英文證券卷二 HKSI Paper 2 第一章
This post is also available in: 繁體中文 English (英語)

HKSIP2ET1
測驗概述
已完成 0/567 個問題
問題:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
- 341
- 342
- 343
- 344
- 345
- 346
- 347
- 348
- 349
- 350
- 351
- 352
- 353
- 354
- 355
- 356
- 357
- 358
- 359
- 360
- 361
- 362
- 363
- 364
- 365
- 366
- 367
- 368
- 369
- 370
- 371
- 372
- 373
- 374
- 375
- 376
- 377
- 378
- 379
- 380
- 381
- 382
- 383
- 384
- 385
- 386
- 387
- 388
- 389
- 390
- 391
- 392
- 393
- 394
- 395
- 396
- 397
- 398
- 399
- 400
- 401
- 402
- 403
- 404
- 405
- 406
- 407
- 408
- 409
- 410
- 411
- 412
- 413
- 414
- 415
- 416
- 417
- 418
- 419
- 420
- 421
- 422
- 423
- 424
- 425
- 426
- 427
- 428
- 429
- 430
- 431
- 432
- 433
- 434
- 435
- 436
- 437
- 438
- 439
- 440
- 441
- 442
- 443
- 444
- 445
- 446
- 447
- 448
- 449
- 450
- 451
- 452
- 453
- 454
- 455
- 456
- 457
- 458
- 459
- 460
- 461
- 462
- 463
- 464
- 465
- 466
- 467
- 468
- 469
- 470
- 471
- 472
- 473
- 474
- 475
- 476
- 477
- 478
- 479
- 480
- 481
- 482
- 483
- 484
- 485
- 486
- 487
- 488
- 489
- 490
- 491
- 492
- 493
- 494
- 495
- 496
- 497
- 498
- 499
- 500
- 501
- 502
- 503
- 504
- 505
- 506
- 507
- 508
- 509
- 510
- 511
- 512
- 513
- 514
- 515
- 516
- 517
- 518
- 519
- 520
- 521
- 522
- 523
- 524
- 525
- 526
- 527
- 528
- 529
- 530
- 531
- 532
- 533
- 534
- 535
- 536
- 537
- 538
- 539
- 540
- 541
- 542
- 543
- 544
- 545
- 546
- 547
- 548
- 549
- 550
- 551
- 552
- 553
- 554
- 555
- 556
- 557
- 558
- 559
- 560
- 561
- 562
- 563
- 564
- 565
- 566
- 567
資訊
HKSIP2ET1
您已完成過測驗,因此您不能再測驗。
測驗載入中...
您必須登入或註冊才能開始測驗。
您必須先完成以下測驗才能開始:
百分比
答對 0/567 個問題
答題時間:
時間已花費
您獲得 0/0 分數 (0)
| 平均分數 |
|
| 您的成績 |
|
類別
- Topic 1 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
- 341
- 342
- 343
- 344
- 345
- 346
- 347
- 348
- 349
- 350
- 351
- 352
- 353
- 354
- 355
- 356
- 357
- 358
- 359
- 360
- 361
- 362
- 363
- 364
- 365
- 366
- 367
- 368
- 369
- 370
- 371
- 372
- 373
- 374
- 375
- 376
- 377
- 378
- 379
- 380
- 381
- 382
- 383
- 384
- 385
- 386
- 387
- 388
- 389
- 390
- 391
- 392
- 393
- 394
- 395
- 396
- 397
- 398
- 399
- 400
- 401
- 402
- 403
- 404
- 405
- 406
- 407
- 408
- 409
- 410
- 411
- 412
- 413
- 414
- 415
- 416
- 417
- 418
- 419
- 420
- 421
- 422
- 423
- 424
- 425
- 426
- 427
- 428
- 429
- 430
- 431
- 432
- 433
- 434
- 435
- 436
- 437
- 438
- 439
- 440
- 441
- 442
- 443
- 444
- 445
- 446
- 447
- 448
- 449
- 450
- 451
- 452
- 453
- 454
- 455
- 456
- 457
- 458
- 459
- 460
- 461
- 462
- 463
- 464
- 465
- 466
- 467
- 468
- 469
- 470
- 471
- 472
- 473
- 474
- 475
- 476
- 477
- 478
- 479
- 480
- 481
- 482
- 483
- 484
- 485
- 486
- 487
- 488
- 489
- 490
- 491
- 492
- 493
- 494
- 495
- 496
- 497
- 498
- 499
- 500
- 501
- 502
- 503
- 504
- 505
- 506
- 507
- 508
- 509
- 510
- 511
- 512
- 513
- 514
- 515
- 516
- 517
- 518
- 519
- 520
- 521
- 522
- 523
- 524
- 525
- 526
- 527
- 528
- 529
- 530
- 531
- 532
- 533
- 534
- 535
- 536
- 537
- 538
- 539
- 540
- 541
- 542
- 543
- 544
- 545
- 546
- 547
- 548
- 549
- 550
- 551
- 552
- 553
- 554
- 555
- 556
- 557
- 558
- 559
- 560
- 561
- 562
- 563
- 564
- 565
- 566
- 567
- 已答
- 回顧
-
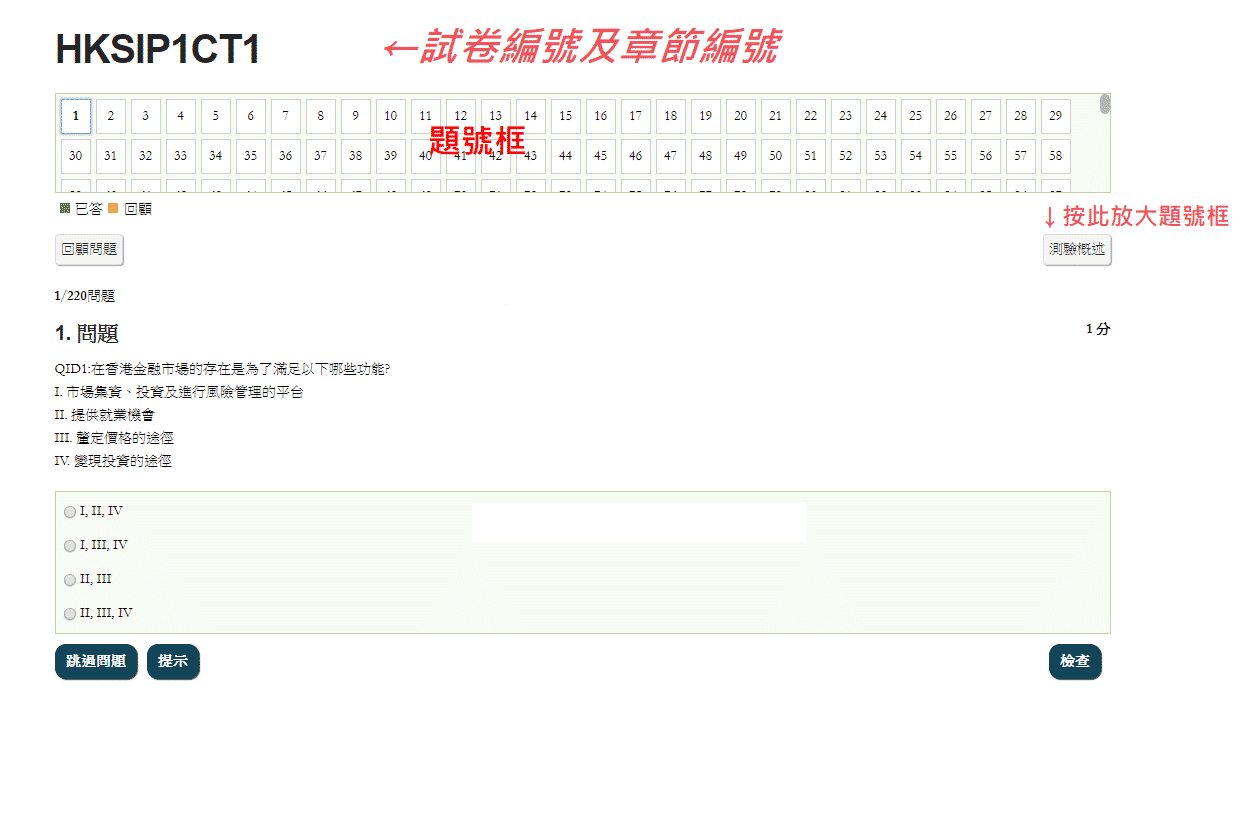
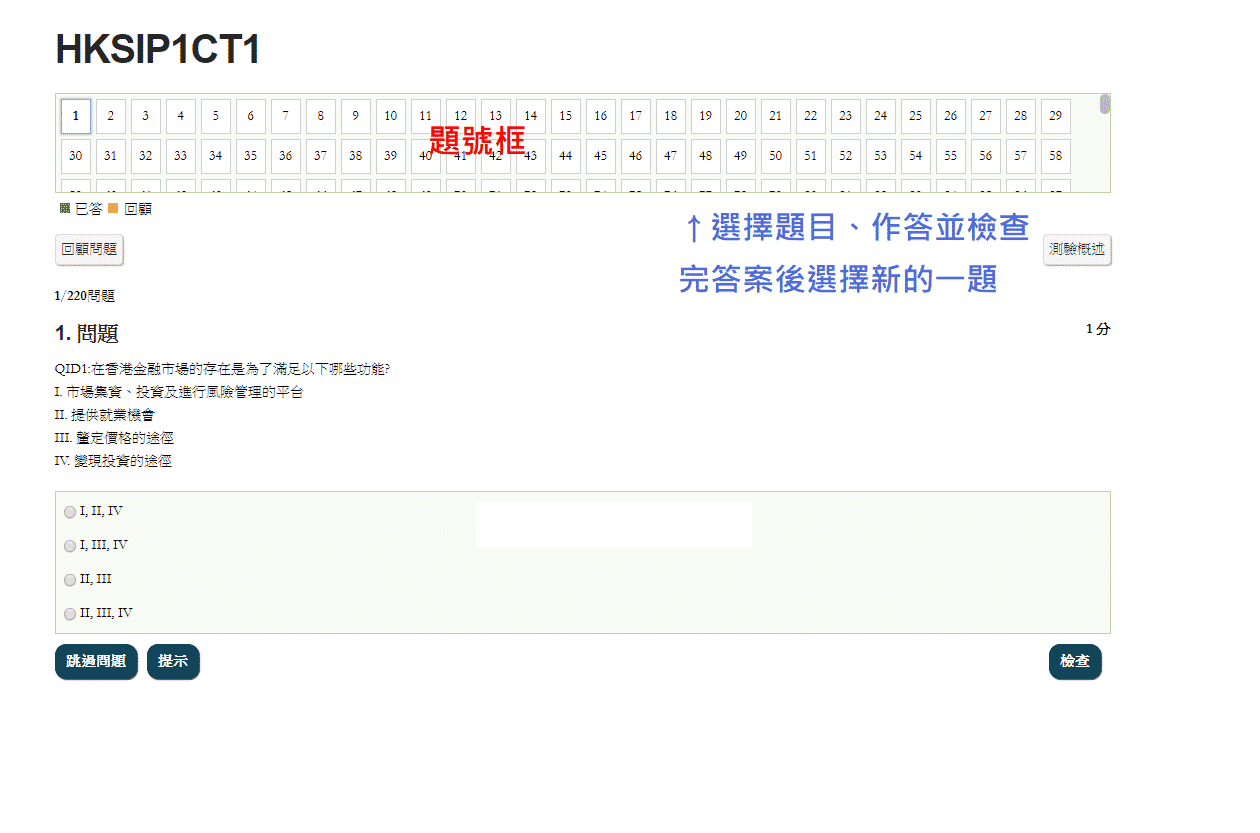
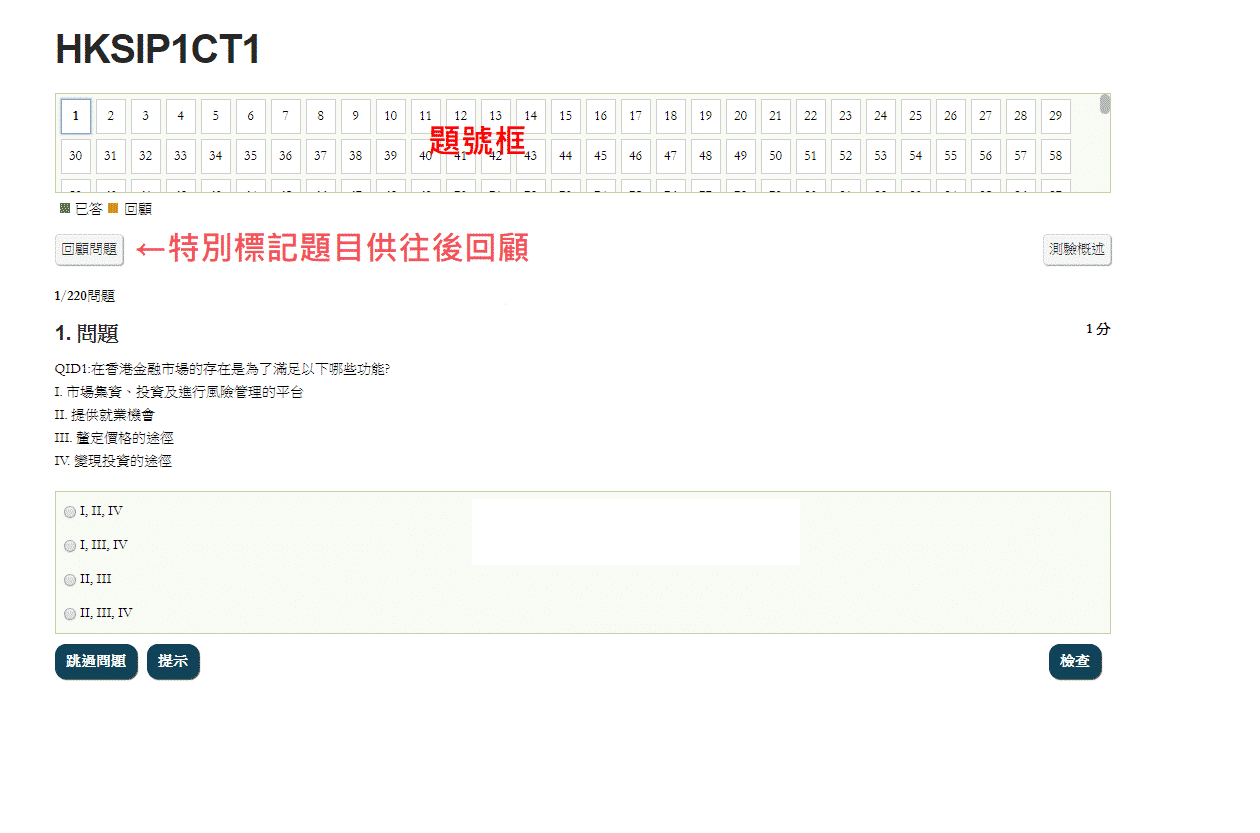
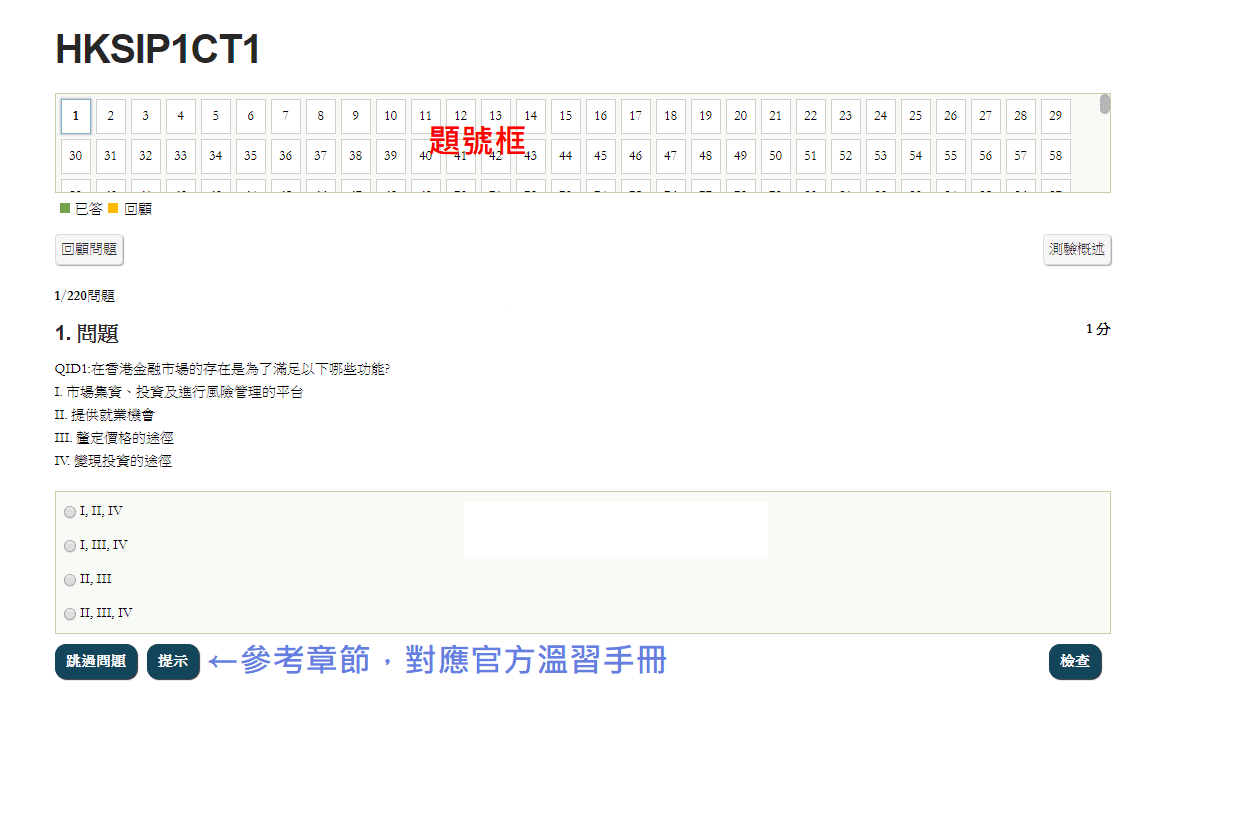
1/567問題
1. 問題
1 分QID2680:Which of the following description does not fit financial regulators in Hong Kong?
正確
Decisions made by the regulators can be overturned or overruled.
錯誤
Decisions made by the regulators can be overturned or overruled.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.1
-
2/567問題
2. 問題
1 分QID1034:Globalisation and advances in technology have enabled investors to
I. Participate in different markets
II. Arbitrage between markets
III. Arbitrage between products
IV. Increase investment returns by diversifying正確
Globalisation and advances in technology have enabled investors to move rapidly from one market to another, arbitraging between markets, products and transactions.
The main purpose of diversification is not to increase investment returns, but to reduce risk.錯誤
Globalisation and advances in technology have enabled investors to move rapidly from one market to another, arbitraging between markets, products and transactions.
The main purpose of diversification is not to increase investment returns, but to reduce risk.提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.1
-
3/567問題
3. 問題
1 分QID780:Which of the following demands have to be satisfied by the wide range of financial products and services available in Hong Kong?
I. Meet demands for investmentII. Employment opportunities for locals
III. Employment opportunities for expatriates
IV. Capital and investment protection
正確
Hong Kong’s status as an international financial centre is reflected in the wide range of financial products and services available in Hong Kong, developed to meet demands for investment, capital and income formation and capital raising, the facilitation of cash and capital flows, capital and investment protection (for example, hedging), safe custody and security, speculation and insurance. The financial markets also provide an avenue for price discovery and liquidity of investments.
錯誤
Hong Kong’s status as an international financial centre is reflected in the wide range of financial products and services available in Hong Kong, developed to meet demands for investment, capital and income formation and capital raising, the facilitation of cash and capital flows, capital and investment protection (for example, hedging), safe custody and security, speculation and insurance. The financial markets also provide an avenue for price discovery and liquidity of investments.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.1
-
4/567問題
4. 問題
1 分QID784:A risk-based regulatory system refers to a system in which:
正確
The regulatory approach adopted by the SFC is a risk-based one, meaning that regulation is weighted towards the areas where the SFC perceives the highest risk to lie.
錯誤
The regulatory approach adopted by the SFC is a risk-based one, meaning that regulation is weighted towards the areas where the SFC perceives the highest risk to lie.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.2
-
5/567問題
5. 問題
1 分QID785:The SFC regime adopts which of the following regulatory approaches?
正確
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
錯誤
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.2
-
6/567問題
6. 問題
1 分QID782:The SFC is a/an _______ in Hong Kong.
正確
The SFC was created by law under the Securities and Futures Commission Ordinance (now repealed and subsumed in the SFO). It is independent, meaning that it is not part of the
Government machinery of the Civil Service or the ministerial system. Nevertheless, it reports to and is accountable to the Government as described in section 2 above. It is considered the securities and futures market prime regulator.錯誤
The SFC was created by law under the Securities and Futures Commission Ordinance (now repealed and subsumed in the SFO). It is independent, meaning that it is not part of the
Government machinery of the Civil Service or the ministerial system. Nevertheless, it reports to and is accountable to the Government as described in section 2 above. It is considered the securities and futures market prime regulator.提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.2
-
7/567問題
7. 問題
1 分QID10:Which approach to regulation is adopted by the SFC to regulate securities and futures markets?
正確
The SFC adopts a“risk-based”approach towards regulations. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
錯誤
The SFC adopts a“risk-based”approach towards regulations. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.2
-
8/567問題
8. 問題
1 分QID786:Which of the following regulatory approaches adopted by the SFC is given more regulatory attention towards the areas where the SFC perceives the highest risks to lie?
正確
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
錯誤
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.2
-
9/567問題
9. 問題
1 分QID783:What approach does the SFC take to regulate market intermediaries?
正確
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
錯誤
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.2
-
10/567問題
10. 問題
1 分QID3103:Which of the following best describes the role of the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) in Hong Kong?
正確
The SFC’s role includes the supervision of licensed corporations and their associated entities, focusing on areas where it perceives the highest risk. It is not primarily responsible for regulating international trade laws, supervising the banking system, or providing cybersecurity training.
錯誤
The SFC’s role includes the supervision of licensed corporations and their associated entities, focusing on areas where it perceives the highest risk. It is not primarily responsible for regulating international trade laws, supervising the banking system, or providing cybersecurity training.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.2
-
11/567問題
11. 問題
1 分QID3080:What is the primary approach adopted by the SFC for regulating market intermediaries?
正確
The SFC employs a risk-based supervision approach, focusing on regulation in areas where the risks are perceived to be greatest to ensure the integrity and stability of the financial markets.
錯誤
The SFC employs a risk-based supervision approach, focusing on regulation in areas where the risks are perceived to be greatest to ensure the integrity and stability of the financial markets.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.2
-
12/567問題
12. 問題
1 分QID3076:Which of the following entities is responsible for the regulation of securities-related products such as equities, warrants, and bonds in Hong Kong?
正確
The Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) is the principal regulator of the securities industry in Hong Kong, overseeing the regulation and discipline of participants in the securities and futures markets. The SFC adopts a risk-based regulatory approach, focusing on areas perceived to have the highest risk. In contrast, HKMA is Hong Kong’s central banking institution, SEHK is a securities exchange, and HKFE is a futures exchange, making options A, B, and D incorrect.
錯誤
The Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) is the principal regulator of the securities industry in Hong Kong, overseeing the regulation and discipline of participants in the securities and futures markets. The SFC adopts a risk-based regulatory approach, focusing on areas perceived to have the highest risk. In contrast, HKMA is Hong Kong’s central banking institution, SEHK is a securities exchange, and HKFE is a futures exchange, making options A, B, and D incorrect.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.2
-
13/567問題
13. 問題
1 分QID787:Which of the following regulatory approach is adopted by the SFC?
正確
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
錯誤
An expression used by the SFC to explain its approach to regulation is that it is “risk-based”. This basically means that regulation is weighted towards the areas that pose the greatest risk to the markets and the participants.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.2
-
14/567問題
14. 問題
1 分QID781:The principal regulator of the securities industry in Hong Kong is the
正確
The principal regulator of the securities industry in Hong Kong is the SFC, which assumes responsibility for front-line regulation and discipline of participants trading on the securities and futures exchanges and also of other securities intermediaries.
錯誤
The principal regulator of the securities industry in Hong Kong is the SFC, which assumes responsibility for front-line regulation and discipline of participants trading on the securities and futures exchanges and also of other securities intermediaries.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.2
-
15/567問題
15. 問題
1 分QID2832:Which of the following is not a financial regulator in Hong Kong?
正確
The Securities Commission option is wrong, the correct name is Securities and Futures Commission.
錯誤
The Securities Commission option is wrong, the correct name is Securities and Futures Commission.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.3
-
16/567問題
16. 問題
1 分QID1188:Which of the following organizations cooperate closely with the SFC on issues of common interest?
I. HKMA
II. Companies Registry
III. Inland Revenue Department
IV. Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing正確
There are fewer opportunities for cooperation between the SFCand the tax bureau than other agencies.
錯誤
There are fewer opportunities for cooperation between the SFCand the tax bureau than other agencies.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.3
-
17/567問題
17. 問題
1 分QID1658:Hong Kong Financial Regulatory Regime is
正確
Hong Kong Financial Regulatory Regime is able to address new and complex financial products.
錯誤
Hong Kong Financial Regulatory Regime is able to address new and complex financial products.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.3
-
18/567問題
18. 問題
1 分QID903:Which of the following are not common objectives of financial regulators in Hong Kong?
I. Promote intervention to enhance international and local market confidence.
II. Provide investment advice to retail investors
III. Encourage the installation of a sound technical infrastructure for the functioning of the financial markets
IV. Ensure that the legal framework of financial regulation is certain, adequate and fairly enforced正確
Frequent Intervention is not an objective of financial regulators in Hong Kong. Providing Investment advice is not a job that regulators will do, it’s the job of intermediaries.
錯誤
Frequent Intervention is not an objective of financial regulators in Hong Kong. Providing Investment advice is not a job that regulators will do, it’s the job of intermediaries.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.3
-
19/567問題
19. 問題
1 分QID3077:Which of the following products are included in the securities-related products addressed by the manual for the licensing regime?
I. Unit trusts/mutual funds
II. Equity linked instruments
III. Virtual assets regarded as securities IV. Exchange-traded futures正確
Unit trusts/mutual funds (I), equity-linked instruments(II), and virtual assets regarded as securities (III) are traded on SEHK. However, Exchange-traded futures (IV) are traded on HKFE.
錯誤
Unit trusts/mutual funds (I), equity-linked instruments(II), and virtual assets regarded as securities (III) are traded on SEHK. However, Exchange-traded futures (IV) are traded on HKFE.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.4
-
20/567問題
20. 問題
1 分QID3073:Which of the following securities-related products is NOT traded on The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited (SEHK)?
正確
Exchange-traded futures are traded on the Hong Kong Futures Exchange Limited (HKFE) and not on The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited (SEHK), making option D the correct answer.
錯誤
Exchange-traded futures are traded on the Hong Kong Futures Exchange Limited (HKFE) and not on The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited (SEHK), making option D the correct answer.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.4
-
21/567問題
21. 問題
1 分QID3074:Which of the following are securities-related products addressed in the context of the licensing regime?
I. Equities
II. Bonds and other debt instruments
III. Equity linked instruments
IV. Standard futures contracts正確
Equities (I), bonds and other debt instruments (II), and equity-linked instruments (III) are securities-related products under the licensing regime. However, Standard futures contracts (IV) are not regarded as securities-related products.
錯誤
Equities (I), bonds and other debt instruments (II), and equity-linked instruments (III) are securities-related products under the licensing regime. However, Standard futures contracts (IV) are not regarded as securities-related products.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.4
-
22/567問題
22. 問題
1 分QID790:Which of the following categories does not fall under the securities and futures services in Hong Kong?
正確
Advising a trust is not a securities and futures service in Hong Kong.
錯誤
Advising a trust is not a securities and futures service in Hong Kong.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.6
-
23/567問題
23. 問題
1 分QID789:Which of the following activities falls under Hong Kong’s securities and futures services?
I. Trading securities on behalf of clients on the Stock Exchange of Hong Kong (SEHK).
II. Providing margin financing and accommodation on securities trading
III. Acting as an “introducing agent”
IV. Conducting stock borrowing and lending transactions.正確
All of these services fall under Hong Kong’s securities and futures services.
錯誤
All of these services fall under Hong Kong’s securities and futures services.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.6
-
24/567問題
24. 問題
1 分QID4:Which of the following activities is a financial service provided by a financial intermediary?
正確
Financial intermediaries must be compensated to be classified as providers of financial transactions and services. Establishing a tutorial company offers educational services, not financial ones. Managing assets without compensation doesn’t fall under financial services. Therefore, signing a rental agreement for a bank, which is not a financial contract but a real estate contract, is not considered a financial intermediary service. However, loaning money to others and charging interest for the principal is a financial service that involves compensation for a financial transaction.
錯誤
Financial intermediaries must be compensated to be classified as providers of financial transactions and services. Establishing a tutorial company offers educational services, not financial ones. Managing assets without compensation doesn’t fall under financial services. Therefore, signing a rental agreement for a bank, which is not a financial contract but a real estate contract, is not considered a financial intermediary service. However, loaning money to others and charging interest for the principal is a financial service that involves compensation for a financial transaction.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.6
-
25/567問題
25. 問題
1 分QID2674:Which of the following activity is subject to supervision by the financial regulators?
正確
Providing loans and collecting interest is money lending and is a regulated financial intermediary activity.
