of a security in respect of which the seller, or a person for whose benefit or on whose behalf the sale is made, has a currently exercisable and unconditional right to vest the security in the purchaser by virtue of:
(a) having under an securities borrowing and lending (“SBL”) agreement.
(b) a title to other security which is convertible into or exchangeable for the security to which the sale relates;
© an option to acquire the security to which the sale relates;
(d) rights or warrants to subscribe for and receive the security to which the sale relates; or
€ having entered into with another person an agreement or an arrangement of a description prescribed by rules made under s. 397, SFO.Incorrect
Regulated short selling is defined in Schedule 1, SFO and in the Eleventh Schedule of the Rules of the Exchange to mean the sale of a security in respect of which the seller, or a person for whose benefit or on whose behalf the sale is made, has a currently exercisable and unconditional right to vest the security in the purchaser by virtue of:
(a) having under an securities borrowing and lending (“SBL”) agreement.
(b) a title to other security which is convertible into or exchangeable for the security to which the sale relates;
© an option to acquire the security to which the sale relates;
(d) rights or warrants to subscribe for and receive the security to which the sale relates; or
€ having entered into with another person an agreement or an arrangement of a description prescribed by rules made under s. 397, SFO.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.32
-
Question 41 of 108
41. Question
1 pointsQID2366:Which of the following is correct regarding the Investor Compensation Fund?
Correct
The Investor Compensation Fund is managed by the Investor Compensation Company Limited in terms of operation, management, and administration. The Investor Compensation Fund is designed to deal with listed stocks of the SEHK and products traded at the Hong Kong Futures Exchange Limited. The Investor Compensation Fund sets a limited quota for each claimant.
Incorrect
The Investor Compensation Fund is managed by the Investor Compensation Company Limited in terms of operation, management, and administration. The Investor Compensation Fund is designed to deal with listed stocks of the SEHK and products traded at the Hong Kong Futures Exchange Limited. The Investor Compensation Fund sets a limited quota for each claimant.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.36
-
Question 42 of 108
42. Question
1 pointsQID2497:Why is the Investor Compensation Fund important?
Correct
The Investor Compensation Fund is important because it can enhance the confidence of investors.
Incorrect
The Investor Compensation Fund is important because it can enhance the confidence of investors.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.38
-
Question 43 of 108
43. Question
1 pointsQID189:According to the SFO, an intermediary could mean
I. A Registered Institution
II. A Licensed Corporation
III. A Trust Company
IV. An Authorised Financial InstitutionCorrect
Only corporations may become intermediaries. A corporation that obtains a licence will be regarded as a “licensed corporation” unless it is an AFI, in which case it will be regarded as a “registered institution”. Together they are referred to as “intermediaries”. The distinction between the licensing of corporations and the registration of AFIs is reviewed in further detail in section 1 of Topic 4.
Incorrect
Only corporations may become intermediaries. A corporation that obtains a licence will be regarded as a “licensed corporation” unless it is an AFI, in which case it will be regarded as a “registered institution”. Together they are referred to as “intermediaries”. The distinction between the licensing of corporations and the registration of AFIs is reviewed in further detail in section 1 of Topic 4.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.4
-
Question 44 of 108
44. Question
1 pointsQID740:Mr Ko is a representative of a licensed corporation, Kaohsiung Securities. Mr Ko has violated the code of conduct recently. What are the consequences of Mr Ko’s actions?
Correct
Breaches of the SFO and subsidiary legislation are legal offences and will be investigated by the SFC and enforcement action taken; the SFC may refer serious cases to law enforcement agencies such as the Commercial Crimes Bureau (“CCB”) of the Hong Kong Police Force or the Independent Commission Against Corruption (“ICAC”) for investigation and action.
Incorrect
Breaches of the SFO and subsidiary legislation are legal offences and will be investigated by the SFC and enforcement action taken; the SFC may refer serious cases to law enforcement agencies such as the Commercial Crimes Bureau (“CCB”) of the Hong Kong Police Force or the Independent Commission Against Corruption (“ICAC”) for investigation and action.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.4
-
Question 45 of 108
45. Question
1 pointsQID1663:Are Registered Institutions bound by the code of conduct?
Correct
Registered Institutions need to adhere to the Code of Conduct.
Incorrect
Registered Institutions need to adhere to the Code of Conduct.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.4
-
Question 46 of 108
46. Question
1 pointsQID110:Which of the following correctly describes the level of regulatory protection required by Professional Investors?
Correct
PIs are generally persons who are highly experienced in making investments and investment decisions. They would include the class of persons described above as institutional investors.
Details of the definitions of PIs will be discussed in section 2 of Topic 5. Under the SFC’s regulations, PIs are not automatically provided with the same level of regulatory protection as retail investors.Incorrect
PIs are generally persons who are highly experienced in making investments and investment decisions. They would include the class of persons described above as institutional investors.
Details of the definitions of PIs will be discussed in section 2 of Topic 5. Under the SFC’s regulations, PIs are not automatically provided with the same level of regulatory protection as retail investors.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.41
-
Question 47 of 108
47. Question
1 pointsQID188:Which of the following description about the single licence regime is correct?
Correct
Although there are ten types of regulated activity, the SFC will grant to a person only one licence (or registration) which will enable the holder to undertake one or more of the ten regulated activities. This is normally referred to as the “single licence regime”.