錯誤
Providing loans and collecting interest is money lending and is a regulated financial intermediary activity.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.6
-
26/567問題
26. 問題
1 分QID792:Which of the following individuals/institutions is NOT a provider of securities and futures investment products and services in Hong Kong?
正確
Intermediaries are providers of securities and futures investment products and services in Hong Kong. Institutional investors are participants but not providers.
錯誤
Intermediaries are providers of securities and futures investment products and services in Hong Kong. Institutional investors are participants but not providers.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.7
-
27/567問題
27. 問題
1 分QID5:Which of the followings is not a financial service provider?
正確
In financial markets, providers of financial products and services include principals and intermediaries. Fund managers, stockbrokers, and independent financial advisers are all intermediaries. Auditors are professionals supporting financial markets.
錯誤
In financial markets, providers of financial products and services include principals and intermediaries. Fund managers, stockbrokers, and independent financial advisers are all intermediaries. Auditors are professionals supporting financial markets.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.7
-
28/567問題
28. 問題
1 分QID791:Which of the following are major providers of securities investment and advisory service in Hong Kong?
I. An intermediary trading securities on the Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited (SEHK)
II. An intermediary acting on behalf of a foreign intermediary
III. An underwriter
IV. Insurance companies正確
The principal service providers in the securities investment and advising business are:
(a) intermediaries who are participants of the SEHK;
(b) intermediaries who act for foreign securities companies;
(c) underwriters;
(d) fund and portfolio managers;
(e) approved agents who introduce clients to exchange participants or other brokers but do not handle client assets;
(f) corporate finance advisers;
(g) advisers to retail investors;
(h) virtual asset service providers;
(i) financial planners for collective investment schemes (“CISs”);
(j) securities analysts;
(k) licensed banks;
(l) trust companies;
(m) securities margin financiers;
(n) support service providers: lawyers, accountants, auditors and valuers;
(o) listed companies;
(p) financial journalists and radio broadcasters;
(q) market operators who provide exchange and/or clearing functions for transactions in securities, i.e. HKEX, including the SEHK and Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited;
(r) The Investor Compensation Company Limited (“ICC”): the ICC is an independent company recognised by the SFC for dealing with investor compensation matters;
(s) ATS providers: provide by means of electronic facilities, a trading mechanism for securities and futures contracts other than the operations of a recognised exchange company or a recognised clearing house (at the moment this would only cover the SEHK, HKFE and their related clearing houses), for example, trade confirmation and matching systems provided by brokers;
(t) exchanges from outside Hong Kong: there are dealers in Hong Kong who provide local investors with access to overseas exchanges;
(u) share registrars (who have formed a Federation of Share Registrars, with the approval of the SFC) providing share registry services to issuers of listed securities; and
(v) nominee companies that hold client assets of intermediaries.錯誤
The principal service providers in the securities investment and advising business are:
(a) intermediaries who are participants of the SEHK;
(b) intermediaries who act for foreign securities companies;
(c) underwriters;
(d) fund and portfolio managers;
(e) approved agents who introduce clients to exchange participants or other brokers but do not handle client assets;
(f) corporate finance advisers;
(g) advisers to retail investors;
(h) virtual asset service providers;
(i) financial planners for collective investment schemes (“CISs”);
(j) securities analysts;
(k) licensed banks;
(l) trust companies;
(m) securities margin financiers;
(n) support service providers: lawyers, accountants, auditors and valuers;
(o) listed companies;
(p) financial journalists and radio broadcasters;
(q) market operators who provide exchange and/or clearing functions for transactions in securities, i.e. HKEX, including the SEHK and Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited;
(r) The Investor Compensation Company Limited (“ICC”): the ICC is an independent company recognised by the SFC for dealing with investor compensation matters;
(s) ATS providers: provide by means of electronic facilities, a trading mechanism for securities and futures contracts other than the operations of a recognised exchange company or a recognised clearing house (at the moment this would only cover the SEHK, HKFE and their related clearing houses), for example, trade confirmation and matching systems provided by brokers;
(t) exchanges from outside Hong Kong: there are dealers in Hong Kong who provide local investors with access to overseas exchanges;
(u) share registrars (who have formed a Federation of Share Registrars, with the approval of the SFC) providing share registry services to issuers of listed securities; and
(v) nominee companies that hold client assets of intermediaries.提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.7
-
29/567問題
29. 問題
1 分QID3081:Which of the following entities provides electronic facilities for trading and clearing mechanisms for securities and futures contracts, other than the operations of a recognized exchange company or a recognized clearing house?
正確
ATS providers offer electronic facilities that include both trading and clearing mechanisms for securities and futures contracts, which are distinct from the operations of recognized exchange companies or recognized clearing houses.
錯誤
ATS providers offer electronic facilities that include both trading and clearing mechanisms for securities and futures contracts, which are distinct from the operations of recognized exchange companies or recognized clearing houses.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.1.7
-
30/567問題
30. 問題
1 分QID2718:Which of the following is not a common consequence of inadequate corporate governance standards?
正確
Common consequences of deficit in corporate governance standards:
I. Insider trading and other forms of market misconduct
II. Misfeasance, fraud, and misconduct by directors, managers, and other staff causing losses to the company or shareholders
IV. The price of the connected transaction deviates from the market price, causing losses to the company and shareholders錯誤
Common consequences of deficit in corporate governance standards:
I. Insider trading and other forms of market misconduct
II. Misfeasance, fraud, and misconduct by directors, managers, and other staff causing losses to the company or shareholders
IV. The price of the connected transaction deviates from the market price, causing losses to the company and shareholders提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.10
-
31/567問題
31. 問題
1 分QID1243:In order to achieve the goal of supervising the industry, the SFC:
I. Regular inspections, including on-site inspections.
II. Unscheduled inspections, including on-site inspections.
III. Obtaining information from Licensed Corporations (LC)s.
IV. Obtaining information from the Registered Institutions (RI)s.正確
In furtherance of these aims, the SFC conducts regular inspections of licensed corporations which may be conducted either on-site or via a request for information to be provided. The maintenance of proper documentation is critical in this regard.
錯誤
In furtherance of these aims, the SFC conducts regular inspections of licensed corporations which may be conducted either on-site or via a request for information to be provided. The maintenance of proper documentation is critical in this regard.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.12
-
32/567問題
32. 問題
1 分QID1244:In order to facilitate compliance with applicable legal and regulatory requirements in Hong Kong and overseas jurisdictions, which of the following measures can intermediaries take for better coordination?
I. Engage a dedicated compliance officer to oversee adherence to the compliance manual.
II. Appoint a director to serve as a Compliance Officer to oversee adherence to the compliance manual.
III. Maintain close contact with the regulators.
IV. Complement the manual with well defined operational procedures and practices.正確
In order to facilitate compliance with applicable legal and regulatory requirements (in Hong Kong and, where applicable, in overseas jurisdictions), there is a growing tendency to adopt a detailed compliance manual which sets out the securities dealer’s or adviser’s policies and procedures in relation to matters of regulatory concern. In many cases, a dedicated compliance officer is engaged to oversee adherence to the manual, maintain close contact with the regulators and keep abreast of regulatory developments affecting the securities dealer’s or adviser’s business.
錯誤
In order to facilitate compliance with applicable legal and regulatory requirements (in Hong Kong and, where applicable, in overseas jurisdictions), there is a growing tendency to adopt a detailed compliance manual which sets out the securities dealer’s or adviser’s policies and procedures in relation to matters of regulatory concern. In many cases, a dedicated compliance officer is engaged to oversee adherence to the manual, maintain close contact with the regulators and keep abreast of regulatory developments affecting the securities dealer’s or adviser’s business.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.14
-
33/567問題
33. 問題
1 分QID507:Which of the following functions are related to the compliance function of a licensed corporation?
I. The review of record keeping
II. The review of prevention of money laundering
III. The review of client, proprietary and staff dealings
IV. The review of Compliance with all legal and regulator requirements正確
All of these functions are essential as stated in different regulations and guidelines such as the Code of Conduct, the FMCC, AMLO, PDPO, and others.
錯誤
All of these functions are essential as stated in different regulations and guidelines such as the Code of Conduct, the FMCC, AMLO, PDPO, and others.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.3
-
34/567問題
34. 問題
1 分QID1238:To promote, encourage and enforce good compliance practices. Senior management of Licensed Corporations (LC)s and Registered Institutions (RI)s must establish:
I. Good line and reporting structures.
II. Well defined functions and responsibilities.
III. Effective communications channels.
IV. Appropriate transparency and disclosure practices.正確
Senior management must provide the leadership and drive to promote, encourage and enforce, if necessary, good compliance practices. It must establish:
(a) good line and reporting structures;
(b) clearly defined functions and responsibilities;
(c.) effective communications;
(d) appropriate transparency and disclosure practices.錯誤
Senior management must provide the leadership and drive to promote, encourage and enforce, if necessary, good compliance practices. It must establish:
(a) good line and reporting structures;
(b) clearly defined functions and responsibilities;
(c.) effective communications;
(d) appropriate transparency and disclosure practices.提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.3
-
35/567問題
35. 問題
1 分QID2441:A good corporate-governance is not related to which of the following people?
正確
A good corporate-governance is not related to former employees.
錯誤
A good corporate-governance is not related to former employees.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.5
-
36/567問題
36. 問題
1 分QID1237:Which of the following descriptions about corporate governance are correct?
I. It can be seen as primarily concerned with the proper relationship between a company’s management, its board and its shareholders, and possibly also its stakeholders.
II. The governance issue is also concerned with the system by which companies are directed and controlled.
III. The activities of intermediaries frequently concern listed corporations. Accordingly, in addition to considering their own regulatory and corporate governance position, intermediaries need to be aware of the wider impact of corporate governance on their clients and the market.
IV. Markets which exhibit a higher degree of good corporate governance are regarded as more competitive in the international arena.正確
Corporate governance has been defined in various ways. It can be seen as primarily concerned with the proper relationship between a company’s management, its board and its shareholders, and possibly also its stakeholders (i.e. groups who have a stake in the healthy existence of a corporation, such as employees, creditors and customers). The governance issue is therefore also concerned with the system by which companies are directed and controlled.
The activities of intermediaries frequently concern listed corporations. Accordingly, in addition to considering their own regulatory and corporate governance position, intermediaries need to be aware of the wider impact of corporate governance on their clients and the market. It is now generally accepted that investors attach considerable importance to corporate governance when assessing the value of a stock, and that markets which exhibit a higher degree of good corporate governance are regarded as more competitive in the international arena.錯誤
Corporate governance has been defined in various ways. It can be seen as primarily concerned with the proper relationship between a company’s management, its board and its shareholders, and possibly also its stakeholders (i.e. groups who have a stake in the healthy existence of a corporation, such as employees, creditors and customers). The governance issue is therefore also concerned with the system by which companies are directed and controlled.
The activities of intermediaries frequently concern listed corporations. Accordingly, in addition to considering their own regulatory and corporate governance position, intermediaries need to be aware of the wider impact of corporate governance on their clients and the market. It is now generally accepted that investors attach considerable importance to corporate governance when assessing the value of a stock, and that markets which exhibit a higher degree of good corporate governance are regarded as more competitive in the international arena.提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.5
-
37/567問題
37. 問題
1 分QID508:Which of the following is NOT included the set of core principles of corporate governance?
正確
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (“OECD”) has issued a set of core principles of corporate governance practices to include fairness, transparency, accountability and responsibility. Leadership is not one of those principles.
錯誤
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (“OECD”) has issued a set of core principles of corporate governance practices to include fairness, transparency, accountability and responsibility. Leadership is not one of those principles.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.5
-
38/567問題
38. 問題
1 分QID1239:Corporate governance describes which of the following relationship?
正確
Corporate governance has been defined in various ways. It can be seen as primarily concerned with the proper relationship between a company’s management, its board and its shareholders, and possibly also its stakeholders (i.e. groups who have a stake in the healthy existence of a corporation, such as employees, creditors and customers).
錯誤
Corporate governance has been defined in various ways. It can be seen as primarily concerned with the proper relationship between a company’s management, its board and its shareholders, and possibly also its stakeholders (i.e. groups who have a stake in the healthy existence of a corporation, such as employees, creditors and customers).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.5
-
39/567問題
39. 問題
1 分QID509:Corporate governance refers to the system of by which companies are directed and controlled and concerns which of the following groups of people?
I. Company management.
II. Board of Directors.
III. Shareholders.
IV. Stakeholders.正確
Corporate governance has been defined in various ways. It can be seen as primarily concerned with the proper relationship between a company’s management, its board and its shareholders, and possibly also its stakeholders (i.e. groups who have a stake in the healthy existence of a corporation, such as employees, creditors and customers).
錯誤
Corporate governance has been defined in various ways. It can be seen as primarily concerned with the proper relationship between a company’s management, its board and its shareholders, and possibly also its stakeholders (i.e. groups who have a stake in the healthy existence of a corporation, such as employees, creditors and customers).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.5
-
40/567問題
40. 問題
1 分QID512:Good governance practices can include which of the following ways?
I. Installing appropriate checks and balances on the board of
directors and senior management.
II. Having sufficient transparency and disclosure of important facts and information to stakeholders.
III. Installing strong protective structures for majority shareholder.
IV. Identifying and penalizing corporate wrongdoing.正確
A key objective of good governance in any corporate business is to avoid management taking improper advantage of its position to benefit itself in preference to the legitimate interests of the company. Having regard to the general concepts set out by the OECD, some of the ways a company may improve its governance are as follows:
(a) installing appropriate checks and balances.
(b) increasing transparency and disclosure to shareholders, stakeholders and the public;
(c) installing strong protective structures for minority shareholders, creditors and other lenders.
(d) identifying and penalising corporate wrongdoing.錯誤
A key objective of good governance in any corporate business is to avoid management taking improper advantage of its position to benefit itself in preference to the legitimate interests of the company. Having regard to the general concepts set out by the OECD, some of the ways a company may improve its governance are as follows:
(a) installing appropriate checks and balances.
(b) increasing transparency and disclosure to shareholders, stakeholders and the public;
(c) installing strong protective structures for minority shareholders, creditors and other lenders.
(d) identifying and penalising corporate wrongdoing.提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.9
-
41/567問題
41. 問題
1 分QID510:Good corporate governance includes which of the following features?
I. The recruitment of experienced executive directors who are realistically rewarded to ensure that the business is run
efficiently.
II. The installation of a well regulated structure incorporating close and detailed top managerial supervision of day-to-day
operations of the business.
III. The recruitment of experienced non-executive directors with the objective of ensuring a good balance between executive
and non-executive directors.
IV. Installation of audit and remuneration committees who will ensure independent audits and fair performance geared reward structures.正確
A key objective of good governance in any corporate business is to avoid management taking improper advantage of its position to benefit itself in preference to the legitimate interests of the company. Having regard to the general concepts set out by the OECD, some of the ways a company may improve its governance are as follows:
(a) installing appropriate checks and balances, such as separating the functions of Chairman and CEO; appointment of independent non-executive directors; establishment of independent audit committees; setting up committees to control the remuneration and benefits of directors and senior management.錯誤
A key objective of good governance in any corporate business is to avoid management taking improper advantage of its position to benefit itself in preference to the legitimate interests of the company. Having regard to the general concepts set out by the OECD, some of the ways a company may improve its governance are as follows:
(a) installing appropriate checks and balances, such as separating the functions of Chairman and CEO; appointment of independent non-executive directors; establishment of independent audit committees; setting up committees to control the remuneration and benefits of directors and senior management.提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.9
-
42/567問題
42. 問題
1 分QID929:Which of the following are not examples of good corporate governance?
I. Set up remuneration committee to control the remuneration of management.
II. Assign the management to multiple roles to cut cost.
III. Offer high degree of discretionary powers to the management to allow them to enhance efficiency.
IV. Install check and balances to limited the power of the management正確
The essence of corporate governance is to enhance transparency and check and balance. The powers of the management should be limited, therefore, installation of check and balances and limiting the management’s remuneration are good practices.
錯誤
The essence of corporate governance is to enhance transparency and check and balance. The powers of the management should be limited, therefore, installation of check and balances and limiting the management’s remuneration are good practices.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.9
-
43/567問題
43. 問題
1 分QID1240:Which of the following is NOT a probable measure that can be taken to improve corporate governance?
正確
It’s not required to protect the interests of the management.
錯誤
It’s not required to protect the interests of the management.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.9
-
44/567問題
44. 問題
1 分QID1241:The primary objective of good corporate governance is to:
正確
A key objective of good governance in any corporate business is to avoid management taking improper advantage of its position to benefit itself in preference to the legitimate interests of the company.
錯誤
A key objective of good governance in any corporate business is to avoid management taking improper advantage of its position to benefit itself in preference to the legitimate interests of the company.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.9
-
45/567問題
45. 問題
1 分QID1242:A company may improve its corporate governance through the following means with the exception of:
正確
Having regard to the general concepts set out by the OECD, some of the ways a company may improve its governance are as follows:
(a) installing appropriate checks and balances, such as separating the functions of the chairman and chief executive officer, appointment of independent non-executive directors, establishment of independent audit committees, and setting up committees to control the remuneration and benefits of directors and senior management;
(b) increasing transparency and disclosure to shareholders, stakeholders and the public;
(c.) adopting international accounting and auditing standards;
(d) installing strong protective structures for minority shareholders, creditors and other lenders.
(e) identifying and penalising corporate wrongdoing.錯誤
Having regard to the general concepts set out by the OECD, some of the ways a company may improve its governance are as follows:
(a) installing appropriate checks and balances, such as separating the functions of the chairman and chief executive officer, appointment of independent non-executive directors, establishment of independent audit committees, and setting up committees to control the remuneration and benefits of directors and senior management;
(b) increasing transparency and disclosure to shareholders, stakeholders and the public;
(c.) adopting international accounting and auditing standards;
(d) installing strong protective structures for minority shareholders, creditors and other lenders.
(e) identifying and penalising corporate wrongdoing.提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.9
-
46/567問題
46. 問題
1 分QID511:Which of the following measures reflect effective corporate governance?
I. Installing appropriate checks and balances.
II. Increasing transparency and disclosure to shareholders , stakeholders and the public.
III. Adopting international accounting and auditing standards.
IV. Installing strong protective structures for minority shareholders, creditors and other lenders.正確
A key objective of good governance in any corporate business is to avoid management taking improper advantage of its position to benefit itself in preference to the legitimate interests of the company. Having regard to the general concepts set out by the OECD, some of the ways a company may improve its governance are as follows:
(a) installing appropriate checks and balances.
(b) increasing transparency and disclosure to shareholders, stakeholders and the public;
(c) adopting international accounting and auditing standards;
(d) installing strong protective structures for minority shareholders, creditors and other lenders.錯誤
A key objective of good governance in any corporate business is to avoid management taking improper advantage of its position to benefit itself in preference to the legitimate interests of the company. Having regard to the general concepts set out by the OECD, some of the ways a company may improve its governance are as follows:
(a) installing appropriate checks and balances.
(b) increasing transparency and disclosure to shareholders, stakeholders and the public;
(c) adopting international accounting and auditing standards;
(d) installing strong protective structures for minority shareholders, creditors and other lenders.提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.9
-
47/567問題
47. 問題
1 分QID2676:Whats the objective of SFC requiring the disclosure of rights?
正確
Disclosure requiremetns are in place to enhance transperancy
錯誤
Disclosure requiremetns are in place to enhance transperancy
提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.9
-
48/567問題
48. 問題
1 分QID1684:Good Corporate governance are not required to be responsible for the interest of which of the following
正確
A key objective of good governance in any company is to avoid management taking improper advantage of its position to benefit itself in preference to the legitimate interests of thecompany.
Good Corporate governance are not required to be responsible for the interest of Former Employees.錯誤
A key objective of good governance in any company is to avoid management taking improper advantage of its position to benefit itself in preference to the legitimate interests of thecompany.
Good Corporate governance are not required to be responsible for the interest of Former Employees.提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.9
-
49/567問題
49. 問題
1 分QID971:Good corporate governance should separate the functions of
正確
Good corporate governance should separate the functions of Chairman and CEO.
錯誤
Good corporate governance should separate the functions of Chairman and CEO.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.9
-
50/567問題
50. 問題
1 分QID2757:Which of the following is a concept provided by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development that a company can improve the level of corporate governance?
I. Distinguish between the Chief Executive Officer and the Chairman of the Board
II. Enhance transparency disclosure to shareholders and stakeholders
III. Establish a compensation committee to monitor senior management compensation
IV. Establish a robust protection structure for minority shareholders, creditors or other stakeholders正確
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development offers the concept that companies can improve the level of corporate governance by the following methods:
I. Distinguish between the Chief Executive Officer and the Chairman
II. Enhance transparency disclosure to shareholders and stakeholders
III. Establish a compensation committee to monitor senior management compensation
IV. Establish a strong protection structure for minority shareholders, creditors, or other stakeholders
V. Establish an independent audit committee
VI. Identify business misconduct
VII. Adopt international accounting and auditing standards錯誤
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development offers the concept that companies can improve the level of corporate governance by the following methods:
I. Distinguish between the Chief Executive Officer and the Chairman
II. Enhance transparency disclosure to shareholders and stakeholders
III. Establish a compensation committee to monitor senior management compensation
IV. Establish a strong protection structure for minority shareholders, creditors, or other stakeholders
V. Establish an independent audit committee
VI. Identify business misconduct
VII. Adopt international accounting and auditing standards提示
Reference Chapter:1.10.9
-
51/567問題
51. 問題
1 分QID90:In which of the following circumstances will the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) investigate a licensed corporation?
I. When the licensed corporation’s operations deteriorate and it is unable to pay the licence fee.
II. When clients lodge complaints against the licensed corporation for failing to inform them about the whereabouts of deposited funds upon their requests.
III. When an informant provides information that the licensed corporation is mismanaged, growth has slowed, and it is contemplating a sale.
IV. When an informant provides information that the licensed corporation is mismanaged and is incurring losses.正確
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes, and guidelines.
Failure to pay license fees on time is a violation of the Securities and Futures (Fees) Rules;
Failure to tell clients where their money is going is a breach of the Securities and Futures (Client Money) Rules.
So options I and II are correct.錯誤
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes, and guidelines.
Failure to pay license fees on time is a violation of the Securities and Futures (Fees) Rules;
Failure to tell clients where their money is going is a breach of the Securities and Futures (Client Money) Rules.
So options I and II are correct.提示
Reference Chapter:1.11.3
-
52/567問題
52. 問題
1 分QID888:Can the SFC conduct supervisory inspections on the associated entity of an intermediary?
正確
The SFC can conduct supervisory inspections on an intermediary or an associated entity of an intermediary.
錯誤
The SFC can conduct supervisory inspections on an intermediary or an associated entity of an intermediary.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.11.3
-
53/567問題
53. 問題
1 分QID206:These are key provisions of the SFO that give the SFC considerable powers to investigate, among other things, possible breaches of the SFO, misfeasance and activities not in the public interest. The powers that SFC possesses include which of the followings?
I. SFC can only investigate licenced corporation
II. SFC can require an individual to provide evidence to an investigation, regardless of whether the individual is an intermediary or not.
III. SFC may apply to the court to order a person who does not comply with requirements made by the authorised person or investigator under relevant provisions to do so.
IV. SFC may require an individual under investigation to make a statutory declaration that he is unable to provide the evidence for reasons to be stated, if such is the case.正確
The SFC may authorise an employee (or another person with the consent of the Financial Secretary) to carry out an investigation. The person so authorised may investigate any person. A person under investigation is required to:
(a) provide documents and explanations;
(e.) make a statutory declaration that he is unable to provide the evidence for reasons to be stated, if such is the case.
The SFC may apply to the court to order a person who does not comply with requirements made by the authorised person or investigator under relevant provisions to do so (s. 185, SFO).錯誤
The SFC may authorise an employee (or another person with the consent of the Financial Secretary) to carry out an investigation. The person so authorised may investigate any person. A person under investigation is required to:
(a) provide documents and explanations;
(e.) make a statutory declaration that he is unable to provide the evidence for reasons to be stated, if such is the case.
The SFC may apply to the court to order a person who does not comply with requirements made by the authorised person or investigator under relevant provisions to do so (s. 185, SFO).提示
Reference Chapter:1.11.6
-
54/567問題
54. 問題
1 分QID2690:Ms. Lam, a private investor, is requested by the SFC to assist in an investigation under the SFO. Which of the following statements about her obligations and potential legal consequences is correct?
正確
Under the SFO, the SFC is authorized to investigate any person and to require assistance in these investigations.A person is guilty of an offense if, without reasonable excuse, they fail to comply with the requests of an investigator, or if they provide a response that is false or misleading. Such offenses can lead to criminal prosecution.
錯誤
Under the SFO, the SFC is authorized to investigate any person and to require assistance in these investigations.A person is guilty of an offense if, without reasonable excuse, they fail to comply with the requests of an investigator, or if they provide a response that is false or misleading. Such offenses can lead to criminal prosecution.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.11.6
-
55/567問題
55. 問題
1 分QID205:The Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) is conducting an investigation on insider trading. Miss Ko, a retail investor, is required to provide information in the course of the investigation. While Miss Ko is not involved in insider trading, is she required to provide information to the SFC?
正確
The SFC has the power to investigate any person in connection with suspicions of malpractice, fraud, or other market misconduct or situations where the interest of the investing public may be jeopardised. It can require the person under investigation to provide information during such investigations. This includes retail investors like Miss Ko. If the person under investigation is unable to provide evidence, they must make a statutory declaration stating the reasons for their inability.
錯誤
The SFC has the power to investigate any person in connection with suspicions of malpractice, fraud, or other market misconduct or situations where the interest of the investing public may be jeopardised. It can require the person under investigation to provide information during such investigations. This includes retail investors like Miss Ko. If the person under investigation is unable to provide evidence, they must make a statutory declaration stating the reasons for their inability.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.11.7
-
56/567問題
56. 問題
1 分QID219:Mdm. Liu is a senior citizen. She is a stock investment enthusiast but suffers losses often. The SFC recently conducted an investigation on a company called Sana Seoi Bean Curd and discovered that Mdm. Liu traded the company’s stocks frequently. Thus, the SFC suspected Mdm. Liu of being involved in acts of market misconduct such as the manipulation of the stock market and requested that she participate in the investigation process. Mdm. Liu had neither knowledge, nor intention of manipulating the stock market. As the SFC investigations were going on for a long time, Mdm. Liu wanted to end the meeting earlier and thus deliberately provided false information perfunctorily to the SFC so as to complete the investigation. Had Mdm. Liu committed an offence according to the Securities and Futures Ordinance?
正確
A person commits an offence if he provides to the SFC (whether in applications or in other circumstances) false or misleading information as to a material particular knowingly or recklessly as to whether it is false or misleading (ss. 383 and 384, SFO).
錯誤
A person commits an offence if he provides to the SFC (whether in applications or in other circumstances) false or misleading information as to a material particular knowingly or recklessly as to whether it is false or misleading (ss. 383 and 384, SFO).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.11.8
-
57/567問題
57. 問題
1 分QID208:The issue of warrant that SFC receives when it applies to the magistrate does NOT include which of the following items of power?
正確
Six months is the longest period permitted for an order to retain documents established by a regular warrant. Any period beyond that must be requested.
錯誤
Six months is the longest period permitted for an order to retain documents established by a regular warrant. Any period beyond that must be requested.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.11.9
-
58/567問題
58. 問題
1 分QID207:An employee of the SFC, an authorised person or an investigator may, under which of the following appropriate circumstances, apply to a magistrate for the issue of a warrant?
I. Authorizing specified persons, a police officer and such other persons as may be necessary to assist in the execution of the warrant to enter specified premises, if necessary by force, at any time within 7 days.
II. Requiring any person on the premises to produce any relevant documents.
III. Prohibiting any person to erase or alter or remove any relevant documents.
IV. Authorizing the specified persons to search for, seize and remove any relevant documents.正確
An employee of the SFC, an authorised person or an investigator may, in appropriate circumstances, apply to a magistrate for the issue of a warrant:
(a) authorising specified persons, a police officer and such other persons as may be necessary to assist in the execution of the warrant to enter specified premises, if necessary by force, at any time within seven days;
(b) requiring any person on the premises to produce any relevant documents;
© prohibiting any person to erase or alter or remove any relevant documents; and
(d) authorising the specified persons to:
(i) search for, seize and remove any relevant documents錯誤
An employee of the SFC, an authorised person or an investigator may, in appropriate circumstances, apply to a magistrate for the issue of a warrant:
(a) authorising specified persons, a police officer and such other persons as may be necessary to assist in the execution of the warrant to enter specified premises, if necessary by force, at any time within seven days;
(b) requiring any person on the premises to produce any relevant documents;
© prohibiting any person to erase or alter or remove any relevant documents; and
(d) authorising the specified persons to:
(i) search for, seize and remove any relevant documents提示
Reference Chapter:1.11.9
-
59/567問題
59. 問題
1 分QID794:Please rank the importance of the following in descending order
正確
Breaches of the SFO and subsidiary legislation are legal offences and will be investigated by the SFC and enforcement action taken. A failure on the part of an intermediary or its representative to comply with a code of conduct is not a breach of law and does not by itself constitute an offence under the law.
錯誤
Breaches of the SFO and subsidiary legislation are legal offences and will be investigated by the SFC and enforcement action taken. A failure on the part of an intermediary or its representative to comply with a code of conduct is not a breach of law and does not by itself constitute an offence under the law.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.2.
-
60/567問題
60. 問題
1 分QID1035:The Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO) is the principal legislative document governing which markets in Hong Kong?
正確
The SFO is the principal legislative document governing the securities market in Hong Kong.