Incorrect
Although there are ten types of regulated activity, the SFC will grant to a person only one licence (or registration) which will enable the holder to undertake one or more of the ten regulated activities. This is normally referred to as the “single licence regime”.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.5
-
Question 48 of 108
48. Question
1 pointsQID2803:The objectives of the SFO are to provide a regulatory framework with which of the following characteristics?
I. Promotes a fair, orderly and transparent market.
II. Is flexible enough to cope with new products and other innovations, and further advances in technological infrastructure.
III. Is administered by a regulator with sufficient powers and discretion whose operations are transparent and directly under the government.
IV. Is a system that can satisfy PRC mainland legal standards, being compatible with PRC mainland laws and practices and meet local needs.Correct
The objectives of the SFO are to provide a regulatory framework which:
(a) promotes a fair, orderly and transparent market;
(b) is flexible enough to cope with new products and other innovations, and further advances in technological infrastructure;
(c) is administered by a regulator with sufficient powers and discretion whose operations are transparent and who is accountable to the stakeholders through a system of adequate
checks and balances.Incorrect
The objectives of the SFO are to provide a regulatory framework which:
(a) promotes a fair, orderly and transparent market;
(b) is flexible enough to cope with new products and other innovations, and further advances in technological infrastructure;
(c) is administered by a regulator with sufficient powers and discretion whose operations are transparent and who is accountable to the stakeholders through a system of adequate
checks and balances.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.6
-
Question 49 of 108
49. Question
1 pointsQID171:The objectives of the SFO are to provide a regulatory framework with which of the following characteristics?
I. Promotes a fair, orderly and transparent market.
II. Is flexible enough to cope with new products and other innovations, and further advances in technological infrastructure.
III. Is administered by a regulator with sufficient powers and discretion whose operations are transparent and who is accountable to the stakeholders through a system of adequate checks and balance.
IV. Is a system that can satisfy PRC mainland legal standards, being compatible with PRC mainland laws and practices and meet local needs.Correct
The objectives of the SFO are to provide a regulatory framework which:
(a) promotes a fair, orderly and transparent market;
(b) is flexible enough to cope with new products and other innovations, and further advances in technological infrastructure;
(c) is administered by a regulator with sufficient powers and discretion whose operations are transparent and who is accountable to the stakeholders through a system of adequate
checks and balances.Incorrect
The objectives of the SFO are to provide a regulatory framework which:
(a) promotes a fair, orderly and transparent market;
(b) is flexible enough to cope with new products and other innovations, and further advances in technological infrastructure;
(c) is administered by a regulator with sufficient powers and discretion whose operations are transparent and who is accountable to the stakeholders through a system of adequate
checks and balances.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.2.6
-
Question 50 of 108
50. Question
1 pointsQID2738:The Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) is a/an
Correct
The SFC is an independent statutory body, not a government department.
Incorrect
The SFC is an independent statutory body, not a government department.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.1
-
Question 51 of 108
51. Question
1 pointsQID781:The principal regulator of the securities industry in Hong Kong is the
Correct
The SFC was created by law under the Securities and Futures Commission Ordinance (now repealed and subsumed in the SFO). It is independent, meaning that it is not part of the Government machinery of the Civil Service or the ministerial system. Nevertheless, it reports to and is accountable to the Government as described in section 2 above.
Incorrect
The SFC was created by law under the Securities and Futures Commission Ordinance (now repealed and subsumed in the SFO). It is independent, meaning that it is not part of the Government machinery of the Civil Service or the ministerial system. Nevertheless, it reports to and is accountable to the Government as described in section 2 above.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.1
-
Question 52 of 108
52. Question
1 pointsQID782:The SFC is a/an _______ in Hong Kong.
Correct
The SFC was created by law under the Securities and Futures Commission Ordinance (now repealed and subsumed in the SFO). It is independent, meaning that it is not part of the
Government machinery of the Civil Service or the ministerial system. Nevertheless, it reports to and is accountable to the Government as described in section 2 above. It is considered the securities and futures market prime regulator.Incorrect
The SFC was created by law under the Securities and Futures Commission Ordinance (now repealed and subsumed in the SFO). It is independent, meaning that it is not part of the
Government machinery of the Civil Service or the ministerial system. Nevertheless, it reports to and is accountable to the Government as described in section 2 above. It is considered the securities and futures market prime regulator.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.1
-
Question 53 of 108
53. Question
1 pointsQID732:Which of the following descriptions about the SFC is correct?
Correct
The SFC was created by law under the Securities and Futures Commission Ordinance (now repealed and subsumed in the SFO). It is independent, meaning that it is not part of the
Government machinery of the Civil Service or the ministerial system. Nevertheless, it reports to and is accountable to the Government.Incorrect
The SFC was created by law under the Securities and Futures Commission Ordinance (now repealed and subsumed in the SFO). It is independent, meaning that it is not part of the
Government machinery of the Civil Service or the ministerial system. Nevertheless, it reports to and is accountable to the Government.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.1
-
Question 54 of 108
54. Question
1 pointsQID2834:Which department of the SFC is responsible for monitoring listed companies’ announcements and identifying misconduct or non-compliance?
Correct
The SFC’s Corporate Finance Division monitors listed companies’ announcements and identifies misconduct or non-compliance by listed companies.
Incorrect
The SFC’s Corporate Finance Division monitors listed companies’ announcements and identifies misconduct or non-compliance by listed companies.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.10
-
Question 55 of 108
55. Question
1 pointsQID73:Which of the following are functions of the Corporate Finance Division of the SFC?
I. Administer the Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs and regulates takeovers, mergers and share buy- backs of applicable companies
II. Provide advice on corporate restructuring to listed company in
Hong Kong
III. Supervise the listing-related activities of The Stock Exchange
of Hong Kong Limited (“SEHK”)
IV. Provide advice on takeover activities to minority shareholdersCorrect
Corporate Finance Division:
(a) administers The Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs and regulates takeovers, mergers and share buy-backs of applicable companies;
(b) supervises the listing-related activities of The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited (“SEHK”).Incorrect
Corporate Finance Division:
(a) administers The Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs and regulates takeovers, mergers and share buy-backs of applicable companies;
(b) supervises the listing-related activities of The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited (“SEHK”).Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.10
-
Question 56 of 108
56. Question
1 pointsQID998:The SFC is not responsible for supervising which of the following?
Correct
Exchanges and clearing houses are supervised by the Supervision of Markets Division of the SFC. Intermediaries are supervised by the Intermediaries Division of the SFC. Market Misconduct Tribunal is independent of the SFC and not supervised by it.
Incorrect
Exchanges and clearing houses are supervised by the Supervision of Markets Division of the SFC. Intermediaries are supervised by the Intermediaries Division of the SFC. Market Misconduct Tribunal is independent of the SFC and not supervised by it.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.13
-
Question 57 of 108
57. Question
1 pointsQID104:Which of the following entity is responsible for monitoring the exchanges and clearing houses in Hong Kong?
Correct
The SFC supervises and monitors the activities of HKEX, the exchange companies and the clearing houses, approves their rules and amendments to the rules, approves the fees they charge, and administers and enforces the applicable legislation. It also carries out regular reviews of these activities.
Incorrect
The SFC supervises and monitors the activities of HKEX, the exchange companies and the clearing houses, approves their rules and amendments to the rules, approves the fees they charge, and administers and enforces the applicable legislation. It also carries out regular reviews of these activities.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.13
-
Question 58 of 108
58. Question
1 pointsQID2761:Which of the following statements about the SFC is correct?
Correct
The SFC is responsible for the regulation of all securities and futures activities, including the regulatory activities carried out by banks. It is also responsible for regulating the exchange controller.
Incorrect
The SFC is responsible for the regulation of all securities and futures activities, including the regulatory activities carried out by banks. It is also responsible for regulating the exchange controller.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.13
-
Question 59 of 108
59. Question
1 pointsQID105:Which of the following organization is responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants?
Correct
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants, which is carried out by the SFC.
Incorrect
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants, which is carried out by the SFC.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.14
-
Question 60 of 108
60. Question
1 pointsQID78:Which department/division of the SFC licenses asset management corporation and their staff and approves responsible officers?
Correct
Licensing Department:
(a) licenses corporations and individuals seeking to conduct business in Hong Kong in the regulated activities for which a licence is required under the SFO.Incorrect
Licensing Department:
(a) licenses corporations and individuals seeking to conduct business in Hong Kong in the regulated activities for which a licence is required under the SFO.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.15
-
Question 61 of 108
61. Question
1 pointsQID79:Which department/division of the SFC supervises licensed corporations and individual licensees on an ongoing basis?
Correct
Intermediaries Supervision Department:
(a) supervises the business conduct of licensed corporations and individual licensees on an ongoing basis, by conducting on-site inspection and off-site monitoring; and
(b) monitors the financial integrity of licensed corporations.Incorrect
Intermediaries Supervision Department:
(a) supervises the business conduct of licensed corporations and individual licensees on an ongoing basis, by conducting on-site inspection and off-site monitoring; and
(b) monitors the financial integrity of licensed corporations.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.16
-
Question 62 of 108
62. Question
1 pointsQID90:In which of the following circumstances will the Securities and
Futures Commission (SFC) investigate a licensed corporation?
I. When the licensed corporation’s operations go downhill and it
is unable to pay the license fee.
II. When clients lodge complaints against the licensed corporation for its failure to inform clients about the whereabouts of funds deposited by clients upon clients requests.
III. When an informant provides information that the licensed corporation is being mismanaged, the growth has slowed down and it is planning a sale.
IV. When an informant provides information that the licensed corporation is being mismanaged and it is suffering from losses.Correct
The SFC may (i) conduct supervisory inspections for the purposes of ascertaining whether an intermediary or an associated entity of an intermediary has complied with the SFO and
any related notices and requirements, any terms and condition of any licence or registration, or any other imposed condition; or (ii) require copies of documents or inquire into the affairs of a licensed corporation or its related corporations for the purpose of providing assistance, in relation to the licensed corporation, to an authority or regulatory organisation outside Hong Kong.Incorrect
The SFC may (i) conduct supervisory inspections for the purposes of ascertaining whether an intermediary or an associated entity of an intermediary has complied with the SFO and
any related notices and requirements, any terms and condition of any licence or registration, or any other imposed condition; or (ii) require copies of documents or inquire into the affairs of a licensed corporation or its related corporations for the purpose of providing assistance, in relation to the licensed corporation, to an authority or regulatory organisation outside Hong Kong.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.16
-
Question 63 of 108
63. Question
1 pointsQID788:Which of the following regulators in Hong Kong assumes responsibility for front-line regulation and discipline of participants of the securities and futures industry?