錯誤
The SFO is the principal legislative document governing the securities market in Hong Kong.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.2.1
-
61/567問題
61. 問題
1 分QID847:The rules issued by the SFC, such as Client Securities Rules, are
正確
These are some of the Major Subsidiary Legislation including:
1.1 Securities and Futures (Financial Resources) Rules
1.2 Securities and Futures (Client Securities) Rules
1.3 Securities and Futures (Client Money) Rules
1.4 Securities and Futures (Keeping of Records) Rules
1.5 Securities and Futures (Contract Notes, Statements of Account and Receipts) Rules
1.6 Securities and Futures (Accounts and Audit) Rules,
plus many others.錯誤
These are some of the Major Subsidiary Legislation including:
1.1 Securities and Futures (Financial Resources) Rules
1.2 Securities and Futures (Client Securities) Rules
1.3 Securities and Futures (Client Money) Rules
1.4 Securities and Futures (Keeping of Records) Rules
1.5 Securities and Futures (Contract Notes, Statements of Account and Receipts) Rules
1.6 Securities and Futures (Accounts and Audit) Rules,
plus many others.提示
Reference Chapter:1.2.2
-
62/567問題
62. 問題
1 分QID1036:Which of the following are the power that the Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO) empowers the SFC with?
I. The power to introduce subsidiary legislation.
II. The power to issue codes and guidelines.
III. The power to amend the Securities and Futures Ordinance.
IV. The power to revoke the Securities and Futures Ordinance.正確
Part VII empowers the SFC to make subsidiary legislation (s. 168, SFO) and/or codes (s. 169, SFO).
錯誤
Part VII empowers the SFC to make subsidiary legislation (s. 168, SFO) and/or codes (s. 169, SFO).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.2.2
-
63/567問題
63. 問題
1 分QID190:The SFO has provided powers for the SFC to make detailed rules relating to which of the following?
I. Financial Resources
II. Handling of client money and other client assets
III. The keeping of accounts and records
IV. Auditing matters正確
The SFO grants the SFC powers to make detailed rules relating to:
(a.) their financial resources;
(b.) the handling of client money and other client assets;
(c.) the keeping of accounts and records; and
(d.) auditing matters.錯誤
The SFO grants the SFC powers to make detailed rules relating to:
(a.) their financial resources;
(b.) the handling of client money and other client assets;
(c.) the keeping of accounts and records; and
(d.) auditing matters.提示
Reference Chapter:1.2.3
-
64/567問題
64. 問題
1 分QID85:What is the legal status of codes and guidelines issued by the SFC?
I. Codes of conduct are subsidiary legislation and have the force of law.
II. Guidelines are subsidiary legislation and have the force of law.
III. Codes of conduct do not have the force of law, a breach does not by itself render a person liable to any judicial or other proceedings.
IV. Guidelines do not have the force of law, a breach does not by itself render a person liable to any judicial or other proceedings.正確
Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable.
However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.錯誤
Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable.
However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.提示
Reference Chapter:1.2.3
-
65/567問題
65. 問題
1 分QID83:Which of the following correctly describes the status of SFC’s code of conducts and guidelines?
正確
Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable.
However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.錯誤
Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable.
However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.提示
Reference Chapter:1.2.3
-
66/567問題
66. 問題
1 分QID87:Under the provisions of the Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO), which of the following statements relating to rules and codes of conduct are correct?
I. Failure by a licensed person to comply with a material provision of a code of conduct will of itself make the person liable to judicial proceedings.
II. A code of conduct violation shall be admissible as evidence in court proceedings.
III. The Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) is empowered under the SFO to make rules or codes of conduct.
IV. A breach of a provision in a code of conduct by a licensed person may cast doubts on his fitness and properness to hold the licence.正確
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines:
i) Breaches of the SFO and subsidiary legislation are legal offenses and will be investigated by the SFC and enforcement action taken; the SFC may refer serious cases to law enforcement agencies such as the Commercial Crimes Bureau of the Hong Kong Police Force or the Independent Commission Against Corruption (“ICAC”) for investigation
and action.
Ii) The SFC may also apply to the courts for an injunction to restrain a person from dealing with his assets or carrying on all or a part of his business if it can make a case to show that it is in the public interest to issue such an order.
Iii) Persons prejudiced by the perpetration of market misconduct may take civil action against the wrongdoer through the courts to obtain redress. The SFO has provisions for the findings of the Market Misconduct Tribunal to be admissible in evidence in private civil
actions.
Iv) Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable. However, the SFC can penalize licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the
licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.
V) The SFC has the power to reprimand (privately or publicly), to fine, and to suspend or revoke a license or registration concerning all or any part of the regulated activities specified on the license or certificate of registration.錯誤
The SFC may enquire into or investigate suspected breaches of the SFO and any subsidiary legislation, codes and guidelines:
i) Breaches of the SFO and subsidiary legislation are legal offenses and will be investigated by the SFC and enforcement action taken; the SFC may refer serious cases to law enforcement agencies such as the Commercial Crimes Bureau of the Hong Kong Police Force or the Independent Commission Against Corruption (“ICAC”) for investigation
and action.
Ii) The SFC may also apply to the courts for an injunction to restrain a person from dealing with his assets or carrying on all or a part of his business if it can make a case to show that it is in the public interest to issue such an order.
Iii) Persons prejudiced by the perpetration of market misconduct may take civil action against the wrongdoer through the courts to obtain redress. The SFO has provisions for the findings of the Market Misconduct Tribunal to be admissible in evidence in private civil
actions.
Iv) Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable. However, the SFC can penalize licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the
licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.
V) The SFC has the power to reprimand (privately or publicly), to fine, and to suspend or revoke a license or registration concerning all or any part of the regulated activities specified on the license or certificate of registration.提示
Reference Chapter:1.2.3
-
67/567問題
67. 問題
1 分QID420:Which of the following codes specifies conduct requirements for SFC licensees involved in the discretionary management of CISs, and supplements the SFC’s codes and requirements for all licensees?
正確
The FMCC applies to intermediaries conducting discretionary management of CISs (whether or not the CISs are authorised by the SFC) and their representatives (“Fund Managers”).
錯誤
The FMCC applies to intermediaries conducting discretionary management of CISs (whether or not the CISs are authorised by the SFC) and their representatives (“Fund Managers”).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.2.3
-
68/567問題
68. 問題
1 分QID1037:Failing to follow SFC-issued codes, guidelines and guidance notes may result in which of the following?
I. Reflect adversely on the fitness and properness of licensed or registered persons to continue to be so licensed or registered.
II. Imprisonment.
III. Civil consequences.
IV. A higher tax bracket.正確
The SFO also empowers the SFC to issue codes, guidelines and guidance notes. These do not have the force of law and do not override the provisions of any applicable law. However, a
failure to follow the spirit of the codes, guidelines and guidance notes may reflect adversely on the fitness and properness of licensed or registered persons to continue to be so licensed or
registered.錯誤
The SFO also empowers the SFC to issue codes, guidelines and guidance notes. These do not have the force of law and do not override the provisions of any applicable law. However, a
failure to follow the spirit of the codes, guidelines and guidance notes may reflect adversely on the fitness and properness of licensed or registered persons to continue to be so licensed or
registered.提示
Reference Chapter:1.2.3
-
69/567問題
69. 問題
1 分QID415:Codes and guidelines issued by the SFC which apply to licensed or registered persons in the Asset Management Industries includes
I. The Conduct Guidelines of Intermediaries
II. The Code of Conduct
III. The Internal Control Guidelines (ICG)
IV. The Guideline on Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Financing of Terrorism (“GAML”)正確
Option I included in the question is not a real code, the other three do exist and apply to asset managers.
錯誤
Option I included in the question is not a real code, the other three do exist and apply to asset managers.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.2.3
-
70/567問題
70. 問題
1 分QID773:The SFC-issued codes, guidelines and guidance notes
正確
Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable. However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.
錯誤
Codes and guidelines do not have the force of law and are not legally enforceable. However, the SFC is able to penalise licensed or registered persons breaching the codes and guidelines by applying the blanket principle that a breach of these may impugn the licensed or registered person’s fitness and properness to remain licensed or registered.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.2.3
-
71/567問題
71. 問題
1 分QID163:According to the CO, which of the following methods of liquidation is accepted?
I. Compulsory Liquidation
II. Members’ Voluntary Winding-Up
III. Creditors’ Voluntary Winding-Up
IV. Director Compulsory Liquidation正確
A compulsory winding-up is ordered by the court, which will appoint a liquidator; a voluntary winding-up is started by the members. If the members declare that the company can meet its debts within one year, there will be a members’ voluntary winding-up; if not, it will be a creditors’ voluntary winding-up with a committee of inspection that will supervise the process.
錯誤
A compulsory winding-up is ordered by the court, which will appoint a liquidator; a voluntary winding-up is started by the members. If the members declare that the company can meet its debts within one year, there will be a members’ voluntary winding-up; if not, it will be a creditors’ voluntary winding-up with a committee of inspection that will supervise the process.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.
-
72/567問題
72. 問題
1 分QID1050:According to the new regulations of the New Company Ordinance (NCO), which of the following is NOT included in the articles of association?
正確
Model articles of association for private companies, public companies and guarantee companies are provided in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice. Model articles of private
companies and public companies consist broadly of four parts including matters relating to:
(a) officers, including powers, duties, appointments and disqualifications of directors, appointments and removal of company secretaries;
(b) members, including meetings and voting procedures;
© capital, such as share capital, rights and dealings with shares and dividends; and
(d) miscellaneous provisions such as communications to and by the company and administrative arrangements.錯誤
Model articles of association for private companies, public companies and guarantee companies are provided in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice. Model articles of private
companies and public companies consist broadly of four parts including matters relating to:
(a) officers, including powers, duties, appointments and disqualifications of directors, appointments and removal of company secretaries;
(b) members, including meetings and voting procedures;
© capital, such as share capital, rights and dealings with shares and dividends; and
(d) miscellaneous provisions such as communications to and by the company and administrative arrangements.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.10
-
73/567問題
73. 問題
1 分QID137:Which of the following are included in the model articles of association for private companies and public companies?
I. Capital
II. Members
III. Officers
IV. Miscellaneous provision正確
Model articles of association for private companies, public companies and guarantee companies are provided in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice. Model articles of private companies and public companies consist broadly of four parts including matters relating to:
(a) officers, including powers, duties, appointments and disqualifications of directors, appointments and removal of company secretaries;
(b) members, including meetings and voting procedures;
© capital, such as share capital, rights and dealings with shares and dividends; and
(d) miscellaneous provisions such as communications to and by the company and administrative arrangements.錯誤
Model articles of association for private companies, public companies and guarantee companies are provided in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice. Model articles of private companies and public companies consist broadly of four parts including matters relating to:
(a) officers, including powers, duties, appointments and disqualifications of directors, appointments and removal of company secretaries;
(b) members, including meetings and voting procedures;
© capital, such as share capital, rights and dealings with shares and dividends; and
(d) miscellaneous provisions such as communications to and by the company and administrative arrangements.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.10
-
74/567問題
74. 問題
1 分QID1042:Which of the following should be included and defined in the articles of association?
I. Members, including meeting and procedures
II. Officers, including powers, duties, appointments and disqualifications of directors, appointment of managing directors and company secretaries
III. Capital, such as dividends, reserves, accounts and audit.
IV. Miscellaneous provisions such as communications to and by the company and administrative arrangements.正確
Model articles of association for private companies, public companies and guarantee companies are provided in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice. Model articles of private companies and public companies consist broadly of four parts including matters relating to:
(a) officers, including powers, duties, appointments and disqualifications of directors, appointments and removal of company secretaries;
(b) members, including meetings and voting procedures;
© capital, such as share capital, rights and dealings with shares and dividends; and
(d) miscellaneous provisions such as communications to and by the company and administrative arrangements.錯誤
Model articles of association for private companies, public companies and guarantee companies are provided in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice. Model articles of private companies and public companies consist broadly of four parts including matters relating to:
(a) officers, including powers, duties, appointments and disqualifications of directors, appointments and removal of company secretaries;
(b) members, including meetings and voting procedures;
© capital, such as share capital, rights and dealings with shares and dividends; and
(d) miscellaneous provisions such as communications to and by the company and administrative arrangements.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.10
-
75/567問題
75. 問題
1 分QID1056:Which of the following may cast votes in company AGM that passes ordinary resolution and special resolutions?
正確
Company meetings of shareholders are very important as they provide the only opportunity for shareholders to exercise any control over the affairs of the company or take part in its operations.
錯誤
Company meetings of shareholders are very important as they provide the only opportunity for shareholders to exercise any control over the affairs of the company or take part in its operations.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.11
-
76/567問題
76. 問題
1 分QID1048:General meetings of shareholders are very important as
正確
Company meetings of shareholders are very important as they provide the only opportunity for shareholders to exercise any control over the affairs of the company or take part in its operations.
錯誤
Company meetings of shareholders are very important as they provide the only opportunity for shareholders to exercise any control over the affairs of the company or take part in its operations.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.11
-
77/567問題
77. 問題
1 分QID1053:Companies are required to held an annual general meeting of shareholders, unless
正確
A company is required by the CO to hold an annual general meeting of shareholders (s. 610, CO). Companies are permitted to dispense with the requirement to hold annual general meetings by passing a written resolution or a resolution at a general meeting with unanimous shareholders’ consent.
錯誤
A company is required by the CO to hold an annual general meeting of shareholders (s. 610, CO). Companies are permitted to dispense with the requirement to hold annual general meetings by passing a written resolution or a resolution at a general meeting with unanimous shareholders’ consent.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.12
-
78/567問題
78. 問題
1 分QID2422:Which of the following can call a meeting other than the annual general meetings?
I. Shareholders
II. Directors
III. Creditors
IV. Court正確
Which of the following can call a meeting other than the annual general meetings?
I. Shareholders
II. Directors
III. Court錯誤
Which of the following can call a meeting other than the annual general meetings?
I. Shareholders
II. Directors
III. Court提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.13
-
79/567問題
79. 問題
1 分QID1054:Company meetings can be requested by which of the following
I. Directors
II. The court
III. Shareholders
IV. Liquidator正確
Other general meetings may be requested by directors, shareholders and the court.
錯誤
Other general meetings may be requested by directors, shareholders and the court.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.13
-
80/567問題
80. 問題
1 分QID1058:The first AGM should be held within how many months of incorporation of a public company?
正確
Unless exempted, companies must hold an annual general meeting within six months (for public companies) or nine months (for private companies or guarantee companies) after the end of their accounting reference period by reference to which its financial year is determined.
錯誤
Unless exempted, companies must hold an annual general meeting within six months (for public companies) or nine months (for private companies or guarantee companies) after the end of their accounting reference period by reference to which its financial year is determined.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.14
-
81/567問題
81. 問題
1 分QID1055:After a company is incorporated and holds its first annual general meeting, at least how many months should it hold general meetings?
正確
In Hong Kong, a company must hold its first Annual General Meeting (AGM) within 18 months of its incorporation. This allows new companies some flexibility to organize their initial statutory meeting without the immediate annual pressure. After the first AGM, subsequent AGMs must be held every calendar year, and the interval between the AGM and the next must not exceed 15 months, as stated previously.
錯誤
In Hong Kong, a company must hold its first Annual General Meeting (AGM) within 18 months of its incorporation. This allows new companies some flexibility to organize their initial statutory meeting without the immediate annual pressure. After the first AGM, subsequent AGMs must be held every calendar year, and the interval between the AGM and the next must not exceed 15 months, as stated previously.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.14
-
82/567問題
82. 問題
1 分QID1059:What should an auditor do if he/she believes that there is something seriously wrong with a company’s financial position?
正確
The usual audit report does not give much opportunity for questions as it is normally in a standard format stating that the accounts present a “true and fair view” of the company’s financial position, unless something is seriously wrong, when the auditors will include a qualification in the report.
錯誤
The usual audit report does not give much opportunity for questions as it is normally in a standard format stating that the accounts present a “true and fair view” of the company’s financial position, unless something is seriously wrong, when the auditors will include a qualification in the report.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.14
-
83/567問題
83. 問題
1 分QID1057:The AGM includes the presentation and approval of which of the following?
I. Annual accounts and audit reports
II. Declaration of dividends
III. Assignment of Directors
IV. Assignment of Auditors正確
The business of an annual general meeting includes the consideration of the annual accounts, the declaration of dividends, the election of directors to replace retiring ones, and the appointment of auditors.
錯誤
The business of an annual general meeting includes the consideration of the annual accounts, the declaration of dividends, the election of directors to replace retiring ones, and the appointment of auditors.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.14
-
84/567問題
84. 問題
1 分QID1604:Which of the following resolutions cannot be passed by circularisation and signed by all members?
I. The removal of a director before his term expires
II. Reduction of share capital
III. Alteration of objects and articles of association
IV. The removal of auditors before the expiration of their term of office正確
According to the Companies Ordinance, all the mentioned items require formal resolutions at a members’ meeting, rather than being accomplished merely by issuing a circular and obtaining member signatures. This includes the removal of a director or an auditor before their term has ended, reduction of share capital, and amendments to the objects or articles of association, all of which need to be resolved through a meeting to ensure transparency and fairness in the company’s decision-making process.
錯誤
According to the Companies Ordinance, all the mentioned items require formal resolutions at a members’ meeting, rather than being accomplished merely by issuing a circular and obtaining member signatures. This includes the removal of a director or an auditor before their term has ended, reduction of share capital, and amendments to the objects or articles of association, all of which need to be resolved through a meeting to ensure transparency and fairness in the company’s decision-making process.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.15
-
85/567問題
85. 問題
1 分QID1062:Which of the following descriptions about resolutions is correct?
正確
Under s. 548, CO, resolutions may be passed by circularisation and signed by all members.
錯誤
Under s. 548, CO, resolutions may be passed by circularisation and signed by all members.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.15
-
86/567問題
86. 問題
1 分QID1060:If the shareholder are not happy with the performance of the directors, how can they replace the directors?
正確
Under s. 548, CO, resolutions may be passed by circularisation and signed by all members except for:
(b) the removal of a director before his term expires.錯誤
Under s. 548, CO, resolutions may be passed by circularisation and signed by all members except for:
(b) the removal of a director before his term expires.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.15
-
87/567問題
87. 問題
1 分QID145:Most corporate resolutions can be passed in which of the following ways?
正確
Under s. 548, CO, resolutions may be passed by circularisation and signed by all members except for:
(a) the removal of auditors before the expiration of their term of office; or
(b) the removal of a director before his term expires.
These must be put to members at a general meeting as ordinary resolutions.錯誤
Under s. 548, CO, resolutions may be passed by circularisation and signed by all members except for:
(a) the removal of auditors before the expiration of their term of office; or
(b) the removal of a director before his term expires.
These must be put to members at a general meeting as ordinary resolutions.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.15
-
88/567問題
88. 問題
1 分QID2839:Which of the following can be done by ordinary resolution?
正確
Removal of auditors and directors can be done by ordinary resolution.
Reduction of share capital, liquidation, amendment of articles of association all require special resolutions.
錯誤
Removal of auditors and directors can be done by ordinary resolution.
Reduction of share capital, liquidation, amendment of articles of association all require special resolutions.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.15
-
89/567問題
89. 問題
1 分QID1061:Which of the following matters must be passed by ordinary resolutions?
I. Dismissal of an auditor before his term of office expires.
II. Dismissal of a director before his term of office expires.
III. Dismissal of an auditor when his term of office expires.
IV. Dismissal of a director when his term of office expires.正確
Under Section 548 of the Companies Ordinance, resolutions may be passed by circulating them to all members and obtaining their signatures, except for the removal of auditors before the expiration of their term of office and the removal of a director before his term expires. These must be presented to members at a general meeting as ordinary resolutions.
錯誤
Under Section 548 of the Companies Ordinance, resolutions may be passed by circulating them to all members and obtaining their signatures, except for the removal of auditors before the expiration of their term of office and the removal of a director before his term expires. These must be presented to members at a general meeting as ordinary resolutions.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.15
-
90/567問題
90. 問題
1 分QID1063:What is the passing rate of a special resolution?
正確
A special resolution is one passed by at least 75% of members at a general meeting (voting in person or, where proxies are allowed, by proxy).
錯誤
A special resolution is one passed by at least 75% of members at a general meeting (voting in person or, where proxies are allowed, by proxy).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.17
-
91/567問題
91. 問題
1 分QID1069:Which of the following matters need to be passed through special resolutions?
I. Reduction of share capital
II. Winding up of the company
III. Deletion, alteration, and addition to the company’s articles of association
IV. Replacement of directors and/or auditors正確
Examples of matters which need special resolutions are:
(a) reduction of share capital;
(b) winding up of the company voluntarily or by court; and
(c) alteration of objects, articles of association (for companies formed and registered under the NCO) and conditions in memoranda of association that could have been included in the articles of association (for existing companies).錯誤
Examples of matters which need special resolutions are:
(a) reduction of share capital;
(b) winding up of the company voluntarily or by court; and
(c) alteration of objects, articles of association (for companies formed and registered under the NCO) and conditions in memoranda of association that could have been included in the articles of association (for existing companies).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.17
-
92/567問題
92. 問題
1 分QID1068:Which of the following descriptions about a special resolution is correct?
I. It may be passed by circularisation and signed by all members
II. It must be passed by at least 75% of members.
III. A notice period of not less than 14 days’ must be given.
IV. A printed copy of a special resolution must be lodged with the Registrar of Companies within 15 days of it being passed.正確
A special resolution is one passed by at least 75% of members at a general meeting (voting in person or, where proxies are allowed, by proxy), of which not less than 14 days’ notice specifying the intention to pass the resolution has been given. Examples of matters which need special resolutions are:
(a) reduction of share capital;
(b) winding up of the company voluntarily or by court; and
© alteration of objects, articles of association (for companies formed and registered under the NCO) and conditions in memoranda of association that could have been included in the articles of association (for existing companies).
A copy of a special resolution must be lodged with the Registrar of Companies within 15 days of it being passed.錯誤
A special resolution is one passed by at least 75% of members at a general meeting (voting in person or, where proxies are allowed, by proxy), of which not less than 14 days’ notice specifying the intention to pass the resolution has been given. Examples of matters which need special resolutions are:
(a) reduction of share capital;
(b) winding up of the company voluntarily or by court; and
© alteration of objects, articles of association (for companies formed and registered under the NCO) and conditions in memoranda of association that could have been included in the articles of association (for existing companies).
A copy of a special resolution must be lodged with the Registrar of Companies within 15 days of it being passed.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.17
-
93/567問題
93. 問題
1 分QID1067:A printed copy of a special resolution must be lodged with the Company Registrar within how many days after being passed?
正確
A copy of a special resolution must be lodged with the Registrar of Companies within 15 days of it being passed.
錯誤
A copy of a special resolution must be lodged with the Registrar of Companies within 15 days of it being passed.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.17
-
94/567問題
94. 問題
1 分QID1066:Which of the following shall be passed under a special resolution?
I. Reduction of share capital
II. Winding up of the company voluntarily or by court
III. Alteration of objects, articles or conditions in the articles of association.
IV. Assignment and removal of Directors正確
Examples of matters which need special resolutions are:
(a) reduction of share capital;
(b) winding up of the company voluntarily or by court; and
(c) alteration of objects, articles of association (for companies formed and registered under the NCO) and conditions in memoranda of association that could have been included in the articles of association (for existing companies).錯誤
Examples of matters which need special resolutions are:
(a) reduction of share capital;
(b) winding up of the company voluntarily or by court; and
(c) alteration of objects, articles of association (for companies formed and registered under the NCO) and conditions in memoranda of association that could have been included in the articles of association (for existing companies).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.17
-
95/567問題
95. 問題
1 分QID1064:Which of the following matters are passed under special resolutions?
I. Reduction of share capital
II. Winding up of the company voluntarily or by court
III. Alteration of objects in articles of association
IV. Disposal of company assets正確
Examples of matters which need special resolutions are:
(a) reduction of share capital;
(b) winding up of the company voluntarily or by court; and
(c) alteration of objects, articles of association (for companies formed and registered under the NCO) and conditions in memoranda of association that could have been included in the articles of association (for existing companies).錯誤
Examples of matters which need special resolutions are:
(a) reduction of share capital;
(b) winding up of the company voluntarily or by court; and
(c) alteration of objects, articles of association (for companies formed and registered under the NCO) and conditions in memoranda of association that could have been included in the articles of association (for existing companies).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.17
-
96/567問題
96. 問題
1 分QID144:Special Resolutions are passed by which of the following individuals or entities?
正確
A special resolution is one passed by at least 75% of members at a general meeting (voting in person or, where proxies are allowed, by proxy), of which not less than 14 days’ notice
specifying the intention to pass the resolution has been given.錯誤
A special resolution is one passed by at least 75% of members at a general meeting (voting in person or, where proxies are allowed, by proxy), of which not less than 14 days’ notice
specifying the intention to pass the resolution has been given.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.17
-
97/567問題
97. 問題
1 分QID141:Which of the following are required to pass a special resolution?
I. Reduction of share capital
II. Winding up the company
III. Determining and declaring dividends and profits
IV. Alteration of objects and articles of association正確
Examples of matters which need special resolutions are:
(a) reduction of share capital;
(b) winding up of the company voluntarily or by court; and
(C) alteration of objects, articles of association (for companies formed and registered under the CO) and conditions in memoranda of association that could have been included in
the articles of association (for existing companies).錯誤
Examples of matters which need special resolutions are:
(a) reduction of share capital;
(b) winding up of the company voluntarily or by court; and
(C) alteration of objects, articles of association (for companies formed and registered under the CO) and conditions in memoranda of association that could have been included in
the articles of association (for existing companies).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.17
-
98/567問題
98. 問題
1 分QID2790:How long the notice period should be for a special resolution?
正確
Special resolutions should have a 14-day notice period.
錯誤
Special resolutions should have a 14-day notice period.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.17
-
99/567問題
99. 問題
1 分QID140:Which of the following statements about special resolutions are correct?
I. It is a resolution that is passed by at least 50% of members at a general meeting.
II. It is a resolution that is passed by at least 75% of members at a general meeting.
III. The notice period of an intention to pass a special resolution must be no less than 14 days.
IV. The notice period of an intention to pass a special resolution must be no less than 21 days.正確
A special resolution is one passed by at least 75% of members at a general meeting (voting in person or, where proxies are allowed, by proxy), of which not less than 14 days’ notice
specifying the intention to pass the resolution has been given.錯誤
A special resolution is one passed by at least 75% of members at a general meeting (voting in person or, where proxies are allowed, by proxy), of which not less than 14 days’ notice
specifying the intention to pass the resolution has been given.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.17
-
100/567問題
100. 問題
1 分QID1065:A special resolution requires how many days’ notice specifying the intention to pass the resolution to been given?
正確
A special resolution is one passed by at least 75% of members at a general meeting (voting in person or, where proxies are allowed, by proxy), of which not less than 14 days’ notice specifying the intention to pass the resolution has been given.
錯誤
A special resolution is one passed by at least 75% of members at a general meeting (voting in person or, where proxies are allowed, by proxy), of which not less than 14 days’ notice specifying the intention to pass the resolution has been given.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.17
-
101/567問題
101. 問題
1 分QID1070:What is the passing rate of an ordinary resolution?
正確
An ordinary resolution is a resolution which may be passed by a simple majority of those present and voting at a meeting of members. Notice must be given.
錯誤
An ordinary resolution is a resolution which may be passed by a simple majority of those present and voting at a meeting of members. Notice must be given.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.18
-
102/567問題
102. 問題
1 分QID1071:An ordinary resolution is a resolution which may be passed by what percentage of voting at a meeting of members?
正確
An ordinary resolution is a resolution which may be passed by a simple majority of those present and voting at a meeting of members. Notice must be given.
錯誤
An ordinary resolution is a resolution which may be passed by a simple majority of those present and voting at a meeting of members. Notice must be given.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.18
-
103/567問題
103. 問題
1 分QID1073:Which of the following are NOT powers exercisable by members in the general meeting?
正確
These include:
(a) changes to articles of association and company name;
© issue of shares at a discount;
(d) alteration of capital including reduction.錯誤
These include:
(a) changes to articles of association and company name;
© issue of shares at a discount;
(d) alteration of capital including reduction.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.19
-
104/567問題
104. 問題
1 分QID1072:Which of the following are powers exercisable by members in general meeting?
I. Removal of directors
II. Disposal of assets
III. Approval of payments for loss of office
IV. Approval of payments for profit of office正確
These include:
(h) removal of directors;
(i) disposal of company assets;
(j) approval of payments for loss of office錯誤
These include:
(h) removal of directors;
(i) disposal of company assets;
(j) approval of payments for loss of office提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.19
-
105/567問題
105. 問題
1 分QID1039:What are the major features of the Companies Ordinance?
I. The CO permits the formation of a company by one or more persons (s. 67, CO).
II. The CO provides that one member constitutes a quorum for a meeting of a company having only one member.
III. The CO permits the formation of a company by one or more companies.
IV. The CO permits the permits the formation of a company by two or more persons (s. 67, CO).正確
The CO permits the formation of a company by one or more persons (s. 67, CO). The CO also provides that one member
constitutes a quorum for a meeting of a company having only one member.錯誤
The CO permits the formation of a company by one or more persons (s. 67, CO). The CO also provides that one member
constitutes a quorum for a meeting of a company having only one member.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.2
-
106/567問題
106. 問題
1 分QID1075:If a variation of the rights of the holders of a class of a shares in a company occurs, shareholders who believe that such variation is against their interests may petition the court to have the variation cancelled. What is the threshold for such a petition to occur?