Correct
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants, which is carried out by the SFC.
Incorrect
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants, which is carried out by the SFC.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.2
-
Question 64 of 108
64. Question
1 pointsQID2751:Which of the following descriptions about the HKEX is incorrect?
Correct
HKEX is not responsible for front-line prudential regulation of market participants. Such task is the responsibility of the SFC.
Incorrect
HKEX is not responsible for front-line prudential regulation of market participants. Such task is the responsibility of the SFC.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.2
-
Question 65 of 108
65. Question
1 pointsQID2832:Which of the following is not a financial regulator in Hong Kong?
Correct
The Securities Commission option is wrong, the correct name is Securities and Futures Commission.
Incorrect
The Securities Commission option is wrong, the correct name is Securities and Futures Commission.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.2
-
Question 66 of 108
66. Question
1 pointsQID783:What approach does the SFC take to regulate market intermediaries?
Correct
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
Incorrect
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.3
-
Question 67 of 108
67. Question
1 pointsQID787:Which of the following regulatory approach is adopted by the SFC?
Correct
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
Incorrect
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.3
-
Question 68 of 108
68. Question
1 pointsQID784:A risk-based regulatory system refers to a system in which:
Correct
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
Incorrect
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.3
-
Question 69 of 108
69. Question
1 pointsQID785:The SFC regime adopts which of the following regulatory approaches?
Correct
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
Incorrect
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.3
-
Question 70 of 108
70. Question
1 pointsQID10:Which system or philosophy of regulations is adopted by the SFC to regulate securities and futures markets?
Correct
SFC adopts a“risk-based”approach towards regulations. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
Incorrect
SFC adopts a“risk-based”approach towards regulations. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.3
-
Question 71 of 108
71. Question
1 pointsQID786:Which of the following regulatory approaches adopted by the SFC is given more regulatory attention towards the areas where the SFC perceives the highest risks to lie?
Correct
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
Incorrect
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.3
-
Question 72 of 108
72. Question
1 pointsQID6:Which of the following is a primary objective of Hong Kong financial regulators?
Correct
Encouraging the development of new products, operating profitable exchanges in Hong Kong and reducing trading hours are all actions. They are action verbs but not objective description. Objectives can only be objective description, therefore, these phrases can never be objectives and primary objective of Hong Kong financial regulators. Objectives are status that financial regulators hope for, enhancing confidence is an objective description that financial regulators hope for.
Incorrect
Encouraging the development of new products, operating profitable exchanges in Hong Kong and reducing trading hours are all actions. They are action verbs but not objective description. Objectives can only be objective description, therefore, these phrases can never be objectives and primary objective of Hong Kong financial regulators. Objectives are status that financial regulators hope for, enhancing confidence is an objective description that financial regulators hope for.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.6
-
Question 73 of 108
73. Question
1 pointsQID58:Which of the following is a regulatory objective of the SFC?
I. Provide protection to the investing public
II. Reduce non-systematic risk in the industry
III. Assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps in relation to the industry.
IV. Assist the HKMA in maintaining the stability of currency in
Hong KongCorrect
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(c) provide protection to the investing public;
(f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps in relation to the industry.Incorrect
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(c) provide protection to the investing public;
(f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps in relation to the industry.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.6
-
Question 74 of 108
74. Question
1 pointsQID779:Which of the following is NOT a regulatory objective of the SFC?
Correct
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency and orderliness of the market;
(b) promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning;
© provide protection to the investing public;
(d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
€ reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
(f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps in relation to the industry.
Providing protection for major shareholders is not one of these objectives.Incorrect
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency and orderliness of the market;
(b) promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning;
© provide protection to the investing public;
(d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
€ reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
(f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps in relation to the industry.
Providing protection for major shareholders is not one of these objectives.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.6
-
Question 75 of 108
75. Question
1 pointsQID61:Which of the following is a regulatory objective of the SFC?
Correct
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market.Incorrect
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.6
-
Question 76 of 108
76. Question
1 pointsQID59:Under the SFO, which of the following are objectives of the SFO
I. Promote understanding by the public of financial services including the operation and functioning of the industry.
II. Ensure the regulatory standards are identical to international standards.
III. Check and approve new financial products.
IV. Minimize crime and misconduct within the industry.Correct
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(b) promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning;
(d) minimise crime and misconduct in the marketIncorrect
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(b) promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning;
(d) minimise crime and misconduct in the marketHint
Reference Chapter:1.3.6
-
Question 77 of 108
77. Question
1 pointsQID908:Which of the following is one of the objectives of the SFO
Correct
SFO treats all investors fairly and equally. Regulators should be transparent and its power should be in check.
Incorrect
SFO treats all investors fairly and equally. Regulators should be transparent and its power should be in check.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.6
-
Question 78 of 108
78. Question
1 pointsQID2726:Which of the following is not the primary objective of the SFC in exercising its enforcement powers?