正確
There are provisions in the NCO and in Companies (Model Articles) Notice which enable a
company to vary the rights of the holders of a class of shares. However, if a variation is being processed, the holders of at least 10% of the total voting rights of the shares in that class may petition the court to have the variation cancelled if it is against their interests.錯誤
There are provisions in the NCO and in Companies (Model Articles) Notice which enable a
company to vary the rights of the holders of a class of shares. However, if a variation is being processed, the holders of at least 10% of the total voting rights of the shares in that class may petition the court to have the variation cancelled if it is against their interests.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.20
-
107/567問題
107. 問題
1 分QID2749:If the rights of the shareholders are changed, under what percentage of voting rights can a petition be filed with the court to cancel the change?
正確
When the rights of the shareholders are changed, as long as there are more than 10% of the voting rights, a petition can be filed with the court to cancel the change.
錯誤
When the rights of the shareholders are changed, as long as there are more than 10% of the voting rights, a petition can be filed with the court to cancel the change.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.20
-
108/567問題
108. 問題
1 分QID1076:If a company is functional and can form resolutions through the AGM, the court will generally not interfere in its matters. This practice is based on which of the following principles?
正確
The court will not generally interfere in internal management matters or where the company can deal with the matter by calling a meeting. This is the principle of majority power.
錯誤
The court will not generally interfere in internal management matters or where the company can deal with the matter by calling a meeting. This is the principle of majority power.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.22
-
109/567問題
109. 問題
1 分QID1077:The court will not generally interfere in internal management matters or where the company can deal with the matter by calling a meeting. This is the principle of
正確
The court will not generally interfere in internal management matters or where the company can deal with the matter by calling a meeting. This is the principle of majority power.
錯誤
The court will not generally interfere in internal management matters or where the company can deal with the matter by calling a meeting. This is the principle of majority power.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.22
-
110/567問題
110. 問題
1 分QID146:Under the Companies Ordinance, can members petition the court to wind up the company?
正確
To ensure that the principle of majority power is not abused, certain safeguards are provided under the CO to protect the interests of minority shareholders:
(a) a special resolution is required for certain matters.
(b) Court sanction is required where the decision of the company will directly affectcreditors.
(c) Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
(d) Members with 5% of the paid-up share capital which carries voting rights may request the directors to call a general meeting; if the directors will not, the members may do so.
(e) 100 members or 10% of the holders of the issued shares may ask the Financial Secretary to appoint an investigator into the company’s affairs.
(f) A member may apply to the court for an order if he considers that the affairs of the company are being conducted in a manner prejudicial to the interests of the members generally or of some part of the members.
(g) A member may petition for a winding up.錯誤
To ensure that the principle of majority power is not abused, certain safeguards are provided under the CO to protect the interests of minority shareholders:
(a) a special resolution is required for certain matters.
(b) Court sanction is required where the decision of the company will directly affectcreditors.
(c) Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
(d) Members with 5% of the paid-up share capital which carries voting rights may request the directors to call a general meeting; if the directors will not, the members may do so.
(e) 100 members or 10% of the holders of the issued shares may ask the Financial Secretary to appoint an investigator into the company’s affairs.
(f) A member may apply to the court for an order if he considers that the affairs of the company are being conducted in a manner prejudicial to the interests of the members generally or of some part of the members.
(g) A member may petition for a winding up.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.23
-
111/567問題
111. 問題
1 分QID1082:Vita Milk, a listed company is undergoing structural reform, which includes a series of share placing and new debt financing arrangements. Sharon Chan is a 1% stakeholder of Vita Milk and she believes such actions are against her rights. She can
I. Apply to court for an order if she considers that the affairs of the company are being conducted in a manner prejudicial to interest of member’s.
II. Solely request the directors to call for a meeting; if the directors will not, she may do so on her own.
III. Rally 100 shareholders or 10% of the holders of the issued shares and request the Financial Secretary to appoint an investigator to look into the company’s affairs
IV. Petition to the commercial crime Bureau of Hong Kong to establish a special unit to investigate such actions.正確
To ensure that this principle is not abused, certain safeguards are provided under the NCO to protect the interests of minority shareholders:
(c.) Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
(e.) 100 members or 10% of the holders of the issued shares may ask the Financial Secretary to appoint an investigator into the company’s affairs.
On the other hand,
(d) Members with 5% of the paid-up capital which carries voting rights may request the directors to call a meeting; if the directors will not, the members may do so.
Sharon cannot call a meeting on her own.錯誤
To ensure that this principle is not abused, certain safeguards are provided under the NCO to protect the interests of minority shareholders:
(c.) Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
(e.) 100 members or 10% of the holders of the issued shares may ask the Financial Secretary to appoint an investigator into the company’s affairs.
On the other hand,
(d) Members with 5% of the paid-up capital which carries voting rights may request the directors to call a meeting; if the directors will not, the members may do so.
Sharon cannot call a meeting on her own.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.23
-
112/567問題
112. 問題
1 分QID1081:Mr. Ko is a major stakeholder of Yellow River Trading Limited and owns 15% of outstanding shares of Yellow River Trading Limited. Yellow River Trading Limited plans to sell its shares to Mr. Wan and a number of high net worth individuals through a shares placement at a discount. Mr. Ko believes these actions are diluting his shares without his consent, what are the possible actions that can be taken by Mr Ko?
I. Appeal to the court to cancel such actions.
II. Petition to start an AGM immediately to stop the placement.
III. Request the financial secretary to appoint an investigator into the company’s affairs
IV. Request a special hearing from the ICAC.正確
To ensure that this principle is not abused, certain safeguards are provided under the CO to protect the interests of minority shareholders:
(c.) Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
(d) Members with 5% of the paid-up capital which carries voting rights may request the directors to call a meeting; if the directors will not, the members may do so.
(e.) 100 members or 10% of the holders of the issued shares may ask the Financial Secretary to appoint an investigator into the company’s affairs.錯誤
To ensure that this principle is not abused, certain safeguards are provided under the CO to protect the interests of minority shareholders:
(c.) Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
(d) Members with 5% of the paid-up capital which carries voting rights may request the directors to call a meeting; if the directors will not, the members may do so.
(e.) 100 members or 10% of the holders of the issued shares may ask the Financial Secretary to appoint an investigator into the company’s affairs.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.23
-
113/567問題
113. 問題
1 分QID1080:Mr. Wan is a shareholder of Vita Milk, a company listed on the SEHK. Recently, Vita Milk issued a large number of convertible bonds without legitimate reasons. Mr. Wan believes that he can petition against such actions. Where and to whom should Mr Wan file a petition?
正確
Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
錯誤
Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.23
-
114/567問題
114. 問題
1 分QID1079:To ensure there is no abuse of majority power, which of the following safeguards are provided under the CO to protect the interests of minority shareholders?
I. Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
II. Members with 5% of the paid-up capital which carries voting rights may request the directors to call a meeting; if the directors will not, the members may do so.
III. 100 members or 10% of the holders of the issued shares may ask the Financial Secretary to appoint an investigator into the company’s affairs.
IV. A member may petition for a winding up.正確
To ensure that this principle is not abused, certain safeguards are provided under the NCO to protect the interests of minority shareholders:
(c.) Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
(d) Members with 5% of the paid-up capital which carries voting rights may request the directors to call a meeting; if the directors will not, the members may do so.
(e.) 100 members or 10% of the holders of the issued shares may ask the Financial Secretary to appoint an investigator into the company’s affairs.
(g) A member may petition for a winding up.錯誤
To ensure that this principle is not abused, certain safeguards are provided under the NCO to protect the interests of minority shareholders:
(c.) Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
(d) Members with 5% of the paid-up capital which carries voting rights may request the directors to call a meeting; if the directors will not, the members may do so.
(e.) 100 members or 10% of the holders of the issued shares may ask the Financial Secretary to appoint an investigator into the company’s affairs.
(g) A member may petition for a winding up.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.23
-
115/567問題
115. 問題
1 分QID1084:The court, upon recognizing a petition from the minority shareholder of a company, will most likely
正確
A member may apply to the court for an order if he considers that the affairs of the company are being conducted in a manner prejudicial to the interests of the members generally or of some part of the members.
錯誤
A member may apply to the court for an order if he considers that the affairs of the company are being conducted in a manner prejudicial to the interests of the members generally or of some part of the members.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.23
-
116/567問題
116. 問題
1 分QID1083:To ensure there is no abuse of majority power, which of the following safeguards are provided under the CO to protect the interests of minority shareholders?
I. Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
II. Members with 5% of the paid-up capital which carries voting rights may request the directors to call a meeting; if the directors will not, the members may do so.
III. 100 members or 10% of the holders of the issued shares may ask the Financial Secretary to appoint an investigator into the company’s affairs.
IV. A member may apply to the court for an order if he considers that the affairs of the company are being conducted in a manner prejudicial to the interests of the members generally or of some part of the members.正確
To ensure that this principle is not abused, certain safeguards are provided under the CO to protect the interests of minority shareholders:
(c.) Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
(d) Members with 5% of the paid-up capital which carries voting rights may request the directors to call a meeting; if the directors will not, the members may do so.
(e.) 100 members or 10% of the holders of the issued shares may ask the Financial Secretary to appoint an investigator into the company’s affairs.
(f) A member may apply to the court for an order if he considers that the affairs of the company are being conducted in a manner prejudicial to the interests of the members generally or of some part of the members.錯誤
To ensure that this principle is not abused, certain safeguards are provided under the CO to protect the interests of minority shareholders:
(c.) Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
(d) Members with 5% of the paid-up capital which carries voting rights may request the directors to call a meeting; if the directors will not, the members may do so.
(e.) 100 members or 10% of the holders of the issued shares may ask the Financial Secretary to appoint an investigator into the company’s affairs.
(f) A member may apply to the court for an order if he considers that the affairs of the company are being conducted in a manner prejudicial to the interests of the members generally or of some part of the members.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.23
-
117/567問題
117. 問題
1 分QID1078:Which of the following are safeguards provided under the CO to protect the interest of minority shareholders?
I. The requirement of passing a special resolution for matters of great significance.
II. Court sanctions where the decision of the company will directly affect creditors.
III. Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
IV. A member may petition for a winding up正確
To ensure that this principle is not abused, certain safeguards are provided under the NCO to protect the interests of minority shareholders:
(a) As seen in section 3.17 above, a special resolution is required for certain matters.
(b) Court sanction is required where the decision of the company will directly affect creditors.
© Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
(g) A member may petition for a winding up.錯誤
To ensure that this principle is not abused, certain safeguards are provided under the NCO to protect the interests of minority shareholders:
(a) As seen in section 3.17 above, a special resolution is required for certain matters.
(b) Court sanction is required where the decision of the company will directly affect creditors.
© Dissenting members may appeal to the court to have certain resolutions cancelled.
(g) A member may petition for a winding up.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.23
-
118/567問題
118. 問題
1 分QID2823:Measures to protect minority shareholders do not include
正確
Measures to protect minority shareholders include:
1. Members with 5% of the voting rights may request the directors to call a general meeting. If the directors refuse, they can convene a general meeting on their own.
2. 100 members or 10% of the holder of the issued shares can request the Financial Secretary to investigate the company’s affairs
3. Dissenting members can appeal to the court to revoke certain company resolutions
4. Any member may petition the court for the winding-up of the company.
5. If a member believes that their interests are impaired, they can apply to the court for an order錯誤
Measures to protect minority shareholders include:
1. Members with 5% of the voting rights may request the directors to call a general meeting. If the directors refuse, they can convene a general meeting on their own.
2. 100 members or 10% of the holder of the issued shares can request the Financial Secretary to investigate the company’s affairs
3. Dissenting members can appeal to the court to revoke certain company resolutions
4. Any member may petition the court for the winding-up of the company.
5. If a member believes that their interests are impaired, they can apply to the court for an order提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.23
-
119/567問題
119. 問題
1 分QID1085:The court may NOT intervene to allow an individual to bring an action
正確
The court may intervene to allow an individual member or members to bring an action:
(a) to enforce some personal rights (a personal action);
(b) where a right has been infringed which affects all or a number of members in a similar way (a joint action); or
(c) on behalf of the company where misconduct has been committed against the company, for example by a director of the company or a third party (a derivative action).錯誤
The court may intervene to allow an individual member or members to bring an action:
(a) to enforce some personal rights (a personal action);
(b) where a right has been infringed which affects all or a number of members in a similar way (a joint action); or
(c) on behalf of the company where misconduct has been committed against the company, for example by a director of the company or a third party (a derivative action).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.24
-
120/567問題
120. 問題
1 分QID1087:Which of the following descriptions is an accurate representation of director under theCO?
正確
The CO merely defines a director as including a person who occupies the position of director, by whatever name he is called. The CO itself refers very little to directors but there is more about them in Companies (Model Articles) Notice. The CO says that every company (not being a private company) must have at least two directors (s. 453, CO) and every private company must have at least one director (s. 454, CO).
錯誤
The CO merely defines a director as including a person who occupies the position of director, by whatever name he is called. The CO itself refers very little to directors but there is more about them in Companies (Model Articles) Notice. The CO says that every company (not being a private company) must have at least two directors (s. 453, CO) and every private company must have at least one director (s. 454, CO).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.25
-
121/567問題
121. 問題
1 分QID1086:Which of the following descriptions are accurate representations of director under the CO?
I. A director is a person who occupies the position of director and bears whatever title.
II. Guarantee Companies and Public Companies must have at least two directors.
III. Private Companies must have at least one director.
IV. Directors are appointed by the members acting in general meeting.正確
The CO merely defines a director as including a person who occupies the position of director, by whatever name he is called. The CO itself refers very little to directors but there is more about them in Companies (Model Articles) Notice. The CO says that every company (not being a private company) must have at least two directors (s. 453, CO) and every private company must have at least one director (s. 454, CO). The directors must be appointed by the members acting in general meeting.
錯誤
The CO merely defines a director as including a person who occupies the position of director, by whatever name he is called. The CO itself refers very little to directors but there is more about them in Companies (Model Articles) Notice. The CO says that every company (not being a private company) must have at least two directors (s. 453, CO) and every private company must have at least one director (s. 454, CO). The directors must be appointed by the members acting in general meeting.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.25
-
122/567問題
122. 問題
1 分QID2579:Which of the following is correct based on the NCO regarding director(s) of private companies?
正確
Every private company is required to have at least one director, and at least one director must be a natural person.
錯誤
Every private company is required to have at least one director, and at least one director must be a natural person.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.26
-
123/567問題
123. 問題
1 分QID2686:Under the company ordinance regarding directors of a company, which of the following is true?
正確
Every private company (other than one within the same group as a listed company) is required to have at least one director who is a natural person.
錯誤
Every private company (other than one within the same group as a listed company) is required to have at least one director who is a natural person.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.26
-
124/567問題
124. 問題
1 分QID1088:Every private company is required to have at least one director who is
正確
Every private company (other than one within the same group as a listed company) is required to have at least one director who is a natural person.
錯誤
Every private company (other than one within the same group as a listed company) is required to have at least one director who is a natural person.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.26
-
125/567問題
125. 問題
1 分QID1089:Which of the following is an accurate representation of shadow directors?
正確
Shadow directors are “persons in accordance with whose directions or instructions (excluding advice given in a professional capacity) the directors, or a majority of the directors, of a body corporate are accustomed to act”.
錯誤
Shadow directors are “persons in accordance with whose directions or instructions (excluding advice given in a professional capacity) the directors, or a majority of the directors, of a body corporate are accustomed to act”.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.27
-
126/567問題
126. 問題
1 分QID147:Who among the following individuals can be considered a shadow director?
正確
Shadow directors are “persons in accordance with whose directions or instructions (excluding advice given in a professional capacity) the directors, or a majority of the directors, of a body corporate are accustomed to act”.
錯誤
Shadow directors are “persons in accordance with whose directions or instructions (excluding advice given in a professional capacity) the directors, or a majority of the directors, of a body corporate are accustomed to act”.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.27
-
127/567問題
127. 問題
1 分QID1091:Which of the following are officers of a company under the CO?
I. Managers
II. Company Secretary
III. Major Shareholders
IV. Directors正確
An officer, according to the CO, includes a director, manager or company secretary.
錯誤
An officer, according to the CO, includes a director, manager or company secretary.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.28
-
128/567問題
128. 問題
1 分QID1096:What are the necessary conditions for becoming a director in Hong Kong?
I. Be 18 years old and above.
II. Must not be an undischarged bankrupt.
III. Must not be disqualified by court order.
IV. Be a director of a recently wound up company.正確
Persons to be appointed directors must meet the following requirements:
(a) They must be at least 18 years of age.
(b) They must not be undischarged bankrupts.
(c.) They must not be disqualified by court order.錯誤
Persons to be appointed directors must meet the following requirements:
(a) They must be at least 18 years of age.
(b) They must not be undischarged bankrupts.
(c.) They must not be disqualified by court order.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.29
-
129/567問題
129. 問題
1 分QID148:Which of the following actions may result in disqualification as director by court order?
I. Ms. Chung was persistently in default in relation to the Companies Ordinance or when acting as a liquidator or receiver
II. Mr. Tse committed fraud concerning minor company matters, including the preparation of false accounts
III. Ms. Wang served as a director last year of an insolvent company that was liquidated due to the poor management of other directors
IV. Mr. Ng was convicted of an indictable offence involving fraud, dishonesty, or related to the formation or operation of companies正確
Persons to be appointed directors must not be disqualified by a court order. The four primary grounds for such an order include conviction for an indictable offence involving fraud, dishonesty, or related to the formation or management of companies; persistent default concerning the Companies Ordinance or when acting as a liquidator or receiver; committing fraud in relation to company matters or engaging in fraudulent trading; and being deemed an unfit director while serving in an insolvent company.
錯誤
Persons to be appointed directors must not be disqualified by a court order. The four primary grounds for such an order include conviction for an indictable offence involving fraud, dishonesty, or related to the formation or management of companies; persistent default concerning the Companies Ordinance or when acting as a liquidator or receiver; committing fraud in relation to company matters or engaging in fraudulent trading; and being deemed an unfit director while serving in an insolvent company.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.29
-
130/567問題
130. 問題
1 分QID149:Which of the following are potential barriers of becoming a director of a company?
I. Anyone aged 21 or below
II. Undischarged bankrupts
III. Persistent default in relation to the NCO
IV. A finding of being unfit during directorship of an insolvent company正確
Persons to be appointed directors must meet the following requirements:
(a) They must be at least 18 years of age.
(b) They must not be undischarged bankrupts.
(c) They must not be disqualified by court order; the four principal grounds for such an order being:
(i) conviction of an indictable offence for fraud or dishonesty or relating to forming or operating companies;
(ii) persistent default in relation to the CO or in acting as a liquidator or receiver;
(iii) fraud in relation to company matters or fraudulent trading; or
(iv) a finding of being unfit during directorship of an insolvent company.錯誤
Persons to be appointed directors must meet the following requirements:
(a) They must be at least 18 years of age.
(b) They must not be undischarged bankrupts.
(c) They must not be disqualified by court order; the four principal grounds for such an order being:
(i) conviction of an indictable offence for fraud or dishonesty or relating to forming or operating companies;
(ii) persistent default in relation to the CO or in acting as a liquidator or receiver;
(iii) fraud in relation to company matters or fraudulent trading; or
(iv) a finding of being unfit during directorship of an insolvent company.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.29
-
131/567問題
131. 問題
1 分QID1095:Which of the following condition does not result in being disqualified by court order and the person is able to act as a director of a company?
正確
Persons to be appointed directors must meet the following requirements:
(c.) They must not be disqualified by court order.
(i) conviction of an indictable offence for fraud or dishonesty or relating to forming or operating companies;
(ii) persistent default in relation to the CO or in acting as a liquidator or receiver;
(iii) fraud in relation to company matters or fraudulent trading; or
(iv) a finding of being unfit during directorship of an insolvent company.
Fraud and the other disqualifications apply to directors and shadow directors (e.g. see section 3.5, Topic 7, which describes disqualification orders made by the Market Misconduct Tribunal (“MMT”) preventing persons committing market misconduct from being directors of companies).錯誤
Persons to be appointed directors must meet the following requirements:
(c.) They must not be disqualified by court order.
(i) conviction of an indictable offence for fraud or dishonesty or relating to forming or operating companies;
(ii) persistent default in relation to the CO or in acting as a liquidator or receiver;
(iii) fraud in relation to company matters or fraudulent trading; or
(iv) a finding of being unfit during directorship of an insolvent company.
Fraud and the other disqualifications apply to directors and shadow directors (e.g. see section 3.5, Topic 7, which describes disqualification orders made by the Market Misconduct Tribunal (“MMT”) preventing persons committing market misconduct from being directors of companies).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.29
-
132/567問題
132. 問題
1 分QID1090:Vita Milk is a private company engaging in dairy products trading, which of the following individual can act as a director of Vita Milk?
正確
Persons to be appointed directors must meet the following requirements:
(a) They must be at least 18 years of age.
(b) They must not be undischarged bankrupts.
(c.) They must not be disqualified by court order.
There is Mr. Chan only who satisfies all the conditions above.錯誤
Persons to be appointed directors must meet the following requirements:
(a) They must be at least 18 years of age.
(b) They must not be undischarged bankrupts.
(c.) They must not be disqualified by court order.
There is Mr. Chan only who satisfies all the conditions above.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.29
-
133/567問題
133. 問題
1 分QID1092:Which of the following persons are not qualified to serve as a director?
I. Persons that are under the age of 18.
II. Persons that are undischarged bankrupts.
III. Persons disqualified by court.
IV. Persons who do not satisfy the statutory net worth requirement.正確
Persons to be appointed directors must meet the following requirements:
(a) They must be at least 18 years of age.
(b) They must not be undischarged bankrupts.
(c.) They must not be disqualified by court order.錯誤
Persons to be appointed directors must meet the following requirements:
(a) They must be at least 18 years of age.
(b) They must not be undischarged bankrupts.
(c.) They must not be disqualified by court order.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.29
-
134/567問題
134. 問題
1 分QID1093:Which of the following are principal grounds that a court may disqualify a person from becoming a director?
I. Conviction of an indictable offence for fraud or dishonesty or relating to forming or operating companies
II. Persistent default in relation to the CO or in acting as a liquidator or receiver
III. Fraud in relation to company matters or fraudulent trading
IV. A finding of being unfit during directorship of an insolvent company.正確
Persons to be appointed directors must meet the following requirements:
(c.) They must not be disqualified by court order.
(i) conviction of an indictable offence for fraud or dishonesty or relating to forming or operating companies;
(ii) persistent default in relation to the CO or in acting as a liquidator or receiver;
(iii) fraud in relation to company matters or fraudulent trading; or
(iv) a finding of being unfit during directorship of an insolvent company.錯誤
Persons to be appointed directors must meet the following requirements:
(c.) They must not be disqualified by court order.
(i) conviction of an indictable offence for fraud or dishonesty or relating to forming or operating companies;
(ii) persistent default in relation to the CO or in acting as a liquidator or receiver;
(iii) fraud in relation to company matters or fraudulent trading; or
(iv) a finding of being unfit during directorship of an insolvent company.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.29
-
135/567問題
135. 問題
1 分QID1094:Which of the following criteria must be met before a person can be appointed as a director?
I. Must be at least 18 years of age.
II. Must not be undischarged bankrupts.
III. Must not be disqualified by court order.
IV. Must not be a shareholder of a liquidated company.正確
Persons to be appointed directors must meet the following requirements:
(a) They must be at least 18 years of age.
(b) They must not be undischarged bankrupts.
(c.) They must not be disqualified by court order.錯誤
Persons to be appointed directors must meet the following requirements:
(a) They must be at least 18 years of age.
(b) They must not be undischarged bankrupts.
(c.) They must not be disqualified by court order.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.29
-
136/567問題
136. 問題
1 分QID1040:Which of the following descriptions about the New Companies Ordinance are correct?
I. A company is a legal entity distinct from its members and is a legal person.
II. The company can make contracts.
III. The company can be sued.
IV. The company can be involved in crime and torts.正確
A company is a legal entity distinct from its members. It is a legal person and can make contracts, take legal action, sue and be sued, own property and commit crimes and torts.
錯誤
A company is a legal entity distinct from its members. It is a legal person and can make contracts, take legal action, sue and be sued, own property and commit crimes and torts.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.3
-
137/567問題
137. 問題
1 分QID1041:Which of the following descriptions of a company is NOT correct under the NCO?
正確
A company can be a limited company, the normal form of most companies, where the liability of its members is limited.
錯誤
A company can be a limited company, the normal form of most companies, where the liability of its members is limited.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.3
-
138/567問題
138. 問題
1 分QID134:Which of the following descriptions about companies are correct?
I. An entity that is independent of its members (shareholder).
II. An entity that can sue.
III. An entity that can be sued.
IV. A company can commit crimes and torts正確
A company is a legal entity distinct from its members. It is a legal person and can make contracts, take legal action, sue and be sued, own property and commit crimes and torts. It also has perpetual succession and will only cease to exist if it is dissolved. It can be a limited company, the normal form of most companies, where the liability of its members is limited.
錯誤
A company is a legal entity distinct from its members. It is a legal person and can make contracts, take legal action, sue and be sued, own property and commit crimes and torts. It also has perpetual succession and will only cease to exist if it is dissolved. It can be a limited company, the normal form of most companies, where the liability of its members is limited.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.3
-
139/567問題
139. 問題
1 分QID774:Which of the following descriptions about a limited company is NOT correct?
正確
A company is a legal entity distinct from its members. It is a legal person and can make contracts, take legal action, sue and be sued, own property and commit crimes and torts. It also has perpetual succession and will only cease to exist if it is dissolved. It can be a limited company, the normal form of most companies, where the liability of its members is limited.
Answer A is not included in this definition.錯誤
A company is a legal entity distinct from its members. It is a legal person and can make contracts, take legal action, sue and be sued, own property and commit crimes and torts. It also has perpetual succession and will only cease to exist if it is dissolved. It can be a limited company, the normal form of most companies, where the liability of its members is limited.
Answer A is not included in this definition.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.3
-
140/567問題
140. 問題
1 分QID2849:Which of the following statements about the directors of a company is correct?
I. Except as restricted by the company’s articles of association, company regulations or special resolutions, the directors may exercise all the powers of the company.
II. If the directors are unwilling to act, members may intervene in management matters at a general meeting.
III. Members may limit the powers of directors by resolution at a general meeting.
IV. Directors should hold a meeting (board meeting) before making a decision, and exercise their power only after the resolution is passed at the meeting.正確
Members cannot pass a resolution at a general meeting to limit the powers of a director unless the director is unwilling to act or the director is in breach of fiduciary duty.
錯誤
Members cannot pass a resolution at a general meeting to limit the powers of a director unless the director is unwilling to act or the director is in breach of fiduciary duty.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.30
-
141/567問題
141. 問題
1 分QID1098:Shareholders can interfere and override management actions of the directors if:
I. the directors are unwilling to act
II. the directors’ actions result in operating losses
III. The directors are seeking approval to act beyond their powers
IV. The directors are acting in breach of their fiduciary duties正確
Directors in these circumstances are not bound by resolutions passed by members in a general meeting, nor can the members override future management actions of the directors. Members in general meeting may only intervene in the management if the directors are:
(a) unwilling to act;
(b) seeking approval to act beyond their powers (the members can approve such acts by ordinary resolution); or
(c.) acting in breach of their fiduciary duties (the members may ratify such breaches in general meeting).錯誤
Directors in these circumstances are not bound by resolutions passed by members in a general meeting, nor can the members override future management actions of the directors. Members in general meeting may only intervene in the management if the directors are:
(a) unwilling to act;
(b) seeking approval to act beyond their powers (the members can approve such acts by ordinary resolution); or
(c.) acting in breach of their fiduciary duties (the members may ratify such breaches in general meeting).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.31
-
142/567問題
142. 問題
1 分QID1097:Generally speaking, directors are not bound by resolutions passed by members in a general meeting, nor can the members override future management actions of the directors. Members in general meeting may NOT intervene in the management if:
正確
Directors in these circumstances are not bound by resolutions passed by members in a general meeting, nor can the members override future management actions of the directors. Members in general meeting may only intervene in the management if the directors are:
(a) unwilling to act;
(b) seeking approval to act beyond their powers (the members can approve such acts by ordinary resolution); or
(c.) acting in breach of their fiduciary duties (the members may ratify such breaches in general meeting).錯誤
Directors in these circumstances are not bound by resolutions passed by members in a general meeting, nor can the members override future management actions of the directors. Members in general meeting may only intervene in the management if the directors are:
(a) unwilling to act;
(b) seeking approval to act beyond their powers (the members can approve such acts by ordinary resolution); or
(c.) acting in breach of their fiduciary duties (the members may ratify such breaches in general meeting).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.31
-
143/567問題
143. 問題
1 分QID884:What actions can company members take when directors are unwilling to act, seeking approval to act beyond their powers, or acting in breach of their fiduciary duties?
I. Members may act on behalf of the directors
II. Approve the directors to acts beyond their powers
III. Ratify the breach of fiduciary duties
IV. Remove the directors正確
Members in general meeting may only intervene in the management if the directors are:
(a) unwilling to act;
(b) seeking approval to act beyond their powers (the members can approve such acts by ordinary resolution); or
(c.) acting in breach of their fiduciary duties (the members may ratify such breaches in general meeting).錯誤
Members in general meeting may only intervene in the management if the directors are:
(a) unwilling to act;
(b) seeking approval to act beyond their powers (the members can approve such acts by ordinary resolution); or
(c.) acting in breach of their fiduciary duties (the members may ratify such breaches in general meeting).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.31
-
144/567問題
144. 問題
1 分QID1099:Under common law, how should directors act and make decisions?
I. Exercise their power collaboratively by having meetings with a proper quorum, passing resolutions and have to be minuted.
II. Directors can act independently if the articles of association allow the board to delegate its power to its individual directors, to committees and to the managing director.