Correct
The SFC’s main objectives in exercising its enforcement powers:
I. Protection of investors
II. Maintenance of Market Integrity and Confidence
III. Holding offenders accountable for their actionsIncorrect
The SFC’s main objectives in exercising its enforcement powers:
I. Protection of investors
II. Maintenance of Market Integrity and Confidence
III. Holding offenders accountable for their actionsHint
Reference Chapter:1.3.6
-
Question 79 of 108
79. Question
1 pointsQID60:The regulator objectives of the SFC includes:
I. Consumer rights protection
II. Minimize crime and misconduct within the securities and futures industry.
III. Promote public’s understanding of the securities and futures industry.
IV. Provide advice on the enforcement of economic policies to the governmentCorrect
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(b) promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning;
(d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market.Incorrect
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(b) promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning;
(d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.6
-
Question 80 of 108
80. Question
1 pointsQID2721:The main functions of the SFC include:
I. Empowering self-regulatory bodies and professional bodies to form committees
II. Regulating and monitoring intermediaries who engage in regulated activities
III. Supervising and monitoring exchanges, clearing houses and exchange controllers
IV. Promoting investor education and encouraging investors to understand investment products and make informed decisions
Correct
Authorizing self-regulatory bodies and professional bodies to set up committees is not the main function of the SFC.
Incorrect
Authorizing self-regulatory bodies and professional bodies to set up committees is not the main function of the SFC.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.7
-
Question 81 of 108
81. Question
1 pointsQID62:The major functions of the SFC include﹕
I. Supervise all of the activities conducted by Registered Institution
II. Promote, encourage and enforce the proper conduct, competence and integrity of persons carrying on regulated activities
III. Promote, encourage and enforce internal control and risk management systems by persons carrying on regulated activities, including registered institutions in the case of any regulated activities they conduct.
IV. Maintain market liquidity in the securities and futures markets.Correct
The functions and powers of the SFC are wide and are set out in s. 5, SFO. The principal functions are to:
(c) promote, encourage and enforce the proper conduct, competence and integrity of persons carrying on regulated activities;
(g) promote, encourage and enforce internal control and risk management systems by persons carrying on regulated activities, including registered institutions in the case of any regulated activities they conduct.Incorrect
The functions and powers of the SFC are wide and are set out in s. 5, SFO. The principal functions are to:
(c) promote, encourage and enforce the proper conduct, competence and integrity of persons carrying on regulated activities;
(g) promote, encourage and enforce internal control and risk management systems by persons carrying on regulated activities, including registered institutions in the case of any regulated activities they conduct.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.7
-
Question 82 of 108
82. Question
1 pointsQID63:Which of the following are functions and duties of the SFC?
I. Supervise the securities and futures markets in Hong Kong
II. Regulate the securities and futures industries
III. Provide professional assistance to the government
IV. Supervise all settlement banks in Hong KongCorrect
The functions and powers of the SFC are wide and are set out in s. 5, SFO. The principal functions are to:
(b) supervise, monitor and regulate the activities of:
(i) recognised exchange, clearing houses, exchange controllers and investor compensation companies or persons carrying on regulated activities; and
(ii) registered institutions that are regulated or to be regulated by the SFC under any relevant provisions.Incorrect
The functions and powers of the SFC are wide and are set out in s. 5, SFO. The principal functions are to:
(b) supervise, monitor and regulate the activities of:
(i) recognised exchange, clearing houses, exchange controllers and investor compensation companies or persons carrying on regulated activities; and
(ii) registered institutions that are regulated or to be regulated by the SFC under any relevant provisions.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.7
-
Question 83 of 108
83. Question
1 pointsQID2816:Which of the following is not a function of the SFC?
Correct
Enforcement of the Listing Rules is the job of the SEHK.
Incorrect
Enforcement of the Listing Rules is the job of the SEHK.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.7
-
Question 84 of 108
84. Question
1 pointsQID57:The SFC﹕
I. Reports to the government
II. Was formed under the Securities and Futures Ordinance
III. Is not responsible for licensing of intermediaries
IV. Is a part of the governmentCorrect
The SFC was created by law under the Securities and Futures Commission Ordinance (now repealed and subsumed in the SFO). It is independent, meaning that it is not part of the
Government machinery of the Civil Service or the ministerial system. Nevertheless, it reports to and is accountable to the Government as described in section 2 above.Incorrect
The SFC was created by law under the Securities and Futures Commission Ordinance (now repealed and subsumed in the SFO). It is independent, meaning that it is not part of the
Government machinery of the Civil Service or the ministerial system. Nevertheless, it reports to and is accountable to the Government as described in section 2 above.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.8
-
Question 85 of 108
85. Question
1 pointsQID903:Which of the following are not common objectives of financial regulators in Hong Kong?
I. Promote intervention to enhance international and local market confidence.
II. Provide investment advice to retail investors
III. Encourage the installation of a sound technical infrastructure for the functioning of the financial markets
IV. Ensure that the legal framework of financial regulation is certain, adequate and fairly enforcedCorrect
Frequent Intervention is not an objective of financial regulators in Hong Kong. Providing Investment advice is not a job that regulators will do, it’s the job of intermediaries.