III. For private companies, a written record of a decision made by the sole director of a private company will prevail.正確
Under common law, directors should exercise their powers as a group by having meetings (board of directors’ meetings or board meetings) with a proper quorum, passing resolutions that have to be minuted. This can be avoided as usually the company’s articles of association allow the board to delegate its powers to individual directors, to committees and to the managing director. Under s. 483, NCO, a written record of a decision made by the sole director of a private company shall be sufficient evidence of that decision.
錯誤
Under common law, directors should exercise their powers as a group by having meetings (board of directors’ meetings or board meetings) with a proper quorum, passing resolutions that have to be minuted. This can be avoided as usually the company’s articles of association allow the board to delegate its powers to individual directors, to committees and to the managing director. Under s. 483, NCO, a written record of a decision made by the sole director of a private company shall be sufficient evidence of that decision.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.32
-
145/567問題
145. 問題
1 分QID1102:Under common law, although the directors have a fiduciary relationship with the company, this does not mean they have to:
正確
The directors have a fiduciary relationship with the company. They must act with the utmost good faith towards their principal, i.e. the company; and:
(a) act bona fide for the benefit of the company;
(b) exercise their powers for their proper purpose; and
(c.) not allow any conflict of interest between their duties as directors and their personal interests.錯誤
The directors have a fiduciary relationship with the company. They must act with the utmost good faith towards their principal, i.e. the company; and:
(a) act bona fide for the benefit of the company;
(b) exercise their powers for their proper purpose; and
(c.) not allow any conflict of interest between their duties as directors and their personal interests.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.33
-
146/567問題
146. 問題
1 分QID1100:There is a fiduciary relationship between the directors of a company and the company itself, the directors should act with the utmost good faith towards their principals, which include which of the followings?
I. Determine appropriate remuneration for its directorship through a resolution.
II. Act bona fide for the benefit of the company;
III. Exercise their powers for their proper purpose; and
IV. Not allow any conflict of interest between their duties as directors and their personal interests.正確
The directors have a fiduciary relationship with the company. They must act with the utmost good faith towards their principal, i.e. the company; and:
(a) act bona fide for the benefit of the company;
(b) exercise their powers for their proper purpose; and
(c.) not allow any conflict of interest between their duties as directors and their personal interests.錯誤
The directors have a fiduciary relationship with the company. They must act with the utmost good faith towards their principal, i.e. the company; and:
(a) act bona fide for the benefit of the company;
(b) exercise their powers for their proper purpose; and
(c.) not allow any conflict of interest between their duties as directors and their personal interests.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.33
-
147/567問題
147. 問題
1 分QID1101:Under common law, the directors have a fiduciary relationship with the company and they must:
I. Act with utmost good faith towards the company.
II. Act bona fide for the benefit of the company.
III. Exercise their powers for their proper purpose.
IV. Not allow any conflict of interest between their duties as directors and their personal interests.正確
The directors have a fiduciary relationship with the company. They must act with the utmost good faith towards their principal, i.e. the company; and:
(a) act bona fide for the benefit of the company;
(b) exercise their powers for their proper purpose; and
(c.) not allow any conflict of interest between their duties as directors and their personal interests.錯誤
The directors have a fiduciary relationship with the company. They must act with the utmost good faith towards their principal, i.e. the company; and:
(a) act bona fide for the benefit of the company;
(b) exercise their powers for their proper purpose; and
(c.) not allow any conflict of interest between their duties as directors and their personal interests.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.33
-
148/567問題
148. 問題
1 分QID151:Which of the following are fiduciary duties of directors?
I. Act bona fide for the benefit of the company
II. Exercise their powers for their proper purpose
III. Not allow any conflict of interest between their duties as directors and their personal interests
IV. Not allow any conflict of interest between their duties as directors and the companies interests正確
The directors have a fiduciary relationship with the company. They must act with the utmost
good faith towards their principal, i.e. the company; and:
(a) act bona fide for the benefit of the company;
(b) exercise their powers for their proper purpose; and
(c) not allow any conflict of interest between their duties as directors and their personal interests.錯誤
The directors have a fiduciary relationship with the company. They must act with the utmost
good faith towards their principal, i.e. the company; and:
(a) act bona fide for the benefit of the company;
(b) exercise their powers for their proper purpose; and
(c) not allow any conflict of interest between their duties as directors and their personal interests.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.33
-
149/567問題
149. 問題
1 分QID152:To determine whether a director is diligent, skilful and accountable to the company, which of the following methods are utilized?
I. Qualifying Exam
II. Objective Test
III. Subjective Test
IV. Continuous Professional Assessment正確
The CO provisions set out a mixed objective and subjective test in the determination of the standard of directors’ duty of care, skill and diligence. To determine whether a director of the company has breached the duty of care, skill and diligence owed by him to the company, his conduct is compared to the standard that would be exercised by a reasonably diligent person:
(a) the general knowledge, skill and experience that may reasonably be expected of a person carrying out the functions carried out by the director in relation to the company (objective test); and
(b) the general knowledge, skill and experience that the director has (subjective test).錯誤
The CO provisions set out a mixed objective and subjective test in the determination of the standard of directors’ duty of care, skill and diligence. To determine whether a director of the company has breached the duty of care, skill and diligence owed by him to the company, his conduct is compared to the standard that would be exercised by a reasonably diligent person:
(a) the general knowledge, skill and experience that may reasonably be expected of a person carrying out the functions carried out by the director in relation to the company (objective test); and
(b) the general knowledge, skill and experience that the director has (subjective test).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.34
-
150/567問題
150. 問題
1 分QID1103:A director is expected to perform under the following principles with the exception of
正確
To determine whether a director of the company has breached the duty of care, skill and diligence owed by him to the company, his conduct is compared to the standard that would be exercised by a reasonably diligent person with:
(a) the general knowledge, skill and experience that may reasonably be expected of a person carrying out the functions carried out by the director in relation to the company (objective test); and
(b) the general knowledge, skill and experience that the director has (subjective test).錯誤
To determine whether a director of the company has breached the duty of care, skill and diligence owed by him to the company, his conduct is compared to the standard that would be exercised by a reasonably diligent person with:
(a) the general knowledge, skill and experience that may reasonably be expected of a person carrying out the functions carried out by the director in relation to the company (objective test); and
(b) the general knowledge, skill and experience that the director has (subjective test).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.34
-
151/567問題
151. 問題
1 分QID1104:The NCO imposes on director’s requirement to exercise reasonable care, skill and diligence. To determine whether a director of the company has breached the duty of care, skill and diligence owed by him to the company, his conduct is compared to the standard that would be exercised by a reasonably diligent person with:
I. The general knowledge, skill and experience that may reasonably be expected of a person carrying out the functions carried out by the director in relation to the company (objective test)
II. The general knowledge, skill and experience that the director has (subjective test)
III. The general knowledge, skill and experience that may reasonably be expected of a person carrying out the functions carried out by the director in relation to the company (subjective test)
IV. The general knowledge, skill and experience that the director has (objective test)正確
To determine whether a director of the company has breached the duty of care, skill and diligence owed by him to the company, his conduct is compared to the standard that would be exercised by a reasonably diligent person with:
(a) the general knowledge, skill and experience that may reasonably be expected of a person carrying out the functions carried out by the director in relation to the company (objective test); and
(b) the general knowledge, skill and experience that the director has (subjective test).錯誤
To determine whether a director of the company has breached the duty of care, skill and diligence owed by him to the company, his conduct is compared to the standard that would be exercised by a reasonably diligent person with:
(a) the general knowledge, skill and experience that may reasonably be expected of a person carrying out the functions carried out by the director in relation to the company (objective test); and
(b) the general knowledge, skill and experience that the director has (subjective test).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.34
-
152/567問題
152. 問題
1 分QID153:iss Ko, an employee of Hai Nei Company, has committed an act of market misconduct while undertaking the company’s business and is facing charges. In which of the following scenarios would Mr. Wan, the director of Hoi Nei Company, be legally accountable?
正確
Directors are additionally subject to other, more specific duties
imposed upon them by particular statutory provisions. For example, Twelfth Schedule, the CWUMPO provides for a fine and/or imprisonment for a director that authorises the issue of
a prospectus containing an untrue statement. Where a director breaches strict requirements of the NCO, such as failing to prepare financial statements when required to do so, liability
will also arise. It is therefore important that directors understand both the general and the specific responsibilities imposed upon them, and how to properly discharge them, in order to fulfil their roles as directors and to address their exposure to directors’ liabilities.錯誤
Directors are additionally subject to other, more specific duties
imposed upon them by particular statutory provisions. For example, Twelfth Schedule, the CWUMPO provides for a fine and/or imprisonment for a director that authorises the issue of
a prospectus containing an untrue statement. Where a director breaches strict requirements of the NCO, such as failing to prepare financial statements when required to do so, liability
will also arise. It is therefore important that directors understand both the general and the specific responsibilities imposed upon them, and how to properly discharge them, in order to fulfil their roles as directors and to address their exposure to directors’ liabilities.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.35
-
153/567問題
153. 問題
1 分QID1105:According to the NCO which has defined the statutory liabilities of directors, directors may incur liabilities due to:
I. Breaches of fiduciary duties.
II. Failure to give continuous attention to the affairs of the company.
III. Failure to act with due care and skill.
IV. Breaches of statutory duties.正確
Where a director breaches strict requirements of the CO,
such as failing to prepare financial statements when required to do so, liability will also arise. It is therefore important that directors understand both the general and the specific
responsibilities imposed upon them, and how to properly discharge them, in order to fulfil their roles as directors and to address their exposure to directors’ liabilities.
Any ratification by a company of conduct by a director in relation to negligence, default, breach of duty or breach of trust in relation to the company must be approved by resolution of the members of the company錯誤
Where a director breaches strict requirements of the CO,
such as failing to prepare financial statements when required to do so, liability will also arise. It is therefore important that directors understand both the general and the specific
responsibilities imposed upon them, and how to properly discharge them, in order to fulfil their roles as directors and to address their exposure to directors’ liabilities.
Any ratification by a company of conduct by a director in relation to negligence, default, breach of duty or breach of trust in relation to the company must be approved by resolution of the members of the company提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.35
-
154/567問題
154. 問題
1 分QID885:Mr. Ko is a shareholder of Yellow River Trading. He believes Mr. David Wan, a director of Yellow River Trading, is breaching his statutory duties in recent electronics trading transactions. What are the actions that Mr Ko can take?
I. Obtain an injunction stopping such action.
II. If Mr. Wan has not disclosed a personal interest in a contract he has made on behalf of the company, the contract may be avoided at the option of the company.
III. All directors who have acted in breach of their duties will be jointly and severally liable to the company for damages.
IV. If they have wrongfully profited by dealing with the company’s property, the directors must account to the company for such profits.正確
The company may have the following remedies for a breach of duty by directors:
(a) It may obtain an injunction stopping such action.
(b) If the directors have not disclosed a personal interest in a contract they have made on behalf of the company, the contract may be cancelled at the option of the company, i.e. rescission.
(c.) All directors who have acted in breach of their duties will be jointly and severally liable to the company for damages.
(d) If they have wrongfully profited by dealing with the company’s property, the directors must account to the company for such profits.錯誤
The company may have the following remedies for a breach of duty by directors:
(a) It may obtain an injunction stopping such action.
(b) If the directors have not disclosed a personal interest in a contract they have made on behalf of the company, the contract may be cancelled at the option of the company, i.e. rescission.
(c.) All directors who have acted in breach of their duties will be jointly and severally liable to the company for damages.
(d) If they have wrongfully profited by dealing with the company’s property, the directors must account to the company for such profits.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.36
-
155/567問題
155. 問題
1 分QID883:What are the possible remedies for a breach of duty by directors?
I. It may obtain an injunction stopping such action.
II. If the directors have not disclosed a personal interest in a contract they have made on behalf of the company, the contract may be cancelled at the option of the company.
III. All directors who have acted in breach of their duties will be jointly and severally liable to the company for damages.
IV. If the directors have wrongfully profited by dealing with the company’s property, the directors must account to the members for such profits.正確
The company may have the following remedies for a breach of duty by directors:
(a) It may obtain an injunction stopping such action.
(b) If the directors have not disclosed a personal interest in a contract they have made on behalf of the company, the contract may be cancelled at the option of the company, i.e. rescission.
(c.) All directors who have acted in breach of their duties will be jointly and severally liable to the company for damages.
(d) If they have wrongfully profited by dealing with the company’s property, the directors must account to the company for such profits.錯誤
The company may have the following remedies for a breach of duty by directors:
(a) It may obtain an injunction stopping such action.
(b) If the directors have not disclosed a personal interest in a contract they have made on behalf of the company, the contract may be cancelled at the option of the company, i.e. rescission.
(c.) All directors who have acted in breach of their duties will be jointly and severally liable to the company for damages.
(d) If they have wrongfully profited by dealing with the company’s property, the directors must account to the company for such profits.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.36
-
156/567問題
156. 問題
1 分QID159:What are possible reliefs for directors for a breach?
I. The company can obtain an injunction, request for cancellation of contract or sue for damages
II. The company can submit the case to the SFC Fiduciary Committee.
III. The directors who are in breach should be accountable to the company for profits and damages.
IV. The directors who are in breach should be accountable to the company for profits and damages in addition to the interest owed.正確
The company may have the following remedies for a breach of duty by directors:
(a) It may obtain an injunction stopping such action.
(b) If the directors have not disclosed a personal interest in a contract they have made on behalf of the company, the contract may be cancelled at the option of the company, i.e. rescission.
(d) If they have wrongfully profited by dealing with the company’s property, the directors must account to the company for such profits.錯誤
The company may have the following remedies for a breach of duty by directors:
(a) It may obtain an injunction stopping such action.
(b) If the directors have not disclosed a personal interest in a contract they have made on behalf of the company, the contract may be cancelled at the option of the company, i.e. rescission.
(d) If they have wrongfully profited by dealing with the company’s property, the directors must account to the company for such profits.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.36
-
157/567問題
157. 問題
1 分QID886:What are the possible remedies for a breach of duty by directors?
I. It may obtain an injunction stopping such action.
II. If the directors have disclosed a personal interest in a contract they have made on behalf of the company, the contract may be cancelled at the option of the company.
III. All directors who have acted in breach of their duties will be jointly and severally liable to the company for damages.
IV. If the directors have wrongfully profited by dealing with the company’s property, the directors must account to the company for such profits.正確
The company may have the following remedies for a breach of duty by directors:
(a) It may obtain an injunction stopping such action.
(b) If the directors have not disclosed a personal interest in a contract they have made on behalf of the company, the contract may be cancelled at the option of the company, i.e. rescission.
(c.) All directors who have acted in breach of their duties will be jointly and severally liable to the company for damages.
(d) If they have wrongfully profited by dealing with the company’s property, the directors must account to the company for such profits.錯誤
The company may have the following remedies for a breach of duty by directors:
(a) It may obtain an injunction stopping such action.
(b) If the directors have not disclosed a personal interest in a contract they have made on behalf of the company, the contract may be cancelled at the option of the company, i.e. rescission.
(c.) All directors who have acted in breach of their duties will be jointly and severally liable to the company for damages.
(d) If they have wrongfully profited by dealing with the company’s property, the directors must account to the company for such profits.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.36
-
158/567問題
158. 問題
1 分QID154:Millionaire Securities has recently been convicted of certain acts of market misconduct. Mr. Ip, the director of Millionaire Securities, was unaware of these illegal acts but had diligently tried to oversee and regulate the company’s operations. Under these circumstances, is Mr. Ip guilty?
正確
The court may give relief to a director or directors if they have, in causing the breach, been shown to have acted honestly and reasonably.
錯誤
The court may give relief to a director or directors if they have, in causing the breach, been shown to have acted honestly and reasonably.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.38
-
159/567問題
159. 問題
1 分QID1106:If a director (or his connected entity) can reasonably foresee direct or indirect interest in a transaction, arrangement or contract, or a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract with the company that is significant in relation to the company’s business, he must:
I. For transaction or arrangements that has been entered, he must declare the nature and extent of that interest to other directors.
II. For transaction or arrangements that has been entered, he must declare the nature and extent of that interest to the members.
III. For transaction or arrangements being proposed, he must declare the nature and extent of that interest to other directors.
IV. For transaction or arrangements being proposed, he must declare the nature and extent of that interest to the members.”正確
If a director (or his connected entity) is directly or indirectly interested in a transaction, arrangement or contract, or a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract with the company that is significant in relation to the company’s business, he must declare to other directors the nature and extent of that interest (if it is material):
(a) as soon as reasonably practicable for a transaction or arrangement that has been entered; or
(b) before the company enters into the transaction or arrangement for a proposed transaction or arrangement.錯誤
If a director (or his connected entity) is directly or indirectly interested in a transaction, arrangement or contract, or a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract with the company that is significant in relation to the company’s business, he must declare to other directors the nature and extent of that interest (if it is material):
(a) as soon as reasonably practicable for a transaction or arrangement that has been entered; or
(b) before the company enters into the transaction or arrangement for a proposed transaction or arrangement.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.39
-
160/567問題
160. 問題
1 分QID155:If a director Mr. Ko discovers any conflict of interest with personal benefits in a contract related to the company’s business, he should:
I. Declare the nature and extent of the interest within a reasonable and practicable time, after the contract has been entered into.
II. No declaration is required if the arranged contract is not made in Hong Kong.
III. Declare the nature and extent of the conflict of interest before the contract is entered into.
IV. No declaration is required if the contract is not entered into.正確
If a director (or his connected entity) is directly or indirectly interested in a transaction, arrangement or contract, or a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract with the company that is significant in relation to the company’s business, he must declare to other directors the nature and extent of that interest (if it is material):
(a) as soon as reasonably practicable for a transaction, arrangement or contract that has been entered; or
(b) before the company enters into the transaction, arrangement or contract for a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract.錯誤
If a director (or his connected entity) is directly or indirectly interested in a transaction, arrangement or contract, or a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract with the company that is significant in relation to the company’s business, he must declare to other directors the nature and extent of that interest (if it is material):
(a) as soon as reasonably practicable for a transaction, arrangement or contract that has been entered; or
(b) before the company enters into the transaction, arrangement or contract for a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.39
-
161/567問題
161. 問題
1 分QID1605:Mr. Liu is the only shareholder of Vitamilk and the director of Millionaire Financial Investment. Another director of Millionaire Financial Investment suggested to acquire some of Vitamilk real estates at the board of directors meeting. Does Mr. Liu have to declare to other directors the nature and extent of that interest?
正確
If a director (or his connected entity) is directly or indirectly interested in a transaction, arrangement or contract, or a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract with the company that is significant in relation to the company’s business, he must declare to other directors the nature and extent of that interest (if it is material):
(b) before the company enters into the transaction or arrangement for a proposed transaction or arrangement.錯誤
If a director (or his connected entity) is directly or indirectly interested in a transaction, arrangement or contract, or a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract with the company that is significant in relation to the company’s business, he must declare to other directors the nature and extent of that interest (if it is material):
(b) before the company enters into the transaction or arrangement for a proposed transaction or arrangement.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.39
-
162/567問題
162. 問題
1 分QID795:Mr. Ko is a director of a phone book printing company -Kaohsiung Printing. Mr Ko and Mr Wan jointly own British Construction Bank and are both directors of British Construction Bank. Kaohsiung Printing is going to print a lot of phone books and calendars for British Construction Bank as souvenirs for customers. Should Mr. Ko disclose his interest in Kaohsiung Printing to the board of directors of British Construction Bank?
正確
If a director (or his connected entity) is directly or indirectly interested in a transaction, arrangement or contract, or a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract with the company that is significant in relation to the company’s business, he must declare to other directors the nature and extent of that interest (if it is material):
(a) as soon as reasonably practicable for a transaction or arrangement that has been entered; or
(b) before the company enters into the transaction or arrangement for a proposed transaction or arrangement.錯誤
If a director (or his connected entity) is directly or indirectly interested in a transaction, arrangement or contract, or a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract with the company that is significant in relation to the company’s business, he must declare to other directors the nature and extent of that interest (if it is material):
(a) as soon as reasonably practicable for a transaction or arrangement that has been entered; or
(b) before the company enters into the transaction or arrangement for a proposed transaction or arrangement.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.39
-
163/567問題
163. 問題
1 分QID1108:Yellow River Trading is prepared to acquire a well know local website – Opennoodles.com. The director of Yellow River Trading, Mr. Wan, is the spouse of the owner of Opennoodles.com. Mr. Wan should:
I. Disclose his interest in the general meeting.
II. Take no action because it is his spouse’s interests that are involved in the deal
III. Ensure that the deal is proper, fair and in the interest of Yellow River Trading.
IV. Resign immediately.正確
If a director (or his connected entity) is directly or indirectly interested in a transaction, arrangement or contract, or a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract with the company that is significant in relation to the company’s business, he must declare to other directors the nature and extent of that interest (if it is material):
(a) as soon as reasonably practicable for a transaction or arrangement that has been entered; or
(b) before the company enters into the transaction or arrangement for a proposed transaction or arrangement.錯誤
If a director (or his connected entity) is directly or indirectly interested in a transaction, arrangement or contract, or a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract with the company that is significant in relation to the company’s business, he must declare to other directors the nature and extent of that interest (if it is material):
(a) as soon as reasonably practicable for a transaction or arrangement that has been entered; or
(b) before the company enters into the transaction or arrangement for a proposed transaction or arrangement.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.39
-
164/567問題
164. 問題
1 分QID1107:If a director (or his connected entity) is directly or indirectly interested in a transaction, arrangement or contract, or a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract with the company that is significant in relation to the company’s business, he must declare the nature and extent of that interest:
I. Before the transaction and arrangement has been made, for a proposed transaction or arrangement
II. After the transaction and arrangement has been made, for a proposed transaction or arrangement.
III. As soon as he can reasonably foresee such conflict of interest.
IV. As soon as the annual audit requires him to do so.正確
If a director (or his connected entity) is directly or indirectly interested in a transaction, arrangement or contract, or a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract with the company that is significant in relation to the company’s business, he must declare to other directors the nature and extent of that interest (if it is material):
(a) as soon as reasonably practicable for a transaction or arrangement that has been entered; or
(b) before the company enters into the transaction or arrangement for a proposed transaction or arrangement.錯誤
If a director (or his connected entity) is directly or indirectly interested in a transaction, arrangement or contract, or a proposed transaction, arrangement or contract with the company that is significant in relation to the company’s business, he must declare to other directors the nature and extent of that interest (if it is material):
(a) as soon as reasonably practicable for a transaction or arrangement that has been entered; or
(b) before the company enters into the transaction or arrangement for a proposed transaction or arrangement.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.39
-
165/567問題
165. 問題
1 分QID2812:Which of the following statements about the Companies Ordinance is incorrect?
正確
There is no minimum authorised share capital requirement for a company.
錯誤
There is no minimum authorised share capital requirement for a company.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.4
-
166/567問題
166. 問題
1 分QID1074:Under the Companies Ordinance, which of the following are correct categorization of companies?
I. Private Companies
II. Public Companies
III. Listed Companies
IV. Guarantee Companies正確
Under the CO, every Hong Kong company falls into one of three categories: private companies, public companies and guarantee companies.
錯誤
Under the CO, every Hong Kong company falls into one of three categories: private companies, public companies and guarantee companies.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.4
-
167/567問題
167. 問題
1 分QID778:In Hong Kong, registered companies can be classified into which of the following categories?
I. Private Company
II. Public Company
III. Non-Profit Company
IV. Guarantee Company正確
Under the NCO, a new category of company is added and now every Hong Kong company falls into one of three categories: private companies, public companies and guarantee companies.
錯誤
Under the NCO, a new category of company is added and now every Hong Kong company falls into one of three categories: private companies, public companies and guarantee companies.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.4
-
168/567問題
168. 問題
1 分QID1111:Which of the following descriptions about directors’ remuneration are correct?
I. If the director is also having administrative roles, he does not need to have a separate service with the company. All directors’ fees should include all of his services.
II. The articles of association have designated the powers of determining such remuneration.
III. The articles of association states that director remuneration should be determined by the members in the general meeting.
IV. Directors remuneration usually covers directors’ fees.正確
Authority for payment is provided in the company’s articles. The model articles of association in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice provide that the remuneration of directors is determined by the company in general meeting. This usually covers directors’ fees. If a director holds some other position, such as managing director or executive director, he can have a service contract.
錯誤
Authority for payment is provided in the company’s articles. The model articles of association in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice provide that the remuneration of directors is determined by the company in general meeting. This usually covers directors’ fees. If a director holds some other position, such as managing director or executive director, he can have a service contract.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.40
-
169/567問題
169. 問題
1 分QID157:In general, remuneration of which of the following individuals is determined by the company in general meeting?
正確
The remuneration of directors is determined by the company in general meeting.
錯誤
The remuneration of directors is determined by the company in general meeting.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.40
-
170/567問題
170. 問題
1 分QID158:According to the provisions in the model articles of association in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice, how should the remuneration of directors be determined?
正確
Authority for payment is provided in the company’s articles. The model articles of association in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice provide that the remuneration of directors is determined by the company in general meeting. This usually covers directors’ fees.
錯誤
Authority for payment is provided in the company’s articles. The model articles of association in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice provide that the remuneration of directors is determined by the company in general meeting. This usually covers directors’ fees.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.40
-
171/567問題
171. 問題
1 分QID1109:Who determines the directors’ remuneration?
正確
Authority for payment is provided in the company’s articles. The model articles of association in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice provide that the remuneration of directors is determined by the company in general meeting.
錯誤
Authority for payment is provided in the company’s articles. The model articles of association in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice provide that the remuneration of directors is determined by the company in general meeting.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.40
-
172/567問題
172. 問題
1 分QID156:Which of the following descriptions regarding the remuneration of directors is correct?
正確
Authority for payment is provided in the company’s articles. The model articles of association in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice provide that the remuneration of directors is determined by the company in general meeting. This usually covers directors’ fees. If a director holds some other position, such as managing director or executive director, he can have a service contract.
錯誤
Authority for payment is provided in the company’s articles. The model articles of association in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice provide that the remuneration of directors is determined by the company in general meeting. This usually covers directors’ fees. If a director holds some other position, such as managing director or executive director, he can have a service contract.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.40
-
173/567問題
173. 問題
1 分QID1110:Which of the following are correct descriptions of directors’ remuneration?
I. Authority for payment is provided in the articles
II. If a director holds some other position, such as Managing Director or an executive director, he can have a service contract parallel to his director’s remuneration.
III. The remuneration must include a set of stock options.
IV. The director of a company should treat his directorship as his sole profession.正確
Authority for payment is provided in the company’s articles. The model articles of association in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice provide that the remuneration of directors is determined by the company in general meeting. This usually covers directors’ fees. If a director holds some other position, such as managing director or executive director, he can have a service contract.
錯誤
Authority for payment is provided in the company’s articles. The model articles of association in the Companies (Model Articles) Notice provide that the remuneration of directors is determined by the company in general meeting. This usually covers directors’ fees. If a director holds some other position, such as managing director or executive director, he can have a service contract.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.40
-
174/567問題
174. 問題
1 分QID1178:Mr. David Wan and his spouse are investing in real estate under the name of Yangtze River Investment and he is trying to apply for a loan for assignment. Mr. Wan and his spouse are the only directors and shareholders of Yangtze River Investment. Mr. Wan is also a director of a well-known electronics trading company, Yellow River Trading. To apply for the loan, Mr. Wan can:
I. Apply for a personal loan by assigning Yellow River Trading as the Guarantor.
II. Apply for a personal loan by assigning the subsidiaries of Yellow River Trading as the Guarantor.
III. Apply for a loan from Yellow River Trading.
IV. Apply for a personal loan using his director remuneration from Yellow River Trading as collateral.正確
A company cannot directly or indirectly:
(a) make a loan to a director of the company or a body corporate controlled by such a director; or
(b) enter into a guarantee or provide security for such a loan
without the approval of its members.錯誤
A company cannot directly or indirectly:
(a) make a loan to a director of the company or a body corporate controlled by such a director; or
(b) enter into a guarantee or provide security for such a loan
without the approval of its members.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.41
-
175/567問題
175. 問題
1 分QID1112:Which of the following are exceptions to prohibitions on loans to a director?
I. A de minimum threshold of 5% of the net assets of the company before a transaction is subject to the restriction.
II. Expenditure in connection with defending any proceeding or investigation or regulatory action for misconduct provided that the directors has to repay the company if he is found guilty or to have committed the misconduct.
III. Expenses that are incurred by the director in the course of personal business.
IV. If the director is the sole owner of the company and he agrees to such arrangements.正確
There are exceptions, such as the following:
(a) a de minimum threshold of 5% of the net assets of the company before a transaction is subject to the restriction; and
(b) expenditure in connection with defending any proceeding or investigation or regulatory action for misconduct provided that the directors has to repay the company if he is found guilty or to have committed the misconduct.錯誤
There are exceptions, such as the following:
(a) a de minimum threshold of 5% of the net assets of the company before a transaction is subject to the restriction; and
(b) expenditure in connection with defending any proceeding or investigation or regulatory action for misconduct provided that the directors has to repay the company if he is found guilty or to have committed the misconduct.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.44
-
176/567問題
176. 問題
1 分QID161:Under normal circumstances, a company cannot directly or indirectly make a loan or guarantee to a director of its holding company or a body corporate controlled by such a director. However, which of the following are exceptions?
I. Making a loan of value not exceeding 5% of the company’s net assets.
II. The loan is made with the approval of the members of the company.
III. Expenditure on defending any proceeding, or investigation or regulatory action for misconduct of a director if such expenditure has to be repaid by the director to the company when he is convicted in the proceeding or has committed misconduct.