Incorrect
Frequent Intervention is not an objective of financial regulators in Hong Kong. Providing Investment advice is not a job that regulators will do, it’s the job of intermediaries.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.3.8
-
Question 86 of 108
86. Question
1 pointsQID2353:Hong Kong Exchange is
Correct
Hong Kong Exchange is the exchange designated by Hong Kong and the controller of clearing company. The subsidiary of Hong Kong Exchange includes The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited, which is responsible for the trading and clearing of securities and futures contract.
Incorrect
Hong Kong Exchange is the exchange designated by Hong Kong and the controller of clearing company. The subsidiary of Hong Kong Exchange includes The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited, which is responsible for the trading and clearing of securities and futures contract.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.1
-
Question 87 of 108
87. Question
1 pointsQID92:Which of the following description about the HKEX is correct?
I. The HKEX is a listed company on the SEHK.
II. The HKEX is an exchange controller recognized by the SFC
III. The SEHK, HKFE and the three associated clearing houses are subsidiaries of the HKEX.
IV. The HKEX is responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants.Correct
HKEX is a listed company on the SEHK. On 6 March 2000, the SEHK, HKFE and the three associated clearing houses – Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited, The SEHK
Options Clearing House Limited and HKFE Clearing Corporation Limited – became wholly owned subsidiaries of HKEX. HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC under s. 59, SFO.Incorrect
HKEX is a listed company on the SEHK. On 6 March 2000, the SEHK, HKFE and the three associated clearing houses – Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited, The SEHK
Options Clearing House Limited and HKFE Clearing Corporation Limited – became wholly owned subsidiaries of HKEX. HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC under s. 59, SFO.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.1&2
-
Question 88 of 108
88. Question
1 pointsQID2639:Silver Futures being traded on the HKFE are denominated in?
I. HKD
II. CNH
III. CNY
IV. USDCorrect
HKFE are denominated in
I. USD
II. CNHIncorrect
HKFE are denominated in
I. USD
II. CNHHint
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
Question 89 of 108
89. Question
1 pointsQID516:In Hong Kong, the futures exchange is responsible for the trading of which of the following products?
I. Index futures.
II. Index options.
III. Stock futures.
IV. Stock options.Correct
There are currently two exchanges:
(a) the SEHK, which provides for trading in securities as defined earlier on two boards, the Main Board and Growth Enterprise Market; and
(b) HKFE, which provides for trading in futures contracts. This includes Index futures, options and stocks futures.Incorrect
There are currently two exchanges:
(a) the SEHK, which provides for trading in securities as defined earlier on two boards, the Main Board and Growth Enterprise Market; and
(b) HKFE, which provides for trading in futures contracts. This includes Index futures, options and stocks futures.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
Question 90 of 108
90. Question
1 pointsQID520:Stock futures are traded through which of the following systems?
Correct
The Hong Kong Futures Automated Trading System (“HKATS”) is an electronic screen-based trading system used for trading in HKFE products as well as Traded Options which are products of the SEHK.
Incorrect
The Hong Kong Futures Automated Trading System (“HKATS”) is an electronic screen-based trading system used for trading in HKFE products as well as Traded Options which are products of the SEHK.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
Question 91 of 108
91. Question
1 pointsQID519:Index futures are traded through which of the following systems?
Correct
The Hong Kong Futures Automated Trading System (“HKATS”) is an electronic screen-based trading system used for trading in HKFE products as well as Traded Options which are products of the SEHK.
Incorrect
The Hong Kong Futures Automated Trading System (“HKATS”) is an electronic screen-based trading system used for trading in HKFE products as well as Traded Options which are products of the SEHK.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
Question 92 of 108
92. Question
1 pointsQID518:Index options are traded through which of the following systems?
Correct
The Hong Kong Futures Automated Trading System (“HKATS”) is an electronic screen-based trading system used for trading in HKFE products as well as Traded Options which are products of the SEHK.
Incorrect
The Hong Kong Futures Automated Trading System (“HKATS”) is an electronic screen-based trading system used for trading in HKFE products as well as Traded Options which are products of the SEHK.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
Question 93 of 108
93. Question
1 pointsQID522:Products of Hong Kong Futures Exchange (HKFE) are traded through which of the following systems?
Correct
The Hong Kong Futures Automated Trading System (“HKATS”) is an electronic screen-based trading system used for trading in HKFE products as well as Traded Options which are products of the SEHK.
Incorrect
The Hong Kong Futures Automated Trading System (“HKATS”) is an electronic screen-based trading system used for trading in HKFE products as well as Traded Options which are products of the SEHK.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
Question 94 of 108
94. Question
1 pointsQID524:In Hong Kong, the OTP-C used on the stock exchange may NOT be used in the trading of which of the following products?
Correct
Stock options are traded through the Hong Kong Futures Automated Trading System (HKATS).
Incorrect
Stock options are traded through the Hong Kong Futures Automated Trading System (HKATS).
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
Question 95 of 108
95. Question
1 pointsQID525:In Hong Kong, the ATS used on the futures exchange may be used in the trading of which of the following products?
I. Index futures.
II. Index options.
III. Stock futures.
IV. Stock options.Correct
The Hong Kong Futures Automated Trading System (“HKATS”) is an electronic screen-based trading system used for trading in HKFE products as well as Traded Options which are products of the SEHK.