IV. The loan is made with the approval of the SFC.正確
There are exceptions, such as the following:
(a) making a loan of value not exceeding 5% of the company’s net assets; and
(b) expenditure on defending any proceeding, or investigation or regulatory action for misconduct of a director if such expenditure has to be repaid by the director to the company when he is convicted in the proceeding or has committed the misconduct. Similarly, a company cannot directly or indirectly make a loan or guarantee to a director of its holding company or a body corporate controlled by such a director without the approvals
of its members and the holding companies’ members.錯誤
There are exceptions, such as the following:
(a) making a loan of value not exceeding 5% of the company’s net assets; and
(b) expenditure on defending any proceeding, or investigation or regulatory action for misconduct of a director if such expenditure has to be repaid by the director to the company when he is convicted in the proceeding or has committed the misconduct. Similarly, a company cannot directly or indirectly make a loan or guarantee to a director of its holding company or a body corporate controlled by such a director without the approvals
of its members and the holding companies’ members.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.44
-
177/567問題
177. 問題
1 分QID162:Which of the following entities can appoint inspectors to investigate and report on the
affairs of a company if the court declares that an investigation should be carried out?正確
The Financial Secretary is required to appoint inspectors to investigate and report on the affairs of a company if the court declares that an investigation should be carried out (s. 841, NCO).
錯誤
The Financial Secretary is required to appoint inspectors to investigate and report on the affairs of a company if the court declares that an investigation should be carried out (s. 841, NCO).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.46
-
178/567問題
178. 問題
1 分QID1113:If the court declares that an investigation on a company’s affairs should be carried out, which of the following organization should appoint inspectors to investigate and report on the company?
正確
The Financial Secretary is required to appoint inspectors to investigate and report on the affairs of a company if the court declares that an investigation should be carried out (s. 841, NCO).
錯誤
The Financial Secretary is required to appoint inspectors to investigate and report on the affairs of a company if the court declares that an investigation should be carried out (s. 841, NCO).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.46
-
179/567問題
179. 問題
1 分QID1114:The Financial Secretary is required to appoint inspectors under which of the following circumstances?
I. An application is made by the specified number of members.
II. The company passed a special resolution requesting such inspections.
III. He suspects fraud in the operations or formation of the company, or oppressive conduct, or an intent to defraud creditors.
IV. He suspects the persons concerned with the formation or management of the company have been guilty of fraud or other misconduct.正確
The Financial Secretary may also appoint inspectors if:
(a) an application is made by the specified number of members;
(b) the company passes a special resolution requesting such appointment;
(c.) he suspects fraud in the business or formation of the company, or oppressive conduct, or an intent to defraud creditors; or
(d) he suspects the persons concerned with the formation or management of the company to have been guilty of fraud or other misconduct (ss. 840 to 841, NCO).錯誤
The Financial Secretary may also appoint inspectors if:
(a) an application is made by the specified number of members;
(b) the company passes a special resolution requesting such appointment;
(c.) he suspects fraud in the business or formation of the company, or oppressive conduct, or an intent to defraud creditors; or
(d) he suspects the persons concerned with the formation or management of the company to have been guilty of fraud or other misconduct (ss. 840 to 841, NCO).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.47
-
180/567問題
180. 問題
1 分QID2763:According to the Companies Ordinance, when can the Financial Secretary appoint an inspector to conduct an investigation into a company?
I. The company passes an ordinary resolution
II. The company passes a special resolution
III. Application by more than the nominated number of members
IV. The Financial Secretary considers that the company is involved in fraud or unfairly treating ordinary members正確
Circumstances under which the Financial Secretary may appoint an inspector to conduct an investigation into a company under the Companies Ordinance include:
I. The company passes a special resolution
II. Application by more than the nominated number of members (100 or 10%)
III. The Financial Secretary considers that the company is involved in fraud or unfairly treating ordinary members錯誤
Circumstances under which the Financial Secretary may appoint an inspector to conduct an investigation into a company under the Companies Ordinance include:
I. The company passes a special resolution
II. Application by more than the nominated number of members (100 or 10%)
III. The Financial Secretary considers that the company is involved in fraud or unfairly treating ordinary members提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.47
-
181/567問題
181. 問題
1 分QID2673:The SFC are not authorised to use its power to
正確
Only courst can windup companies.
錯誤
Only courst can windup companies.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.49
-
182/567問題
182. 問題
1 分QID1117:Which of the following descriptions about compulsory liquidation is correct?
I. This is a compulsory winding-up ordered by the court.
II. The liquidator is appointed by the court and acts under its control.
III. The liquidator is appointed through a shareholders’ meeting and acts under the control of the directors.
IV. Liquidation is passed by a special resolution.正確
This is a compulsory winding-up ordered by the court, and the liquidator is appointed by the court and acts under its control.
錯誤
This is a compulsory winding-up ordered by the court, and the liquidator is appointed by the court and acts under its control.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.49
-
183/567問題
183. 問題
1 分QID775:Which of the following are characteristics of a private company?
I. Restrictions on the rights to transfer it shares.
II. No more than 50 share holders.
III. May not offer shares to the public.
IV. Can be bought and sold OTC on the market.正確
A private company is a company that:
(a) restricts the right to transfer its shares;
(b) may not have more than 50 members (excluding present and past employees who are members and continue to be members respectively);
(c.) may not offer shares (or debentures) to the public; and
(d) is not limited by guarantee.錯誤
A private company is a company that:
(a) restricts the right to transfer its shares;
(b) may not have more than 50 members (excluding present and past employees who are members and continue to be members respectively);
(c.) may not offer shares (or debentures) to the public; and
(d) is not limited by guarantee.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.5
-
184/567問題
184. 問題
1 分QID777:Which of the following restrictions about a private company is incorrect?
正確
A private company is a company that:
(a) restricts the right to transfer its shares;
(b) may not have more than 50 members (excluding present and past employees who are members and continue to be members respectively);
© may not offer shares (or debentures) to the public; and
(d) is not limited by guarantee.
A private company doesn’t have to be guarantee companies.錯誤
A private company is a company that:
(a) restricts the right to transfer its shares;
(b) may not have more than 50 members (excluding present and past employees who are members and continue to be members respectively);
© may not offer shares (or debentures) to the public; and
(d) is not limited by guarantee.
A private company doesn’t have to be guarantee companies.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.5
-
185/567問題
185. 問題
1 分QID136:Which of the following description about private company is correct?
I. Must have more than 50 members
II. May not offer shares to the public
III. restricts the right to transfer its share
IV. is not limited by guarantee正確
A private company is a company that:
(a) restricts the right to transfer its shares; members and continue to be members respectively);
(b) may not have more than 50 members (excluding present and past employees who are members and continue to be members respectively);
© may not offer shares (or debentures) to the public; and
(d) is not limited by guarantee.錯誤
A private company is a company that:
(a) restricts the right to transfer its shares; members and continue to be members respectively);
(b) may not have more than 50 members (excluding present and past employees who are members and continue to be members respectively);
© may not offer shares (or debentures) to the public; and
(d) is not limited by guarantee.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.5
-
186/567問題
186. 問題
1 分QID776:A private company is a company that:
I. Has no restrictions in rights to transfer its shares.
II. May not have more than 50 members.
III. May not offer shares to the public.
IV. Is not limited by guarantee.正確
A private company is a company that:
(a) restricts the right to transfer its shares;
(b) may not have more than 50 members (excluding present and past employees who are members and continue to be members respectively);
© may not offer shares (or debentures) to the public; and
(d) is not limited by guarantee.錯誤
A private company is a company that:
(a) restricts the right to transfer its shares;
(b) may not have more than 50 members (excluding present and past employees who are members and continue to be members respectively);
© may not offer shares (or debentures) to the public; and
(d) is not limited by guarantee.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.5
-
187/567問題
187. 問題
1 分QID1118:Which of the following is NOT a possible reason for compulsory liquidation?
正確
A company may be wound up by the court if:
(e) the event occurs on the occurrence of which the memorandum or articles of association provides that the company is to be dissolved; or
(f) the court is of the opinion that it would be just and equitable to wind up the company. Examples are where:
(ii) the company was formed for a fraudulent purpose; or
(iii) the basis of mutual trust, understanding and confidence on which the company was
formed no longer exists.錯誤
A company may be wound up by the court if:
(e) the event occurs on the occurrence of which the memorandum or articles of association provides that the company is to be dissolved; or
(f) the court is of the opinion that it would be just and equitable to wind up the company. Examples are where:
(ii) the company was formed for a fraudulent purpose; or
(iii) the basis of mutual trust, understanding and confidence on which the company was
formed no longer exists.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.50
-
188/567問題
188. 問題
1 分QID2826:Which of the following is less likely to be the main cause of compulsory winding up?
正確
Unless the company has been out of business for more than a year at all, it is relatively unlikely that a company with a small amount of business remaining will be the primary reason for winding up.
錯誤
Unless the company has been out of business for more than a year at all, it is relatively unlikely that a company with a small amount of business remaining will be the primary reason for winding up.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.50
-
189/567問題
189. 問題
1 分QID1116:Which of the following is a reason for compulsory liquidation?
正確
A company may be wound up by the court if:
(a) it has by special resolution resolved that it shall be wound up by the court;
(b) it does not commence its business within a year from its incorporation; or has suspended its business for a whole year;
(c.) it has no members;
(d) it is unable to pay its debts;
(e) the event occurs on the occurrence of which the articles of association provide that the company is to be dissolved; or
(f) the court is of the opinion that it would be just and equitable to wind up the company.錯誤
A company may be wound up by the court if:
(a) it has by special resolution resolved that it shall be wound up by the court;
(b) it does not commence its business within a year from its incorporation; or has suspended its business for a whole year;
(c.) it has no members;
(d) it is unable to pay its debts;
(e) the event occurs on the occurrence of which the articles of association provide that the company is to be dissolved; or
(f) the court is of the opinion that it would be just and equitable to wind up the company.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.50
-
190/567問題
190. 問題
1 分QID1120:Petitioner(s) of compulsory liquidation may NOT be:
正確
The petitioners may be:
(a) the company;
(b) a creditor;
(d) the Financial Secretary, if he thinks it desirable in the public interest.錯誤
The petitioners may be:
(a) the company;
(b) a creditor;
(d) the Financial Secretary, if he thinks it desirable in the public interest.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.51
-
191/567問題
191. 問題
1 分QID164:Which of the following cannot petition the court for a company’s winding-up?
正確
The petitioners may be:
(a) the company;
(b) a creditor;
(c) a contributory (i.e. every person liable to contribute to the assets of a company in the event of its being wound up);
(d) the Financial Secretary, if he thinks it desirable in the public interest;
(e) the Registrar of Companies, if the company has breached provisions of the CO or is being carried on for an unlawful purpose;
(f) the Official Receiver, where there is already a voluntary winding up (s. 179, CWUMPO); and
(g) the SFC, if it appears desirable in the public interest (SFO gives authority to the SFC).錯誤
The petitioners may be:
(a) the company;
(b) a creditor;
(c) a contributory (i.e. every person liable to contribute to the assets of a company in the event of its being wound up);
(d) the Financial Secretary, if he thinks it desirable in the public interest;
(e) the Registrar of Companies, if the company has breached provisions of the CO or is being carried on for an unlawful purpose;
(f) the Official Receiver, where there is already a voluntary winding up (s. 179, CWUMPO); and
(g) the SFC, if it appears desirable in the public interest (SFO gives authority to the SFC).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.51
-
192/567問題
192. 問題
1 分QID1119:Petitioners of compulsory liquidation may be:
I. The Official Receiver.
II. The SFC, in lieu of public interest.
III. The Chief Executive.
IV. The Registrar of Companies.正確
The petitioners may be:
(e) the Registrar of Companies, if the company has breached provisions of the CO or is being carried on for an unlawful purpose;
(f) the Official Receiver, where there is already a voluntary winding up (s. 179, CWUMPO); and
(g) the SFC, if it appears desirable in the public interest (SFO gives authority to the SFC).錯誤
The petitioners may be:
(e) the Registrar of Companies, if the company has breached provisions of the CO or is being carried on for an unlawful purpose;
(f) the Official Receiver, where there is already a voluntary winding up (s. 179, CWUMPO); and
(g) the SFC, if it appears desirable in the public interest (SFO gives authority to the SFC).提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.51
-
193/567問題
193. 問題
1 分QID1121:In the case of a compulsory liquidation, the liquidator should be appointed by:
正確
The court may appoint a liquidator.
錯誤
The court may appoint a liquidator.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.52
-
194/567問題
194. 問題
1 分QID1123:Which of the following can start a Voluntary liquidation?
I. Members
II. Debtors
III. Creditors
IV. Chairman of the Board正確
A voluntary winding-up may be started by members or creditors.
錯誤
A voluntary winding-up may be started by members or creditors.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.53
-
195/567問題
195. 問題
1 分QID1124:Voluntary liquidation may be started by which of the following?
I. Shareholders
II. Creditors
III. Financial Secretary
IV. The Chief Executive正確
A voluntary winding-up may be started by members or creditors.
錯誤
A voluntary winding-up may be started by members or creditors.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.53
-
196/567問題
196. 問題
1 分QID165:According the CO, which of the following can initiate a voluntary liquidation?
I. Directors
II. Creditors
III. Members
IV. Financial Secretary正確
A voluntary winding-up may be started by members or creditors. A voluntary winding-up is started if the directors of a company or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors deliver a winding-up statement that the company should be wound up after passing a resolution to that effect at a board meeting.
錯誤
A voluntary winding-up may be started by members or creditors. A voluntary winding-up is started if the directors of a company or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors deliver a winding-up statement that the company should be wound up after passing a resolution to that effect at a board meeting.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.54
-
197/567問題
197. 問題
1 分QID1122:Voluntary liquidation can be initiated by which of the following parties?
I. Directors
II. Members
III. Creditors
IV. Court正確
A voluntary winding-up may be started by members or creditors.
A voluntary winding-up is started:
(a) when the period fixed for the company’s duration as stated in its articles of association comes to an end;
(b) by the passing of a special resolution for winding up; or
(c) if the directors of a company or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors deliver a winding-up statement under s. 228A, CWUMPO
that the company should be wound up after passing a resolution to that effect at a board meeting. However, no later than 28 days after the delivery of any winding-up statement to the Registrar of Companies to commence the winding-up, a meeting of the company must have been summoned. Also, a provisional liquidator must have been appointed since the commencement of the winding-up. In the case of a private company having only one
director, the sole director may make the winding-up statement.錯誤
A voluntary winding-up may be started by members or creditors.
A voluntary winding-up is started:
(a) when the period fixed for the company’s duration as stated in its articles of association comes to an end;
(b) by the passing of a special resolution for winding up; or
(c) if the directors of a company or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors deliver a winding-up statement under s. 228A, CWUMPO
that the company should be wound up after passing a resolution to that effect at a board meeting. However, no later than 28 days after the delivery of any winding-up statement to the Registrar of Companies to commence the winding-up, a meeting of the company must have been summoned. Also, a provisional liquidator must have been appointed since the commencement of the winding-up. In the case of a private company having only one
director, the sole director may make the winding-up statement.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.54
-
198/567問題
198. 問題
1 分QID1125:Which of the following is/are valid reason(s) for voluntary liquidation?
I. The period of the company’s planned existence as stated in its articles of association comes to an end.
II. A special resolution has been passed to wind up the company.
III. A passing of ordinary resolution that it is advisable to wind up the company, as it cannot continue due to its liabilities.
IV. The directors of a company or, in a case of a company having more than 2 directors, the majority of the directors deliver a winding-up statement under section 228A that the company should be wound up after passing a resolution to that effect at a board meeting.正確
A voluntary winding-up is started:
(a) when the period fixed for the company’s duration as stated in its articles of association
comes to an end;
(b) by the passing of a special resolution for winding up; or
(c) if the directors of a company or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors deliver a winding-up statement under s. 228A, CWUMPO that the company should be wound up after passing a resolution to that effect at a board meeting. However, prior to no later than 28 days after the delivery of any winding-up statement to the Registrar of Companies to commence the winding-up, a meeting of the company must have been summoned and a provisional liquidator must have been appointed. In the case of a private company having only one director, the sole director may make the winding-up statement.錯誤
A voluntary winding-up is started:
(a) when the period fixed for the company’s duration as stated in its articles of association
comes to an end;
(b) by the passing of a special resolution for winding up; or
(c) if the directors of a company or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors deliver a winding-up statement under s. 228A, CWUMPO that the company should be wound up after passing a resolution to that effect at a board meeting. However, prior to no later than 28 days after the delivery of any winding-up statement to the Registrar of Companies to commence the winding-up, a meeting of the company must have been summoned and a provisional liquidator must have been appointed. In the case of a private company having only one director, the sole director may make the winding-up statement.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.54
-
199/567問題
199. 問題
1 分QID2720:The document proving the company’s ability to pay its debts during the member’s (solvent) voluntary winding-up process is?
正確
The document certifying the company’s ability to pay its debts during the members’ (solvent) voluntary winding-up is a certificate of solvency.
錯誤
The document certifying the company’s ability to pay its debts during the members’ (solvent) voluntary winding-up is a certificate of solvency.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.55
-
200/567問題
200. 問題
1 分QID1129:If the directors believe that a company can repay its debt and obligations according to the certificate of solvency, within how long should the company repay all its outstanding obligations?
正確
Members’ voluntary winding up may be undertaken if the directors or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors issue a “certificate of solvency” to the effect that they have:
(b) formed the opinion that the company will be able to pay its debts within 12 months from the commencement of the winding-up as specified in the certificate of solvency.錯誤
Members’ voluntary winding up may be undertaken if the directors or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors issue a “certificate of solvency” to the effect that they have:
(b) formed the opinion that the company will be able to pay its debts within 12 months from the commencement of the winding-up as specified in the certificate of solvency.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.55
-
201/567問題
201. 問題
1 分QID1128:Which of the following are prerequisites to the issuance of Certificate of Solvency?
I. Agreed upon by a simple majority of directors.
II. Directors have made a full inquiry into the affairs of the company.
III. Directors have formed the opinion that the company will be able to pay its debts within 1 month from the commencement of the winding up as specified in the certificate of solvency.
IV. Directors have formed the opinion that the company will be able to pay its debts within 12 months from the commencement of the winding up as specified in the certificate of solvency.正確
Members’ voluntary winding up may be undertaken if the directors or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors issue a “certificate of solvency” to the effect that they have:
(a) made a full enquiry into the affairs of the company; and
(b) formed the opinion that the company will be able to pay its debts within 12 months from the commencement of the winding-up as specified in the certificate of solvency.錯誤
Members’ voluntary winding up may be undertaken if the directors or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors issue a “certificate of solvency” to the effect that they have:
(a) made a full enquiry into the affairs of the company; and
(b) formed the opinion that the company will be able to pay its debts within 12 months from the commencement of the winding-up as specified in the certificate of solvency.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.55
-
202/567問題
202. 問題
1 分QID1127:Voluntary liquidation can take place if the directors of a company or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors, can issue which of the following documents?
正確
Members’ voluntary winding up may be undertaken if the directors or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors issue a “certificate of solvency”.
錯誤
Members’ voluntary winding up may be undertaken if the directors or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors issue a “certificate of solvency”.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.55
-
203/567問題
203. 問題
1 分QID1126:Which of the following are the necessary prerequisites for a member’s voluntary winding-up to be undertaken?
I. The majority of the directors has issued a “certificate of solvency”.
II. The directors have made a full enquiry into the affairs of the company.
III. The directors have formed the opinion that the company will be able to pay its debts within 12 months from the commencement of the winding-up as specified in the certificate of solvency.
IV. The company has not been able to make a profit, or has not commenced business for the past year.正確
Members’ voluntary winding up may be undertaken if the directors or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors issue a “certificate of solvency” to the effect that they have:
(a) made a full enquiry into the affairs of the company; and
(b) formed the opinion that the company will be able to pay its debts within 12 months from the commencement of the winding-up as specified in the certificate of solvency.錯誤
Members’ voluntary winding up may be undertaken if the directors or, in the case of a company having more than two directors, the majority of the directors issue a “certificate of solvency” to the effect that they have:
(a) made a full enquiry into the affairs of the company; and
(b) formed the opinion that the company will be able to pay its debts within 12 months from the commencement of the winding-up as specified in the certificate of solvency.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.55
-
204/567問題
204. 問題
1 分QID1132:The certificate of solvency should be issued within how long preceding the winding-up resolution?
正確
The certificate of solvency must be issued within the 5 weeks preceding the resolution and be delivered to the Registrar of Companies for registration not later than when the copy of the winding-up resolution is delivered.
錯誤
The certificate of solvency must be issued within the 5 weeks preceding the resolution and be delivered to the Registrar of Companies for registration not later than when the copy of the winding-up resolution is delivered.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.57
-
205/567問題
205. 問題
1 分QID166:Which of the following statements about the “certificate of solvency” is correct?
I. It must be issued within the 5 weeks preceding the resolution to winding-up.
II. It must be delivered to the Registrar of Companies for registration.
III. The directors opine in the “certificate of solvency” that the company will be able to settle its debts in full within 12 months.
IV. If, after issuing the “certificate of solvency”, the company fails to settle its debts in full, the directors may bear criminal liability and be responsible for the shortfall正確
A member’s voluntary winding-up may be undertaken if the directors or, in the case of a company having more than two
directors, the majority of the directors issue a “certificate of solvency” to the effect that they have:
(b) formed the opinion that the company will be able to pay its debts within 12 months from the commencement of the winding-up as specified in the certificate of solvency.
The certificate of solvency must be issued within the five weeks preceding the resolution and be delivered to the Registrar of Companies for registration not later than when the copy of the winding-up resolution is delivered, and must include a statement of the company’s assets and liabilities at the latest practicable date.錯誤
A member’s voluntary winding-up may be undertaken if the directors or, in the case of a company having more than two
directors, the majority of the directors issue a “certificate of solvency” to the effect that they have:
(b) formed the opinion that the company will be able to pay its debts within 12 months from the commencement of the winding-up as specified in the certificate of solvency.
The certificate of solvency must be issued within the five weeks preceding the resolution and be delivered to the Registrar of Companies for registration not later than when the copy of the winding-up resolution is delivered, and must include a statement of the company’s assets and liabilities at the latest practicable date.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.57
-
206/567問題
206. 問題
1 分QID1130:The certificate of solvency should be delivered to:
正確
The certificate of solvency must be issued within the 5 weeks preceding the resolution and be delivered to the Registrar of Companies for registration not later than when the copy of the winding-up resolution is delivered.
錯誤
The certificate of solvency must be issued within the 5 weeks preceding the resolution and be delivered to the Registrar of Companies for registration not later than when the copy of the winding-up resolution is delivered.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.57
-
207/567問題
207. 問題
1 分QID1131:The issuance of the “Certificate of Solvency” should be done:
正確
The certificate of solvency must be issued within the 5 weeks preceding the resolution and be delivered to the Registrar of Companies for registration not later than when the copy of the winding-up resolution is delivered.
錯誤
The certificate of solvency must be issued within the 5 weeks preceding the resolution and be delivered to the Registrar of Companies for registration not later than when the copy of the winding-up resolution is delivered.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.57
-
208/567問題
208. 問題
1 分QID1133:The liquidator and committee of inspection of a creditors’ voluntary winding up may be appointed by:
正確
Where a resolution for voluntary winding-up has been proposed, the company must arrange a meeting of the creditors to be held within 14 days thereafter subject to a minimum notice period of 7 days. Advertisements must be run in the Gazette and newspapers. A statement of the position of the company’s affairs will be presented to the meeting, at which a liquidator and a committee of inspection will be appointed to supervise the process.
錯誤
Where a resolution for voluntary winding-up has been proposed, the company must arrange a meeting of the creditors to be held within 14 days thereafter subject to a minimum notice period of 7 days. Advertisements must be run in the Gazette and newspapers. A statement of the position of the company’s affairs will be presented to the meeting, at which a liquidator and a committee of inspection will be appointed to supervise the process.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.58
-
209/567問題
209. 問題
1 分QID167: If a members’ voluntary winding-up is not feasible, a creditors’ voluntary winding-up will take place. Which of the following entities will supervise this winding-up process?
正確
Where a resolution for Creditors’ voluntary winding-up has been proposed, the company must arrange a meeting of the creditors to be held within 14 days thereafter subject to a minimum notice period of seven days. Advertisements must be run in the Gazette and newspapers. A statement of the position of the company’s affairs will be presented to the meeting, at which a liquidator and a committee of inspection will be appointed to supervise the process.
錯誤
Where a resolution for Creditors’ voluntary winding-up has been proposed, the company must arrange a meeting of the creditors to be held within 14 days thereafter subject to a minimum notice period of seven days. Advertisements must be run in the Gazette and newspapers. A statement of the position of the company’s affairs will be presented to the meeting, at which a liquidator and a committee of inspection will be appointed to supervise the process.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.58
-
210/567問題
210. 問題
1 分QID1134:If the creditors decide to summon a meeting for the day when the resolution to wind up is proposed or for the next day, the company must arrange advertisements to be run in the Gazette and newspapers. This form of liquidation is likely to be:
正確
Where a resolution for voluntary winding-up has been proposed, the company must arrange a meeting of the creditors to be held within 14 days thereafter subject to a minimum notice period of 7 days. Advertisements must be run in the Gazette and newspapers. A statement of the position of the company’s affairs will be presented to the meeting, at which a liquidator and a committee of inspection will be appointed to supervise the process.
錯誤
Where a resolution for voluntary winding-up has been proposed, the company must arrange a meeting of the creditors to be held within 14 days thereafter subject to a minimum notice period of 7 days. Advertisements must be run in the Gazette and newspapers. A statement of the position of the company’s affairs will be presented to the meeting, at which a liquidator and a committee of inspection will be appointed to supervise the process.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.58
-
211/567問題
211. 問題
1 分QID1135:If the creditors decide to summon a meeting for the day when the resolution to wind up is proposed or for the next day, what kind of documents will be presented to the meeting?
I. Articles of Association
II. A statement of the position of the company’s affairs
III. List of Proof of Debt provided by Creditors
IV. Balance Sheet of the company正確
Where a resolution for voluntary winding-up has been proposed, the company must arrange a meeting of the creditors to be held within 14 days thereafter subject to a minimum notice period of 7 days. Advertisements must be run in the Gazette and newspapers. A statement of the position of the company’s affairs will be presented to the meeting, at which a liquidator and a committee of inspection will be appointed to supervise the process.
錯誤
Where a resolution for voluntary winding-up has been proposed, the company must arrange a meeting of the creditors to be held within 14 days thereafter subject to a minimum notice period of 7 days. Advertisements must be run in the Gazette and newspapers. A statement of the position of the company’s affairs will be presented to the meeting, at which a liquidator and a committee of inspection will be appointed to supervise the process.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.58
-
212/567問題
212. 問題
1 分QID1136:Which one of the following are accurate representations of creditors’ voluntary winding up?
I. Creditors’ voluntary winding up may be a result of failure in compulsory liquidation.
II. The company arranges a meeting of the creditors to be summoned for the day when the resolution to wind up is proposed or for the next day.
III. Advertisements will have to be run in the Gazette and newspapers.
IV. A statement of assets and liabilities, and a list of creditors and amounts due, will be presented to the meeting at which a liquidator and a committee of inspection will be appointed.正確
Where a resolution for voluntary winding-up has been proposed, the company must arrange a meeting of the creditors to be held within 14 days thereafter subject to a minimum notice period of 7 days. Advertisements must be run in the Gazette and newspapers. A statement of the position of the company’s affairs will be presented to the meeting, at which a liquidator and a committee of inspection will be appointed to supervise the process.
錯誤
Where a resolution for voluntary winding-up has been proposed, the company must arrange a meeting of the creditors to be held within 14 days thereafter subject to a minimum notice period of 7 days. Advertisements must be run in the Gazette and newspapers. A statement of the position of the company’s affairs will be presented to the meeting, at which a liquidator and a committee of inspection will be appointed to supervise the process.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.58
-
213/567問題
213. 問題
1 分QID1137:Which of the following is not an example of making a contract?
正確
A contract is an agreement between two or more persons creating obligations that are enforceable or otherwise recognisable under law, for example:
(a) the purchase or sale of a security or futures contract;
(b) the acceptance by an investor of an initial public offer of securities made by an issuer;
(c.) an undertaking to manage a mutual fund.錯誤
A contract is an agreement between two or more persons creating obligations that are enforceable or otherwise recognisable under law, for example:
(a) the purchase or sale of a security or futures contract;
(b) the acceptance by an investor of an initial public offer of securities made by an issuer;
(c.) an undertaking to manage a mutual fund.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.59
-
214/567問題
214. 問題
1 分QID130:Which of the following scenarios does not constitute a contract?
正確
A contract is an agreement between two or more persons creating obligations that are enforceable or otherwise recognisable under law, for example:
(a.) the purchase or sale of a security or futures contract;
(b.) the acceptance by an investor of an initial public offer of securities made by an issuer;
(c.) an undertaking to manage a mutual fund; and
(d.) the purchase of a leveraged foreign exchange contract.
Case D doesn’t comply with these requirements.錯誤
A contract is an agreement between two or more persons creating obligations that are enforceable or otherwise recognisable under law, for example:
(a.) the purchase or sale of a security or futures contract;
(b.) the acceptance by an investor of an initial public offer of securities made by an issuer;
(c.) an undertaking to manage a mutual fund; and
(d.) the purchase of a leveraged foreign exchange contract.
Case D doesn’t comply with these requirements.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.59
-
215/567問題
215. 問題
1 分QID1052:A public company is one that:
I. Is not a private company.
II. Is not a guarantee company.
III. Must be a listed company.
IV. May not be a listed company.正確
A public company is one that is not a private company, i.e. does not meet the requirements for a private company stated above, and is not a guarantee company.