Incorrect
The Hong Kong Futures Automated Trading System (“HKATS”) is an electronic screen-based trading system used for trading in HKFE products as well as Traded Options which are products of the SEHK.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
Question 96 of 108
96. Question
1 pointsQID108:Which of the following groups of people may directly use the facilities of the Hong Kong Futures Exchange (HKFE)?
I. Professional investors.
II. Institutional investors.
III. Person licensed by or registered with the SFC.
IV. Foreign futures dealer.Correct
Only the SFC’s licensed or registered persons may have access to the trading systems and facilities of HKFE, whether directly or indirectly, in order to carry out the Type 2 regulated activity of dealing in futures contracts.
Incorrect
Only the SFC’s licensed or registered persons may have access to the trading systems and facilities of HKFE, whether directly or indirectly, in order to carry out the Type 2 regulated activity of dealing in futures contracts.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
Question 97 of 108
97. Question
1 pointsQID2470:Which country doesn’t have the remote access to HKATS?
Correct
Korea, Canada, and New Zealand don’t have the remote access to HKATS. The United States, England, and Australia have the remote access to HKATS.
Incorrect
Korea, Canada, and New Zealand don’t have the remote access to HKATS. The United States, England, and Australia have the remote access to HKATS.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.14
-
Question 98 of 108
98. Question
1 pointsQID1642:Remote access of the HKATS currently allows users from which of the following countries?
I. Japan
II. Australia
III. United States
IV. United KingdomCorrect
Remote access is currently allowed from the United States, the United Kingdom and Australia.
Incorrect
Remote access is currently allowed from the United States, the United Kingdom and Australia.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.14
-
Question 99 of 108
99. Question
1 pointsQID905:Which of the following correctly describes the HKEX?
Correct
HKEX is not the venue for buying and selling Hong Kong stocks. HKEX is an exchange controller. HKEX’s subsidiary SEHK is the venue for buying and selling Hong Kong stocks. The SFC is responsible for licensing and registration of intermediaries. Stamp duty is a source of income of the government of the HKSAR.
Incorrect
HKEX is not the venue for buying and selling Hong Kong stocks. HKEX is an exchange controller. HKEX’s subsidiary SEHK is the venue for buying and selling Hong Kong stocks. The SFC is responsible for licensing and registration of intermediaries. Stamp duty is a source of income of the government of the HKSAR.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
Question 100 of 108
100. Question
1 pointsQID99:Which of the following is an exchange controller in Hong Kong?
Correct
HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC under s. 59, SFO.
Incorrect
HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC under s. 59, SFO.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
Question 101 of 108
101. Question
1 pointsQID100:Which of the following securities and futures exchanges are currently in Hong Kong?
I. Stock Exchange of Hong Kong.
II. Hong Kong Futures Exchange Limited.
III. Hong Kong Options Exchange.
IV. Hong Kong Bonds Exchange.Correct
The SEHK and HKFE are recognised under s. 19, SFO as exchange companies that may operate a stock market and a futures market in Hong Kong respectively.
Incorrect
The SEHK and HKFE are recognised under s. 19, SFO as exchange companies that may operate a stock market and a futures market in Hong Kong respectively.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
Question 102 of 108
102. Question
1 pointsQID101:Which of the following is an exchange controller?
Correct
HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC under s. 59, SFO.
Incorrect
HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC under s. 59, SFO.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
Question 103 of 108
103. Question
1 pointsQID102:Which of the following clearing houses are currently in operation in Hong Kong?
I. Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited.
II. The SEHK Options Clearing House Limited.
III. HKFE Clearing Corporation Limited.
IV. Hong Kong Options Clearing Limited.Correct
On 6 March 2000, the SEHK, HKFE and the three
associated clearing houses – Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited, The SEHK Options Clearing House Limited and HKFE Clearing Corporation Limited – became wholly owned subsidiaries of HKEX.Incorrect
On 6 March 2000, the SEHK, HKFE and the three
associated clearing houses – Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited, The SEHK Options Clearing House Limited and HKFE Clearing Corporation Limited – became wholly owned subsidiaries of HKEX.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
Question 104 of 108
104. Question
1 pointsQID514:Which of the following agencies are the 3 major clearing houses in Hong Kong?
I. Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited (HKSCC).
II. The SEHK Options Clearing House Limited (SEOCH).
III. HKFE Clearing Corporation Limited (HKCC).
IV. Hong Kong OTC Clear Limited.Correct
Upon merger and demutualisation, the two exchanges and three
clearing houses (HKSCC, SEOCH and HKCC) became the wholly owned subsidiaries of HKEX and “participantship” of the exchanges and clearing houses was introduced. They became the three major clearing houses in Hong Kong.Incorrect
Upon merger and demutualisation, the two exchanges and three
clearing houses (HKSCC, SEOCH and HKCC) became the wholly owned subsidiaries of HKEX and “participantship” of the exchanges and clearing houses was introduced. They became the three major clearing houses in Hong Kong.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
Question 105 of 108
105. Question
1 pointsQID733:The HKEX is responsible for regulating which of the following entities and matters?