錯誤
A public company is one that is not a private company, i.e. does not meet the requirements for a private company stated above, and is not a guarantee company.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.6
-
216/567問題
216. 問題
1 分QID135:Which of the following statements correctly describe public company under the new company ordinance?
I. It is a company that is not a private company.
II. It is a company that is not a guarantee company.
III. It must have more than 50 members.
IV. It restricts the right to transfer its shares.正確
A public company is one that is not a private company, i.e. does not meet the requirements for a private company stated above, and is not a guarantee company. It also has more than 50 members, contrary to a private company.
錯誤
A public company is one that is not a private company, i.e. does not meet the requirements for a private company stated above, and is not a guarantee company. It also has more than 50 members, contrary to a private company.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.6
-
217/567問題
217. 問題
1 分QID1051:Which of the following descriptions about a public company is correct?
正確
A public company is one that is not a private company, i.e. does not meet the requirements for a private company stated above, and is not a guarantee company.
錯誤
A public company is one that is not a private company, i.e. does not meet the requirements for a private company stated above, and is not a guarantee company.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.6
-
218/567問題
218. 問題
1 分QID1138:Which of the following is NOT an element of a legal contract?
正確
The elements of a legally binding contract are the following:
(a) an intention to create legal obligations;
(c.) there is valuable consideration, which can include an agreement not to sue under the contract; a contract under deed does not need consideration;
(d) the parties must have legal capacity, i.e. they must be at least 18 years of age and have no mental impairment; thus, if a securities dealer enters into a contract with a minor, the dealer may be at risk if the minor disclaims his commitments錯誤
The elements of a legally binding contract are the following:
(a) an intention to create legal obligations;
(c.) there is valuable consideration, which can include an agreement not to sue under the contract; a contract under deed does not need consideration;
(d) the parties must have legal capacity, i.e. they must be at least 18 years of age and have no mental impairment; thus, if a securities dealer enters into a contract with a minor, the dealer may be at risk if the minor disclaims his commitments提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.60
-
219/567問題
219. 問題
1 分QID1139:Which of the following conditions will make the contract void?
I. One party was forced into a contract under pressure.
II. A contract has illegal elements.
III. One or both parties are underage or mentally ill.
IV. The contract would result in financial damages to one party.正確
The elements of a legally binding contract are the following:
(d) the parties must have legal capacity, i.e. they must be at least 18 years of age and have no mental impairment; thus, if a securities dealer enters into a contract with a minor, the dealer may be at risk if the minor disclaims his commitments
(e) a contract may be unenforceable if it has an illegal element, and thus an intermediary may face legal risk; and
(f) the parties must have given their consent to the contract without any form of pressure; if a party was forced to enter into the contract under pressure, the contract will be void.錯誤
The elements of a legally binding contract are the following:
(d) the parties must have legal capacity, i.e. they must be at least 18 years of age and have no mental impairment; thus, if a securities dealer enters into a contract with a minor, the dealer may be at risk if the minor disclaims his commitments
(e) a contract may be unenforceable if it has an illegal element, and thus an intermediary may face legal risk; and
(f) the parties must have given their consent to the contract without any form of pressure; if a party was forced to enter into the contract under pressure, the contract will be void.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.60
-
220/567問題
220. 問題
1 分QID1140:Which of the following descriptions about Terms of a contract are correct?
I. Can be expressly agreed or implied.
II. Contracts must be a form of warranty.
III. A warranty is a term of a contract which is of considerable importance such that a breach of a condition might lead to repudiation by the innocent party or a claim for damage.
IV. There can be conditions precedent (which must be met) or conditions subsequent which, if they fail, may lead to repudiation of the contract.正確
The terms of the contract are important:
(a) They can be expressly agreed or implied (the terms may be implied by court or by common law).
(b) They can be conditions or warranties; a condition is a term of a contract which is of considerable importance such that a breach of a condition might lead to repudiation by the innocent party or a claim for damages; a warranty is a term of lesser importance such that a breach of a warranty may only lead to a claim for damages by an injured party.
(c.) There can be conditions precedent (which must be met) or conditions subsequent which, if they fail, may lead to repudiation of the contract.錯誤
The terms of the contract are important:
(a) They can be expressly agreed or implied (the terms may be implied by court or by common law).
(b) They can be conditions or warranties; a condition is a term of a contract which is of considerable importance such that a breach of a condition might lead to repudiation by the innocent party or a claim for damages; a warranty is a term of lesser importance such that a breach of a warranty may only lead to a claim for damages by an injured party.
(c.) There can be conditions precedent (which must be met) or conditions subsequent which, if they fail, may lead to repudiation of the contract.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.61
-
221/567問題
221. 問題
1 分QID1143:Which of the following statements correctly describes fiduciary relationships?
I. A fiduciary relationship must be either business or monetary interest to both parties.
II. A fiduciary is a person who should be serviced with duties of good faith, trust, confidence, honesty and care by another person.
III. All fiduciary relationships are agencies.
IV. All agencies are fiduciary relationships.正確
Agency is a fiduciary relationship created by express or implied contract or by law.
錯誤
Agency is a fiduciary relationship created by express or implied contract or by law.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.62
-
222/567問題
222. 問題
1 分QID907:Is the principal liable for the acts of wrongdoing of his/her/its agent?
正確
The principal liable for the acts of wrongdoing of his/her/its agent.
錯誤
The principal liable for the acts of wrongdoing of his/her/its agent.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.64
-
223/567問題
223. 問題
1 分QID1141:Which of the following descriptions about agency laws is correct?
正確
A principal is liable for the acts of his agent as, for example, a firm is liable if an account executive it employs and has held out to be acting for the firm cheats a client.
錯誤
A principal is liable for the acts of his agent as, for example, a firm is liable if an account executive it employs and has held out to be acting for the firm cheats a client.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.64
-
224/567問題
224. 問題
1 分QID2578:Which of the following best explains the basis of fiduciary relationship between a stockbroker and a client who signed a client agreement?
正確
A fiduciary relationship means when the fiduciary, here this means the stockbroker, has a duty to act for the best benefit of the other person, meaning the client in this case. The written agreement is only a record of the relationship.
錯誤
A fiduciary relationship means when the fiduciary, here this means the stockbroker, has a duty to act for the best benefit of the other person, meaning the client in this case. The written agreement is only a record of the relationship.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.65
-
225/567問題
225. 問題
1 分QID1142:Agency laws can be applied to which of the following cases?
I. A stock broker and his client.
II. A trustee and a beneficiary.
III. An auditor and a company.
IV. Solicitors and his clients.正確
Agency is a fiduciary relationship created by express or implied contract or by law.
A fiduciary is a person who owes another person duties of good faith, trust, confidence, honesty and care. A fiduciary relationship is one in which one person has a duty to act for the benefit of the other on matters within the scope of their relationship. Examples of fiduciary relationships are those of stockbroker and client, principal and agent, solicitor and client, and trustee and beneficiary.錯誤
Agency is a fiduciary relationship created by express or implied contract or by law.
A fiduciary is a person who owes another person duties of good faith, trust, confidence, honesty and care. A fiduciary relationship is one in which one person has a duty to act for the benefit of the other on matters within the scope of their relationship. Examples of fiduciary relationships are those of stockbroker and client, principal and agent, solicitor and client, and trustee and beneficiary.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.65
-
226/567問題
226. 問題
1 分QID1659:Which of the followings is an example of tort?
正確
When parties who have no contractual relationship are in a situation where one party suffers loss or damage as a result of the act of the other, a wrong or tort may have occurred, and under civil law a liability may have arisen.
Therefore, tort is a loss that is not based on a contractual relationship.A tort are losses that incur without a contractual relationship in place. The careless mistake is not a part of the contract and thus is a tort.
錯誤
When parties who have no contractual relationship are in a situation where one party suffers loss or damage as a result of the act of the other, a wrong or tort may have occurred, and under civil law a liability may have arisen.
Therefore, tort is a loss that is not based on a contractual relationship.A tort are losses that incur without a contractual relationship in place. The careless mistake is not a part of the contract and thus is a tort.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.66
-
227/567問題
227. 問題
1 分QID1144:Which of the following descriptions about law of tort are correct?
I. Law of tort is used in civil law cases.
II. Law of tort are based on ancient roman laws.
III. When parties who have no contractual relationship are in a situation where one party suffers loss or damage as a result of the act of the other, a wrong or tort may have occurred and under civil law a liability may have arisen.
IV. The tort of negligence is a tort committed as a result of a failure to observe the standard of care expected under the law in a particular case.正確
When parties who have no contractual relationship are in a situation where one party suffers loss or damage as a result of the act of the other, a wrong or tort may have occurred, and under civil law a liability may have arisen. There are various branches of the law of tort, of which the tort of negligence has the most direct application to securities and futures business. The tort of negligence is one committed as a result of a failure to observe the standard of care expected under law in a particular case.
錯誤
When parties who have no contractual relationship are in a situation where one party suffers loss or damage as a result of the act of the other, a wrong or tort may have occurred, and under civil law a liability may have arisen. There are various branches of the law of tort, of which the tort of negligence has the most direct application to securities and futures business. The tort of negligence is one committed as a result of a failure to observe the standard of care expected under law in a particular case.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.66
-
228/567問題
228. 問題
1 分QID1145:Which of the following statements correctly describe the employment laws?
I. An employer must provide his employee with remuneration, indemnity for expenses, losses and liabilities incurred while performing his duties.
II. An employee must demonstrate skills and competence, faithful service, obedience and confidentiality.
III. A director service is considered as an employment relationship by the company ordinance.
IV. If the two parties fail to observe these basic elements in the relationship, there can be a breach of the law as well as of the contractual relationship between them.正確
Under common law, an employer must provide his employee with remuneration, indemnity for expenses, losses and liabilities incurred while performing his duties, and a safe working
environment.
Also, under common law, an employee must demonstrate skills and competence, faithful service, obedience and confidentiality.
If the two parties fail to observe these basic elements in the relationship, there can be a breach of the law as well as of the contractual relationship between them.錯誤
Under common law, an employer must provide his employee with remuneration, indemnity for expenses, losses and liabilities incurred while performing his duties, and a safe working
environment.
Also, under common law, an employee must demonstrate skills and competence, faithful service, obedience and confidentiality.
If the two parties fail to observe these basic elements in the relationship, there can be a breach of the law as well as of the contractual relationship between them.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.68
-
229/567問題
229. 問題
1 分QID1043:Which of the following is a correct description of a guarantee company?
正確
A guarantee company is one that:
(a) does not have a share capital; and
(b) the liability of its members is limited by the company’s articles to the amount that the members undertake to contribute to the assets of the company in the event of its being wound up.錯誤
A guarantee company is one that:
(a) does not have a share capital; and
(b) the liability of its members is limited by the company’s articles to the amount that the members undertake to contribute to the assets of the company in the event of its being wound up.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.7
-
230/567問題
230. 問題
1 分QID1044:A guarantee company is one that:
I. does not have a share capital.
II. is not a private company.
III. the liability of its members is limited by the company’s articles to the amount that the members undertake to contribute to the assets of the company in the event of its being wound up.
IV. does not have a director.正確
A guarantee company is one that:
(a) does not have a share capital; and
(b) the liability of its members is limited by the company’s articles to the amount that the members undertake to contribute to the assets of the company in the event of its being wound up.錯誤
A guarantee company is one that:
(a) does not have a share capital; and
(b) the liability of its members is limited by the company’s articles to the amount that the members undertake to contribute to the assets of the company in the event of its being wound up.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.7
-
231/567問題
231. 問題
1 分QID502:According to the Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance, personal data refers to:
正確
“Personal data” means any data relating directly or indirectly to a living individual, from which it is practicable for the identity of the individual to be directly or indirectly ascertained (and are in a form in which access or processing is practicable).
錯誤
“Personal data” means any data relating directly or indirectly to a living individual, from which it is practicable for the identity of the individual to be directly or indirectly ascertained (and are in a form in which access or processing is practicable).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.71
-
232/567問題
232. 問題
1 分QID805:Which of the following are classified as personal data under the PDPO?
正確
“Personal data” means any data relating directly or indirectly to a living individual, from which it is practicable for the identity of the individual to be directly or indirectly ascertained (and are in a form in which access or processing is practicable).
錯誤
“Personal data” means any data relating directly or indirectly to a living individual, from which it is practicable for the identity of the individual to be directly or indirectly ascertained (and are in a form in which access or processing is practicable).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.71
-
233/567問題
233. 問題
1 分QID501:Which of the follow ordinance/codes/rules protect the privacy of individuals in relation to their personal data?
正確
The Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance (“PDPO”) was established to protect the privacy of individuals in relation to personal data.
錯誤
The Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance (“PDPO”) was established to protect the privacy of individuals in relation to personal data.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.71
-
234/567問題
234. 問題
1 分QID1147:Which of the following is responsible for the enforcement of Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance?
正確
The Privacy Commissioner for Personal Data is an independent public officer appointed to enforce and promote compliance with the PDPO.
錯誤
The Privacy Commissioner for Personal Data is an independent public officer appointed to enforce and promote compliance with the PDPO.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.71
-
235/567問題
235. 問題
1 分QID2827:Registration and Electoral Office lost a notebook computer containing voters’ information. This is more likely to violate
正確
The data protection principles set out in the PDPO include:
I. Purpose and manner of collection of personal data
II. Accuracy of Personal Data and Retention Period
III. Use of Personal Data
IV. Security of personal data
V. Information to be available in general
VI. Access to personal dataThe loss of a notebook computer containing personal data likely indicates a failure to secure personal data, which violated principle IV – security of personal data, a requirement to prevent unauthorised or accidental access, processing, erasure, loss, or use of personal data.
錯誤
The data protection principles set out in the PDPO include:
I. Purpose and manner of collection of personal data
II. Accuracy of Personal Data and Retention Period
III. Use of Personal Data
IV. Security of personal data
V. Information to be available in general
VI. Access to personal dataThe loss of a notebook computer containing personal data likely indicates a failure to secure personal data, which violated principle IV – security of personal data, a requirement to prevent unauthorised or accidental access, processing, erasure, loss, or use of personal data.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.71
-
236/567問題
236. 問題
1 分QID808:The PDPO is applicable to which of the following individuals?
I. The user of personal data
II. The collector of personal data
III. The holder of personal data
IV. The processor of personal data正確
The Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance (“PDPO”) was established to protect the privacy of individuals in relation to personal data. It applies to any data user who, in relation to personal data, means a person who alone or jointly, or in common with other persons, controls the collection, holding, processing or use of the data.
錯誤
The Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance (“PDPO”) was established to protect the privacy of individuals in relation to personal data. It applies to any data user who, in relation to personal data, means a person who alone or jointly, or in common with other persons, controls the collection, holding, processing or use of the data.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.71
-
237/567問題
237. 問題
1 分QID2394:People who enforce the Privacy Ordinance are:
正確
People who enforce the Privacy Ordinance are the Privacy Commissioner for Personal Data.
錯誤
People who enforce the Privacy Ordinance are the Privacy Commissioner for Personal Data.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.71
-
238/567問題
238. 問題
1 分QID1149:The data protection principles include:
I. information to be generally available to the public.
II. use of personal data.
III. purpose and manner of collection of personal data.
IV. accuracy and duration of retention of personal data.正確
Principle 1 – purpose and manner of collection of personal data
Principle 2 – accuracy and duration of retention of personal data
Principle 3 – use of personal data
Principle 5 is “information to be generally available”, but not ” information to be generally available to the public”.錯誤
Principle 1 – purpose and manner of collection of personal data
Principle 2 – accuracy and duration of retention of personal data
Principle 3 – use of personal data
Principle 5 is “information to be generally available”, but not ” information to be generally available to the public”.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.72
-
239/567問題
239. 問題
1 分QID505:British Construction Bank is an authorised financial institution. Amid the downfall of the Hong Kong banking sector, it has decided to promote its personal loan service by acquiring a list of clients and contacts from its wholly owned subsidiary British Construction Securities, a licensed corporation. Should British Construction Securities provide such information to British Construction Bank?
正確
Where the data is collected from the data subject, he should be informed, at the prescribed times, of the purpose for which the data is to be used, the classes of persons to whom the data may be transferred and of his rights to access and to request the correction of the data. Also, personal data should not, without the consent of the data subject, be used for a new purpose.
錯誤
Where the data is collected from the data subject, he should be informed, at the prescribed times, of the purpose for which the data is to be used, the classes of persons to whom the data may be transferred and of his rights to access and to request the correction of the data. Also, personal data should not, without the consent of the data subject, be used for a new purpose.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.72
-
240/567問題
240. 問題
1 分QID1146:Under the Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance, the subject is entitled to which of the following rights?
I. The subject shall be notified about the purpose of collection of personal data.
II. The subject’s personal data should not, without the consent of the data subject, be used for any purpose other than that for which it was collected or a directly related purpose
III. The data subject shall be entitled to ascertain whether data of which he is the subject are held, request and receive access to his personal data within a reasonable time at a reasonable fee and in an intelligible form, and to request corrections to the data and to be given reasons for any refusals in relation to the above and to object.
IV. The subject’s personal data shall not be collected unless lawfully and fairly collected for a lawful purpose directly related to a function or activity of the data user, the collection is necessary for or directly related to that purpose and the data is not excessive for the purpose.正確
(a) Principle 1 – purpose and manner of collection of personal data
(i) Personal data shall not be collected unless for a lawful purpose directly related to a function or activity of the data user, and unless the collection is necessary for or directly related to that purpose and the data is not excessive for the purpose.
(ii) Where the data is collected from the data subject, he should be informed, at the prescribed times, of the purpose for which the data is to be used, the classes of persons to whom the data may be transferred and of his rights to access and to request the correction of the data.
(c) Principle 3 – use of personal data
Personal data should not, without the consent of the data subject, be used for a new purpose.
(f) Principle 6 – access to personal data
A data subject shall be entitled to ascertain whether data of which he is the subject is held, request and receive access to his personal data within a reasonable time at a reasonable fee and in an intelligible form, and to request corrections to the data, and to be given reasons for any refusals in relation to the above and to object to the Privacy Commissioner for Personal Data.錯誤
(a) Principle 1 – purpose and manner of collection of personal data
(i) Personal data shall not be collected unless for a lawful purpose directly related to a function or activity of the data user, and unless the collection is necessary for or directly related to that purpose and the data is not excessive for the purpose.
(ii) Where the data is collected from the data subject, he should be informed, at the prescribed times, of the purpose for which the data is to be used, the classes of persons to whom the data may be transferred and of his rights to access and to request the correction of the data.
(c) Principle 3 – use of personal data
Personal data should not, without the consent of the data subject, be used for a new purpose.
(f) Principle 6 – access to personal data
A data subject shall be entitled to ascertain whether data of which he is the subject is held, request and receive access to his personal data within a reasonable time at a reasonable fee and in an intelligible form, and to request corrections to the data, and to be given reasons for any refusals in relation to the above and to object to the Privacy Commissioner for Personal Data.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.72
-
241/567問題
241. 問題
1 分QID503:Which of the following is NOT one of the 6 principles set in the
Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance?正確
Option C, Manner of saving personal data, is not a principle stated in the Schedule 1 of the PDPO.
錯誤
Option C, Manner of saving personal data, is not a principle stated in the Schedule 1 of the PDPO.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.72
-
242/567問題
242. 問題
1 分QID504:What of the following is not a principle of the PDPO?
正確
Option C, Functionality, is not a principle stated in the Schedule 1 of the PDPO.
錯誤
Option C, Functionality, is not a principle stated in the Schedule 1 of the PDPO.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.72
-
243/567問題
243. 問題
1 分QID2395:Which of the following statement is incorrect regarding the Privacy Ordinance?
正確
A data subject shall be entitled to ascertain whether data of which he is the subject is held, request and receive access to his personal data within a reasonable time at a reasonable
fee and in an intelligible form, and to request corrections to the data, and to be given reasons for any refusals in relation to the above and to object to the Privacy Commissioner for Personal Data.
Therefore, securities companies are obliged to provide customers with copies of their personal data, but not necessarily free of charge.錯誤
A data subject shall be entitled to ascertain whether data of which he is the subject is held, request and receive access to his personal data within a reasonable time at a reasonable
fee and in an intelligible form, and to request corrections to the data, and to be given reasons for any refusals in relation to the above and to object to the Privacy Commissioner for Personal Data.
Therefore, securities companies are obliged to provide customers with copies of their personal data, but not necessarily free of charge.提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.72
-
244/567問題
244. 問題
1 分QID1148:Which of the following is NOT a data protection principle according to the PDPO?
正確
Principle 1 – purpose and manner of collection of personal data
Principle 2 – accuracy and duration of retention of personal data
Principle 3 – use of personal data
Principle 4 – security of personal data
Principle 5 – information to be generally available
Principle 6 – access to personal data錯誤
Principle 1 – purpose and manner of collection of personal data
Principle 2 – accuracy and duration of retention of personal data
Principle 3 – use of personal data
Principle 4 – security of personal data
Principle 5 – information to be generally available
Principle 6 – access to personal data提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.72
-
245/567問題
245. 問題
1 分QID2748:The data protection principles set out in the Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance (PDPO) do not include
正確
The data protection principles set out in the PDPO include:
I. Purpose and manner of collection of personal data
II. Accuracy and duration of retention
III. Use of Personal Data
IV. Security of personal data
V. Information to be available in general
VI. Access to personal data錯誤
The data protection principles set out in the PDPO include:
I. Purpose and manner of collection of personal data
II. Accuracy and duration of retention
III. Use of Personal Data
IV. Security of personal data
V. Information to be available in general
VI. Access to personal data提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.72
-
246/567問題
246. 問題
1 分QID2838:The data protection principles set out in the Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance (PDPO) do not include
正確
The data protection principles set out in the PDPO include:
I. Purpose and manner of collection of personal data
II. Accuracy of Personal Data and Retention Period
III. Use of Personal Data
IV. Security of personal data
V. Information to be available in general
VI. Access to personal data錯誤
The data protection principles set out in the PDPO include:
I. Purpose and manner of collection of personal data
II. Accuracy of Personal Data and Retention Period
III. Use of Personal Data
IV. Security of personal data
V. Information to be available in general
VI. Access to personal data提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.72
-
247/567問題
247. 問題
1 分QID1045:A listed company is one that:
正確
A listed company is one that has any of its shares listed on a recognized stock market.
錯誤
A listed company is one that has any of its shares listed on a recognized stock market.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.8
-
248/567問題
248. 問題
1 分QID1049:The articles of association of a company is:
正確
The articles of association of a company is considered to be the single constitutional document of the company and form an agreement between the company and its members. The articles of association prescribe regulations for the internal management and operation of the company.
錯誤
The articles of association of a company is considered to be the single constitutional document of the company and form an agreement between the company and its members. The articles of association prescribe regulations for the internal management and operation of the company.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.9
-
249/567問題
249. 問題
1 分QID1047:Which of the following descriptions about the articles of association under the NCO is correct?
I. The articles of association of a company is considered to be the single constitutional document of the company and form an agreement between the company and its members.
II. The articles of association of a company is considered to be the single constitutional document of the company and form an agreement among its members.
III. The articles of association prescribe regulations for the internal management and operation of the company.
IV. The articles of association are subsidiary to the memorandum of association.正確
The articles of association of a company is considered to be the single constitutional document of the company and form an agreement between the company and its members. The articles of association prescribe regulations for the internal management and operation of the company.
錯誤
The articles of association of a company is considered to be the single constitutional document of the company and form an agreement between the company and its members. The articles of association prescribe regulations for the internal management and operation of the company.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.9
-
250/567問題
250. 問題
1 分QID1046:Which one of the following descriptions about the articles of association under the NCO is correct?
正確
The articles of association of a company is considered to be the single constitutional document of the company and form an agreement between the company and its members.
錯誤
The articles of association of a company is considered to be the single constitutional document of the company and form an agreement between the company and its members.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.3.9
-
251/567問題
251. 問題
1 分QID57:The SFC:
I. Reports to the government
II. Was established under the Securities and Futures Ordinance
III. Is not responsible for licensing of intermediaries
IV. Is a part of the government正確
The SFC was established under the SFO. It is an independent body and is not part of the government machinery or the ministerial system. However, it reports to and is accountable to the Financial Secretary, who is part of the government. Therefore, options I and II are correct. The SFC is indeed responsible for the licensing of intermediaries, so option III is incorrect.
錯誤
The SFC was established under the SFO. It is an independent body and is not part of the government machinery or the ministerial system. However, it reports to and is accountable to the Financial Secretary, who is part of the government. Therefore, options I and II are correct. The SFC is indeed responsible for the licensing of intermediaries, so option III is incorrect.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.1
-
252/567問題
252. 問題
1 分QID2738:The Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) is a/an
正確
The SFC is an independent statutory body, not a government department.
錯誤
The SFC is an independent statutory body, not a government department.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.1
-
253/567問題
253. 問題
1 分QID732:Which of the following descriptions about the SFC is correct?
正確
The SFC was created by law under the Securities and Futures Commission Ordinance (now repealed and subsumed in the SFO). It is independent, meaning that it is not part of the
Government machinery of the Civil Service or the ministerial system. Nevertheless, it reports to and is accountable to the Government.錯誤
The SFC was created by law under the Securities and Futures Commission Ordinance (now repealed and subsumed in the SFO). It is independent, meaning that it is not part of the
Government machinery of the Civil Service or the ministerial system. Nevertheless, it reports to and is accountable to the Government.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.1
-
254/567問題
254. 問題
1 分QID1151:Which of the following descriptions correctly describes the status of the SFC?
正確
The SFC is independent, meaning that it is not part of the
Government machinery of the Civil Service or the ministerial system. Nevertheless, it reports to and is accountable to the Government.錯誤
The SFC is independent, meaning that it is not part of the
Government machinery of the Civil Service or the ministerial system. Nevertheless, it reports to and is accountable to the Government.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.1
-
255/567問題
255. 問題
1 分QID1150:The SFC was created by law under the:
正確
The SFC was created by law under the Securities and Futures Commission Ordinance (now repealed and subsumed in the SFO).
錯誤
The SFC was created by law under the Securities and Futures Commission Ordinance (now repealed and subsumed in the SFO).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.1
-
256/567問題
256. 問題
1 分QID969:Does the Advisory Committee of the SFC have any executive powers?
正確
The Advisory Committee of the SFC has no executive powers, it only advise the SFC on policy matters concerning its regulatory objectives and functions.
錯誤
The Advisory Committee of the SFC has no executive powers, it only advise the SFC on policy matters concerning its regulatory objectives and functions.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.10
-
257/567問題
257. 問題
1 分QID1161:What are the statuses regarding the Advisory Committee of the SFC?
I. It has no executive powers.
II. It does not police the SFC.
III. It is chaired by the financial secretary.
IV. Its members are appointed by the chief executive of the HKSAR.正確
The Advisory Committee is responsible for advising the SFC on policy matters concerning its regulatory objectives and functions. It has no executive powers and does not police the SFC in any way. It is chaired by the SFC Chairman, and comprises the CEO and not more than two other executive directors appointed by the Chairman, and between 8 and 12 other members appointed by the Chief Executive of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (“Hong Kong SAR”) in consultation with the Chairman of the SFC.
錯誤
The Advisory Committee is responsible for advising the SFC on policy matters concerning its regulatory objectives and functions. It has no executive powers and does not police the SFC in any way. It is chaired by the SFC Chairman, and comprises the CEO and not more than two other executive directors appointed by the Chairman, and between 8 and 12 other members appointed by the Chief Executive of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (“Hong Kong SAR”) in consultation with the Chairman of the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.10
-
258/567問題
258. 問題
1 分QID1162:The Advisory Committee is responsible for which of the following matters?
正確
The Advisory Committee is responsible for advising the SFC on policy matters concerning its regulatory objectives and functions. It has no executive powers and does not police the SFC in any way.
錯誤
The Advisory Committee is responsible for advising the SFC on policy matters concerning its regulatory objectives and functions. It has no executive powers and does not police the SFC in any way.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.10
-
259/567問題
259. 問題
1 分QID1163:Which of the following regulatory committees is in charge of the “administering the Investor Compensation Fund and regulating its procedures in accordance with SFO”?
正確
Investor Compensation Fund Committee – administers the Investor Compensation Fund and regulates its procedures in accordance with Part XII of the SFO.
錯誤
Investor Compensation Fund Committee – administers the Investor Compensation Fund and regulates its procedures in accordance with Part XII of the SFO.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
260/567問題
260. 問題
1 分QID1164:Which regulatory committee’s function is described in the following statement:
“Responsible for the Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs. Much of the administration of this code is in practice exercised by the SFC staff, acting as the Takeovers Executive.”正確
Takeovers and Mergers Panel – is responsible for The Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs. Much of the administration of this code is in practice exercised by the SFC staff, acting as the Takeovers Executive.
錯誤
Takeovers and Mergers Panel – is responsible for The Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs. Much of the administration of this code is in practice exercised by the SFC staff, acting as the Takeovers Executive.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
261/567問題
261. 問題
1 分QID64:Which of the following institutions is not independent of the Securities and Futures Commission?
正確
The SFC has established various regulatory committees to which it has delegated some of its functions, e.g.: Takeovers and Mergers Panel,Takeovers Appeal Committee, Products Advisory Committee, Investor Compensation Fund Committee, Academic and Accreditation Advisory Committee, Share Registrars’ Disciplinary Committee.
However, certain tribunals and panels are independent of the SFC, such as the Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal, the Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel, and the Process Review Panel for the Securities and Futures Commission.