I. Listed Companies
II. SEHK
III. HKFE
IV. Investors who participate in securities trading.Correct
HKEX is responsible for ensuring an orderly and fair market in securities and futures contracts traded on or through the SEHK and HKFE, respectively. HKEX is required to ensure that risks are managed prudently, to act in the interests of the public, having
particular regard to the interests of the investing public, and to ensure that where such interests conflict with any other interests the former shall prevail. The SEHK is also responsible for administering the Listing Rules.Incorrect
HKEX is responsible for ensuring an orderly and fair market in securities and futures contracts traded on or through the SEHK and HKFE, respectively. HKEX is required to ensure that risks are managed prudently, to act in the interests of the public, having
particular regard to the interests of the investing public, and to ensure that where such interests conflict with any other interests the former shall prevail. The SEHK is also responsible for administering the Listing Rules.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.3
-
Question 106 of 108
106. Question
1 pointsQID106:Which of the following entity is responsible for the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules?
Correct
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants, which is carried out by the SFC.
Incorrect
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants, which is carried out by the SFC.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.4.5
-
Question 107 of 108
107. Question
1 pointsQID109:Which of the following are characteristics of retail investors?
I. A larger sum of investment
II. Requires more protection
III. Retail investors are proprietary and do not invest on behalf of others as a business
IV. Requires less protectionCorrect
Retail investors are usually defined to be individuals or small businesses and companies who invest in relatively small amounts of money for themselves rather than on behalf anyone else.
From a regulatory point of view, these investors need the most protection under the regulatory regime, as they are less sophisticated.Incorrect
Retail investors are usually defined to be individuals or small businesses and companies who invest in relatively small amounts of money for themselves rather than on behalf anyone else.
From a regulatory point of view, these investors need the most protection under the regulatory regime, as they are less sophisticated.Hint
Reference Chapter:1.5.2
-
Question 108 of 108
108. Question
1 pointsQID809:What is the difference between Licensed Corporations and Registered Institutions?
Correct
Registered institutions are regulated by the HKMA. They have to be registered with the SFC if they wish to carry out SFC regulated activities but the front line regulator will be the HKMA.
Incorrect
Registered institutions are regulated by the HKMA. They have to be registered with the SFC if they wish to carry out SFC regulated activities but the front line regulator will be the HKMA.
Hint
Reference Chapter:1.5.2
✎ Tutorial 操作方法
You can email your questions enquiry to our company email [email protected], please provide:
(1)Client email address which you used to purchase the book
(2)QID (題庫號)
(3)Subject of enquiry
(4)Your enquiry
1. Quiz Summary:Expand the Question Number Section to see the colour marks of all the questions and the total number of questions in the topic
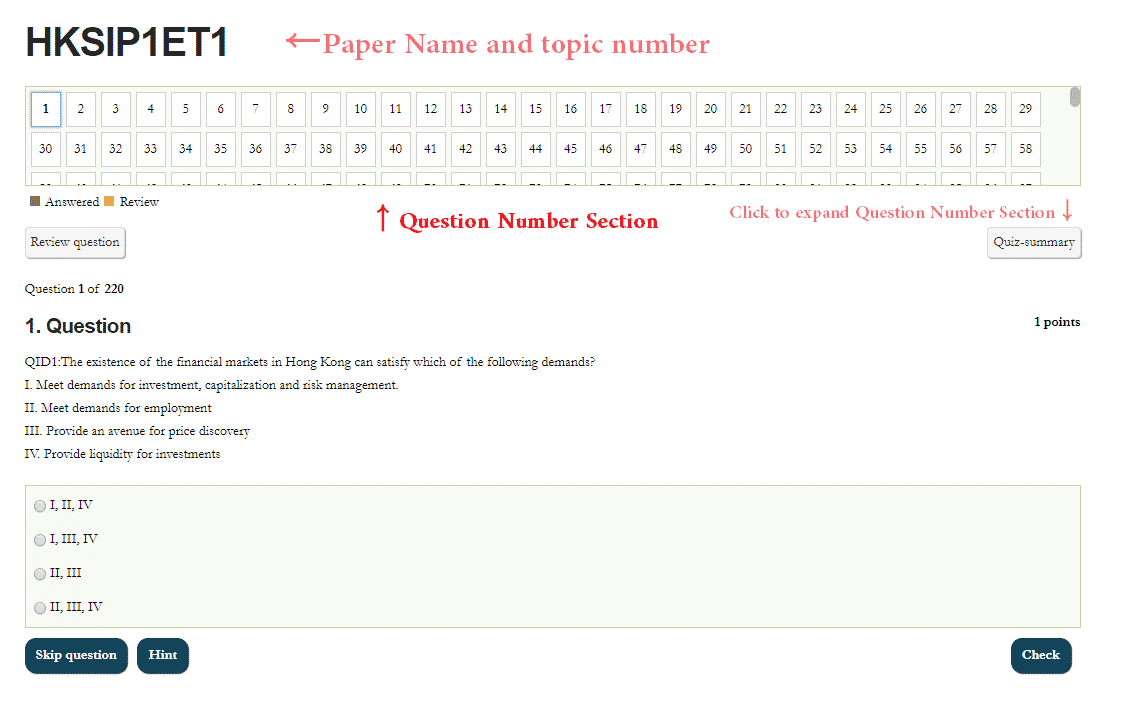
3. Review Question:Mark questions in orange colour so you can quickly find the question next time for studying/ testing again if necessary. Click once more to undo