Therefore, option A is the correct answer.錯誤
The SFC has established various regulatory committees to which it has delegated some of its functions, e.g.: Takeovers and Mergers Panel,Takeovers Appeal Committee, Products Advisory Committee, Investor Compensation Fund Committee, Academic and Accreditation Advisory Committee, Share Registrars’ Disciplinary Committee.
However, certain tribunals and panels are independent of the SFC, such as the Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal, the Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel, and the Process Review Panel for the Securities and Futures Commission.
Therefore, option A is the correct answer.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
262/567問題
262. 問題
1 分QID803:Which of the following regulatory committees is in charge of hearing “appeals against the disciplinary rulings of the Takeovers and Mergers Panel at the request of an aggrieved party for the sole purpose of determining whether any sanction imposed by the Panel is unfair or excessive”?
正確
Takeovers Appeal Committee – hears appeals against the disciplinary rulings of the Takeovers and Mergers Panel at the request of an aggrieved party for the sole purpose of determining whether any sanction imposed by the Panel is unfair or excessive.
錯誤
Takeovers Appeal Committee – hears appeals against the disciplinary rulings of the Takeovers and Mergers Panel at the request of an aggrieved party for the sole purpose of determining whether any sanction imposed by the Panel is unfair or excessive.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
263/567問題
263. 問題
1 分QID1165:Which of the following regulatory committees is in charge of approving “industry-based courses and examinations for meeting the licensing competence requirements, and recognising providers of training for the purposes of the CPT requirements”?
正確
Academic and Accreditation Advisory Committee – approves industry-based courses and examinations for meeting the licensing competence requirements, and recognises providers of training for the purposes of the CPT requirements.
錯誤
Academic and Accreditation Advisory Committee – approves industry-based courses and examinations for meeting the licensing competence requirements, and recognises providers of training for the purposes of the CPT requirements.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
264/567問題
264. 問題
1 分QID1167:Which regulatory committee is responsible for the Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs?
正確
Takeovers and Mergers Panel – is responsible for The Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs. Much of the administration of this code is in practice exercised by the SFC staff, acting as the Takeovers Executive.
錯誤
Takeovers and Mergers Panel – is responsible for The Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs. Much of the administration of this code is in practice exercised by the SFC staff, acting as the Takeovers Executive.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
265/567問題
265. 問題
1 分QID1168:Which of the following regulatory committees is in charge of giving advice on “matters relating to the SFC Handbook for Unit Trusts and Mutual Funds, Investment-Linked Assurance Schemes and Unlisted Structured Investment Products”?
正確
Products Advisory Committee – advises on matters relating to the SFC Handbook for Unit Trusts and Mutual Funds, Investment-Linked Assurance Schemes and Unlisted Structured Investment Products, the SFC Code on MPF Products and the Code on Pooled Retirement Funds, including overall market environment, industry practices and novel product features.
錯誤
Products Advisory Committee – advises on matters relating to the SFC Handbook for Unit Trusts and Mutual Funds, Investment-Linked Assurance Schemes and Unlisted Structured Investment Products, the SFC Code on MPF Products and the Code on Pooled Retirement Funds, including overall market environment, industry practices and novel product features.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
266/567問題
266. 問題
1 分QID66:Which of the following committee, tribunal or panel is a part of the SFC?
正確
The SFC has established various regulatory committees to which it has delegated some of its functions, e.g., Takeovers and Mergers Panel, Takeovers Appeal Committee, Products Advisory Committee, Investor Compensation Fund Committee, Academic and Accreditation Advisory Committee, Share Registrars’ Disciplinary Committee.
錯誤
The SFC has established various regulatory committees to which it has delegated some of its functions, e.g., Takeovers and Mergers Panel, Takeovers Appeal Committee, Products Advisory Committee, Investor Compensation Fund Committee, Academic and Accreditation Advisory Committee, Share Registrars’ Disciplinary Committee.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
267/567問題
267. 問題
1 分QID67:Which of the following committee is not independent of the Securities and Futures Commission?
正確
Certain tribunals and panels are independent of the SFC, such as the Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal, the Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel, and the Process Review Panel for the Securities and Futures Commission. In contrast, The Academic and Accreditation Advisory Committee is a regulatory committee established by the SFC and is not independent of it.
Therefore, option D is the correct answer.錯誤
Certain tribunals and panels are independent of the SFC, such as the Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal, the Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel, and the Process Review Panel for the Securities and Futures Commission. In contrast, The Academic and Accreditation Advisory Committee is a regulatory committee established by the SFC and is not independent of it.
Therefore, option D is the correct answer.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
268/567問題
268. 問題
1 分QID1166:Which of the following regulatory committees is in charge of hearing and determining “disciplinary matters relating to share registrars in the first instance”?
正確
Share Registrars’ Disciplinary Committee – hears and determines disciplinary matters relating to share registrars in the first instance.
錯誤
Share Registrars’ Disciplinary Committee – hears and determines disciplinary matters relating to share registrars in the first instance.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
269/567問題
269. 問題
1 分QID68:Which of the following is not a Committee, tribunal and panel under the SFC?
正確
The SFC has established various regulatory committees to which it has delegated some of its functions, e.g., Takeovers and Mergers Panel, Takeovers Appeal Committee, Products Advisory Committee, Investor Compensation Fund Committee, Academic and Accreditation Advisory Committee, Share Registrars’ Disciplinary Committee. The Corporate Governance Committee doesn’t exist.
錯誤
The SFC has established various regulatory committees to which it has delegated some of its functions, e.g., Takeovers and Mergers Panel, Takeovers Appeal Committee, Products Advisory Committee, Investor Compensation Fund Committee, Academic and Accreditation Advisory Committee, Share Registrars’ Disciplinary Committee. The Corporate Governance Committee doesn’t exist.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
270/567問題
270. 問題
1 分QID65:Which of the following is not a function of the Academic and
Accreditation Advisory Committee of the SFC?正確
The functions of Academic and Accreditation Advisory Committee are: approves industry-based courses and examinations for meeting the licensing competence requirements, and recognises providers of training for the purposes of the continuous professional training requirements.However, it does not recognize all training in the securities and futures industry.
錯誤
The functions of Academic and Accreditation Advisory Committee are: approves industry-based courses and examinations for meeting the licensing competence requirements, and recognises providers of training for the purposes of the continuous professional training requirements.However, it does not recognize all training in the securities and futures industry.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
271/567問題
271. 問題
1 分QID72:Which of the SFC’s divisions is responsible for administering the Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs?
正確
The Corporate Finance Division is responsible for administering the Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs.
錯誤
The Corporate Finance Division is responsible for administering the Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
272/567問題
272. 問題
1 分QID42:Which of the following descriptions of the Product Advisory Committee are true?
I. This committee is part of the SFC
II. This committee is not part of the SFC
III. The committee is responsible for authorizing products in the SFC Handbook for Unit Trusts and Mutual Funds, Investment-Linked Assurance Schemes, and Unlisted Structured Investment Products
IV. The Committee advises on matters relating to the SFC Handbook for Unit Trusts and Mutual Funds, Investment-Linked Assurance Schemes, and Unlisted Structured Investment Products.正確
The Product Advisory Committee was established by the SFC. It mainly advises on matters relating to the SFC Handbook for Unit Trusts and Mutual Funds, Investment-Linked Assurance Schemes and Unlisted Structured Investment Products, the SFC Code on MPF Products, and the Code on Pooled Retirement Funds, including overall market environment, industry practices and novel product features.
錯誤
The Product Advisory Committee was established by the SFC. It mainly advises on matters relating to the SFC Handbook for Unit Trusts and Mutual Funds, Investment-Linked Assurance Schemes and Unlisted Structured Investment Products, the SFC Code on MPF Products, and the Code on Pooled Retirement Funds, including overall market environment, industry practices and novel product features.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
273/567問題
273. 問題
1 分QID74:Which division is responsible for supervising the listing-related activities of the SEHK?
正確
The Corporate Finance Division supervises the listing-related activities of the SEHK; However, the Supervision of Markets Division supervises and monitors activities of the exchange controller, exchanges and clearing houses.
錯誤
The Corporate Finance Division supervises the listing-related activities of the SEHK; However, the Supervision of Markets Division supervises and monitors activities of the exchange controller, exchanges and clearing houses.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.11
-
274/567問題
274. 問題
1 分QID2908:The organization responsible for reviewing the decisions made by the Investor Compensation Company Limited regarding claims made by investors against the Investor Compensation Fund is:
正確
Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal (“SFAT”) is in charge of reviewing the Investor Compensation Company Limited’s determination concerning investors’ claims against the Investor Compensation Fund.
錯誤
Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal (“SFAT”) is in charge of reviewing the Investor Compensation Company Limited’s determination concerning investors’ claims against the Investor Compensation Fund.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
275/567問題
275. 問題
1 分QID1170:SFC’s Process Review Panel is:
正確
Process Review Panel – an independent body appointed by the Chief Executive of the Hong Kong SAR to review and monitor the operational processes of the SFC. It reports to the Financial Secretary and recommends improvements to the SFC.
錯誤
Process Review Panel – an independent body appointed by the Chief Executive of the Hong Kong SAR to review and monitor the operational processes of the SFC. It reports to the Financial Secretary and recommends improvements to the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
276/567問題
276. 問題
1 分QID1171:Which of the following organizations is NOT independent of the SFC?
正確
The SFC has established various regulatory committees to which it has delegated some of its
functions, e.g. Takeovers Appeal Committee.
The following tribunals and panels are independent of the SFC:
(a) Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal (“SFAT”)
(b) Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel
(c.) Process Review Panel錯誤
The SFC has established various regulatory committees to which it has delegated some of its
functions, e.g. Takeovers Appeal Committee.
The following tribunals and panels are independent of the SFC:
(a) Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal (“SFAT”)
(b) Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel
(c.) Process Review Panel提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
277/567問題
277. 問題
1 分QID3089:Which of the following statements correctly describe the roles of the independent bodies related to the SFC?
I. The SFAT reviews the SFC’s regulatory decisions and hears related questions or issues.
II. The Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel hears disputes related to leveraged foreign exchange trading.
III. The Process Review Panel ensures the SFC’s internal procedures are fair and reasonable.
IV. The Investor Compensation Fund Committee reviews the SFC’s regulatory decisions.正確
The SFAT reviews the SFC’s regulatory decisions and hears related questions or issues, the Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel hears disputes related to leveraged foreign exchange trading, and the Process Review Panel reviews the fairness and reasonableness of the SFC’s internal procedures. The Investor Compensation Fund Committee’s role is not to review the SFC’s regulatory decisions.
錯誤
The SFAT reviews the SFC’s regulatory decisions and hears related questions or issues, the Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel hears disputes related to leveraged foreign exchange trading, and the Process Review Panel reviews the fairness and reasonableness of the SFC’s internal procedures. The Investor Compensation Fund Committee’s role is not to review the SFC’s regulatory decisions.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
278/567問題
278. 問題
1 分QID3088:If a client has a dispute with a corporation licensed by the SFC for carrying out leveraged foreign exchange trading, which body is responsible for arbitration?
正確
The Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel is established under rules made by the SFC for the purpose of hearing disputes between corporations licensed by the SFC for carrying out leveraged foreign exchange trading and their clients.
錯誤
The Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel is established under rules made by the SFC for the purpose of hearing disputes between corporations licensed by the SFC for carrying out leveraged foreign exchange trading and their clients.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
279/567問題
279. 問題
1 分QID2760:Which of the following committees is independent of the SFC?
正確
The Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel is independent of the SFC.
錯誤
The Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel is independent of the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
280/567問題
280. 問題
1 分QID1169:Mr. Wan would like to be licensed as a stock broker but was rejected by the SFC. Where can he file an appeal?
正確
Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal (“SFAT”) –established by the SFO as an independent statutory body. Chaired by a High Court judge, the SFAT comprises current and former judges appointed by the Chief Executive of the HKSAR and two other members drawn from a panel appointed by the Financial Secretary under delegated authority. The function of the SFAT is to hear appeals against the decisions made by the
SFC relating to the licensing or registration of intermediaries and certain other matters.錯誤
Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal (“SFAT”) –established by the SFO as an independent statutory body. Chaired by a High Court judge, the SFAT comprises current and former judges appointed by the Chief Executive of the HKSAR and two other members drawn from a panel appointed by the Financial Secretary under delegated authority. The function of the SFAT is to hear appeals against the decisions made by the
SFC relating to the licensing or registration of intermediaries and certain other matters.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
281/567問題
281. 問題
1 分QID3086:Which of the following bodies are independent of the SFC?
I. Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal
II. Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel
III. Process Review Panel for the Securities and Futures Commission
IV. Investor Compensation Fund Committee正確
The Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal, Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel, and the Process Review Panel for the Securities and Futures Commission are independent of the SFC. The Investor Compensation Fund Committee, however, is a regulatory committee of the SFC that administers the Investor Compensation Fund and regulates its procedures. Hence, it is not independent of the SFC.
錯誤
The Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal, Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel, and the Process Review Panel for the Securities and Futures Commission are independent of the SFC. The Investor Compensation Fund Committee, however, is a regulatory committee of the SFC that administers the Investor Compensation Fund and regulates its procedures. Hence, it is not independent of the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
282/567問題
282. 問題
1 分QID1172:An independent statutory body with full-time members headed by a judge appointed by the Chief Executive of the Hong Kong SAR to hear appeals against the decisions made by the SFC relating to the licensing or registration of intermediaries and certain other matters” describes which of the following regulatory organizations?
正確
Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal (“SFAT”) – established by the SFO as an independent statutory body. Chaired by a High Court judge, the SFAT comprises current and former judges appointed by the Chief Executive of the HKSAR and two other members drawn from a panel appointed by the Financial Secretary under delegated authority. The function of the SFAT is to hear appeals against the decisions made by the SFC relating to the licensing or registration of intermediaries and certain other matters.
錯誤
Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal (“SFAT”) – established by the SFO as an independent statutory body. Chaired by a High Court judge, the SFAT comprises current and former judges appointed by the Chief Executive of the HKSAR and two other members drawn from a panel appointed by the Financial Secretary under delegated authority. The function of the SFAT is to hear appeals against the decisions made by the SFC relating to the licensing or registration of intermediaries and certain other matters.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
283/567問題
283. 問題
1 分QID71:In the regulatory framework of Hong Kong, is the power of SFC undisputed?
正確
The SFC Process Review Panel is an independent body appointed by the Chief Executive of the HKSAR to review and monitor the operational processes of the SFC. It reports to the Financial Secretary and recommends improvements to the SFC. In other words, this is an institution that specializes in supervising and balancing the SFC. So the answer is C.
錯誤
The SFC Process Review Panel is an independent body appointed by the Chief Executive of the HKSAR to review and monitor the operational processes of the SFC. It reports to the Financial Secretary and recommends improvements to the SFC. In other words, this is an institution that specializes in supervising and balancing the SFC. So the answer is C.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
284/567問題
284. 問題
1 分QID3083:What is the primary function of the Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal (SFAT)?
正確
The SFAT is established as a review body independent of the SFC, with its primary function being to review the SFC’s regulatory decisions made under the SFO, not to enforce them, regulate markets, or handle criminal prosecutions.
錯誤
The SFAT is established as a review body independent of the SFC, with its primary function being to review the SFC’s regulatory decisions made under the SFO, not to enforce them, regulate markets, or handle criminal prosecutions.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
285/567問題
285. 問題
1 分QID70:Which of the following description about the Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal(SFAT) is correct?
正確
The answer is B.
The functions of the Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal (SFAT) include: (i) reviewing the SFC’s regulatory decisions made under the SFO; (ii) hearing and determining any question or issue arising out of or concerning its reviews; and (iii) reviewing the Investor CompensationCompany Limited’s determination concerning investors’ claims against the Investor Compensation Fund. The SFC is responsible for the licensing of intermediaries; therefore, the review and hearing of relevant decisions fall under the jurisdiction of the SFAT.錯誤
The answer is B.
The functions of the Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal (SFAT) include: (i) reviewing the SFC’s regulatory decisions made under the SFO; (ii) hearing and determining any question or issue arising out of or concerning its reviews; and (iii) reviewing the Investor CompensationCompany Limited’s determination concerning investors’ claims against the Investor Compensation Fund. The SFC is responsible for the licensing of intermediaries; therefore, the review and hearing of relevant decisions fall under the jurisdiction of the SFAT.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
286/567問題
286. 問題
1 分QID3084:Which of the following are functions of the Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal (SFAT)?
I. Reviewing the SFC’s regulatory decisions made under the SFO.
II. Hearing and determining questions or issues arising out of its reviews.
III. Enforcing compliance with the SFO.
IV. Reviewing the Investor Compensation Company Limited’s determination concerning claims against the Investor Compensation Fund.正確
The SFAT’s functions include reviewing the SFC’s regulatory decisions, hearing and determining questions or issues related to its reviews, and reviewing the Investor Compensation Company Limited’s determinations concerning claims against the Investor Compensation Fund. It does not enforce compliance with the SFO.
錯誤
The SFAT’s functions include reviewing the SFC’s regulatory decisions, hearing and determining questions or issues related to its reviews, and reviewing the Investor Compensation Company Limited’s determinations concerning claims against the Investor Compensation Fund. It does not enforce compliance with the SFO.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
287/567問題
287. 問題
1 分QID3085:Which panel is appointed by the Chief Executive of the HKSAR to review the internal operational procedures of the SFC?
正確
The Process Review Panel for the Securities and Futures Commission is the independent body appointed by the Chief Executive of the HKSAR to review the fairness and reasonableness of the SFC’s internal operational procedures.
錯誤
The Process Review Panel for the Securities and Futures Commission is the independent body appointed by the Chief Executive of the HKSAR to review the fairness and reasonableness of the SFC’s internal operational procedures.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
288/567問題
288. 問題
1 分QID69:Which of the following tribunals and panels are independent of the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC)?
I. Takeovers and Mergers Panel
II. Takeover Appeals Committee
III. Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal
IV. Market Misconduct Tribunal正確
Certain tribunals and panels are independent of the SFC, such as the Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal, the Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel, and the Process Review Panel for the Securities and Futures Commission.
Therefore, option B is the correct answer.錯誤
Certain tribunals and panels are independent of the SFC, such as the Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal, the Leveraged Foreign Exchange Trading Arbitration Panel, and the Process Review Panel for the Securities and Futures Commission.
Therefore, option B is the correct answer.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
289/567問題
289. 問題
1 分QID3087:Which of the following are true regarding the functions of the SFAT?
I. It reviews regulatory decisions made under the SFO.
II. It hears disputes between corporations and their clients regarding leveraged foreign exchange trading.
III. It reviews determinations concerning claims against the Investor Compensation Fund.
IV. It ensures the SFC’s procedures are consistently adhered to.正確
The SFAT reviews the SFC’s regulatory decisions made under the SFO and reviews the Investor Compensation Company Limited’s determinations concerning claims against the Investor Compensation Fund. It does not hear disputes related to leveraged foreign exchange trading, nor does it ensure the SFC’s procedures are consistently adhered to; those are functions of other panels and the Process Review Panel, respectively.
錯誤
The SFAT reviews the SFC’s regulatory decisions made under the SFO and reviews the Investor Compensation Company Limited’s determinations concerning claims against the Investor Compensation Fund. It does not hear disputes related to leveraged foreign exchange trading, nor does it ensure the SFC’s procedures are consistently adhered to; those are functions of other panels and the Process Review Panel, respectively.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.12
-
290/567問題
290. 問題
1 分QID73:Which of the following are functions of the Corporate Finance Division of the SFC?
I. Administer the Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs and regulates takeovers, mergers and share buy- backs of applicable companies
II. Provide advice on corporate restructuring to listed company in
Hong Kong
III. Supervise the listing-related activities of The Stock Exchange
of Hong Kong Limited (“SEHK”)
IV. Provide advice on takeover activities to minority shareholders正確
The functions of Corporate Finance Division include:
vetting listing applications together with The SEHK;
monitoring listed companies’ announcements to identify misconduct or irregularities;
administering the Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs;
supervising the listing-related activities of the SEHK;
reviewing and recommends changes to the Listing Rules;
reviewing and authorises prospectuses and marketing materials for unlisted shares or debentures; and
interveneing at an early stage in serious cases of suspected misconduct in listing applications and corporate transactions by the powers under the Securities and Futures (Stock Market Listing) Rules.
The Corporate Finance Division does not provide any advice on the operations of an individual companie.錯誤
The functions of Corporate Finance Division include:
vetting listing applications together with The SEHK;
monitoring listed companies’ announcements to identify misconduct or irregularities;
administering the Codes on Takeovers and Mergers and Share Buy-backs;
supervising the listing-related activities of the SEHK;
reviewing and recommends changes to the Listing Rules;
reviewing and authorises prospectuses and marketing materials for unlisted shares or debentures; and
interveneing at an early stage in serious cases of suspected misconduct in listing applications and corporate transactions by the powers under the Securities and Futures (Stock Market Listing) Rules.
The Corporate Finance Division does not provide any advice on the operations of an individual companie.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.13
-
291/567問題
291. 問題
1 分QID1173:What are the major duties of the Corporate Finance Division?
I. regulates takeovers and mergers of public companies and share repurchases.
II. administers securities and company legislation applicable to listed and unlisted companies.
III. supervises the listing-related activities of the SEHK.
IV. reviews and recommends changes to the listing rules.正確
Corporate Finance Division:
(a) vets listing applications together with the SEHK;
(b) monitors listed companies’ announcements to identify misconduct or irregularities;
(c) administers the Codes;
(d) supervises the listing-related activities of the SEHK;
(e) reviews and recommends changes to the Rules Governing the Listing of Securities on The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited (“Listing Rules”);
(f) reviews and authorises prospectuses and marketing materials for unlisted shares or debentures; and
(g) intervenes at an early stage in serious cases of suspected misconduct in listing applications and corporate transactions by the powers under the Securities and Futures (Stock Market Listing) Rules.錯誤
Corporate Finance Division:
(a) vets listing applications together with the SEHK;
(b) monitors listed companies’ announcements to identify misconduct or irregularities;
(c) administers the Codes;
(d) supervises the listing-related activities of the SEHK;
(e) reviews and recommends changes to the Rules Governing the Listing of Securities on The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited (“Listing Rules”);
(f) reviews and authorises prospectuses and marketing materials for unlisted shares or debentures; and
(g) intervenes at an early stage in serious cases of suspected misconduct in listing applications and corporate transactions by the powers under the Securities and Futures (Stock Market Listing) Rules.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.13
-
292/567問題
292. 問題
1 分QID2834:Which department of the SFC is responsible for monitoring listed companies’ announcements and identifying misconduct or non-compliance?
正確
The SFC’s Corporate Finance Division monitors listed companies’ announcements and identifies misconduct or non-compliance by listed companies.
錯誤
The SFC’s Corporate Finance Division monitors listed companies’ announcements and identifies misconduct or non-compliance by listed companies.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.13
-
293/567問題
293. 問題
1 分QID1174:Which of the following is NOT a duty of the Enforcement Division?
正確
Enforcement Division:
(a) monitors the trading of Hong Kong’s stock and derivative markets and inquires into irregularities;
(b) has the power to discipline dishonest regulated intermediaries who are in breach of SFC’s rules;
(c) inspects the books and records of listed companies if impropriety is suspected, which may involve directors, officers or substantial shareholders etc.; and
(d) cooperates with domestic and overseas law enforcement agencies and regulatory bodies in investigations if required.錯誤
Enforcement Division:
(a) monitors the trading of Hong Kong’s stock and derivative markets and inquires into irregularities;
(b) has the power to discipline dishonest regulated intermediaries who are in breach of SFC’s rules;
(c) inspects the books and records of listed companies if impropriety is suspected, which may involve directors, officers or substantial shareholders etc.; and
(d) cooperates with domestic and overseas law enforcement agencies and regulatory bodies in investigations if required.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.14
-
294/567問題
294. 問題
1 分QID3078:A licensed representative at a securities firm in Hong Kong has been found to have provided investment advice without proper authorization. Under the Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO), which division of the SFC is most likely to investigate this matter?
正確
The Enforcement Division of the SFC is responsible for investigating matters related to breaches of the SFO, such as providing investment advice without proper authorization, making option B the correct answer.
錯誤
The Enforcement Division of the SFC is responsible for investigating matters related to breaches of the SFO, such as providing investment advice without proper authorization, making option B the correct answer.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.14
-
295/567問題
295. 問題
1 分QID2846:Which department of the SFC is responsible for monitoring transactions in the stock market?
正確
The Enforcement Division is responsible for monitoring stock market transactions. The Supervision of Markets Division mainly monitors and regulates the exchange itself, not the transactions that take place in the market.
錯誤
The Enforcement Division is responsible for monitoring stock market transactions. The Supervision of Markets Division mainly monitors and regulates the exchange itself, not the transactions that take place in the market.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.14
-
296/567問題
296. 問題
1 分QID1504:Which department/division deals with the authorization of CISs including the granting of waivers from the CUTMF?
正確
Investment Products Division:
(a) develops and implements codes and guidelines for the authorisation and registration of investment products so as to facilitate market growth and product innovation whilst ensuring appropriate investor protection;
(b) regulates and authorises investment products that are offered to the public and subject to the SFO;
(c) registers and regulates open-ended fund companies (“OFCs”);
(d) monitors disclosures and ongoing compliance of authorised investment products and registered OFCs; and
€ formulates policies concerning the regulation of asset management.錯誤
Investment Products Division:
(a) develops and implements codes and guidelines for the authorisation and registration of investment products so as to facilitate market growth and product innovation whilst ensuring appropriate investor protection;
(b) regulates and authorises investment products that are offered to the public and subject to the SFO;
(c) registers and regulates open-ended fund companies (“OFCs”);
(d) monitors disclosures and ongoing compliance of authorised investment products and registered OFCs; and
€ formulates policies concerning the regulation of asset management.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.15
-
297/567問題
297. 問題
1 分QID75:Which department/division of the SFC deals with the authorization of CISs?
正確
The functions of the Investment Products Division of the SFC include:
developing and implementing codes and guidelines for the authorisation and registration of investment products to facilitate market growth and product innovation whilst ensuring appropriate investor protection;
regulating and authorising investment products that are offered to the public and subject to the SFO;
registering and regulating open-ended fund companies (“OFCs”);
monitoring disclosures and ongoing compliance with authorised investment products and registered OFCs; and
formulating policies concerning the regulation of asset management.錯誤
The functions of the Investment Products Division of the SFC include:
developing and implementing codes and guidelines for the authorisation and registration of investment products to facilitate market growth and product innovation whilst ensuring appropriate investor protection;
regulating and authorising investment products that are offered to the public and subject to the SFO;
registering and regulating open-ended fund companies (“OFCs”);
monitoring disclosures and ongoing compliance with authorised investment products and registered OFCs; and
formulating policies concerning the regulation of asset management.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.15
-
298/567問題
298. 問題
1 分QID76:Which of the following division of the SFC is responsible for the authorisation of CISs?
正確
The Investment Products Division regulates and authorises investment products offered to the public and subject to the SFO and is responsible for authorizing CISs to be marketed to the public.
錯誤
The Investment Products Division regulates and authorises investment products offered to the public and subject to the SFO and is responsible for authorizing CISs to be marketed to the public.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.15
-
299/567問題
299. 問題
1 分QID1175:Which of the following departments of the SFC regulates exchanges and clearing houses?
正確
Supervision of Markets Division:
(a) supervises and monitors activities of the exchange controller, exchanges and clearing
houses;錯誤
Supervision of Markets Division:
(a) supervises and monitors activities of the exchange controller, exchanges and clearing
houses;提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.16
-
300/567問題
300. 問題
1 分QID78:Which department/division of the SFC licenses asset management corporation and their staff and approves responsible officers?
正確
Licensing Department licenses corporations and individuals seeking to conduct business in Hong Kong in the regulated activities for which a licence is required under the SFO.
錯誤
Licensing Department licenses corporations and individuals seeking to conduct business in Hong Kong in the regulated activities for which a licence is required under the SFO.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.18
-
301/567問題
301. 問題
1 分QID1176:Which of the following are duties of the SFC’s Licensing Department:
I. Licenses corporations and individuals seeking to conduct business in Hong Kong in the regulated activities for which a licence is required under the SFO.
II. Issues codes and guidelines concerning the competence and suitability of corporations and individuals to remain licensed.
III. Deals with issues relating to the continuing suitability of licensed corporations and individuals to be licensed.
IV. Monitors licensees by means of annual returns.正確
Licensing Department:
(a) licenses corporations and individuals seeking to conduct RAs as defined under the SFO;
(b) issues codes and guidelines concerning the competence and suitability of corporations and individuals to remain licensed;
(c) monitors the on-going compliance of licensing requirements by licensees, substantial shareholders of listed corporations and directors of licensed corporations and substantial shareholders錯誤
Licensing Department:
(a) licenses corporations and individuals seeking to conduct RAs as defined under the SFO;
(b) issues codes and guidelines concerning the competence and suitability of corporations and individuals to remain licensed;
(c) monitors the on-going compliance of licensing requirements by licensees, substantial shareholders of listed corporations and directors of licensed corporations and substantial shareholders提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.18
-
302/567問題
302. 問題
1 分QID77:The SFC assigns the responsibility of setting up the competence tests for licensed persons and potential licensed persons according to the Fit and proper guidelines to which of the following organizations?
正確
The functions of the Licensing Department include licensing corporations and individuals seeking to conduct regulated activities, issuing codes and guidelines concerning the competence and suitability to remain licensed, monitoring the ongoing compliance of licensing requirements, maintaining a public register of licensed persons and registered institutions, and initiating policies on licensing issues. Therefore, the setting up of the competency test is the responsibility of the Licensing Department of the SFC.
錯誤
The functions of the Licensing Department include licensing corporations and individuals seeking to conduct regulated activities, issuing codes and guidelines concerning the competence and suitability to remain licensed, monitoring the ongoing compliance of licensing requirements, maintaining a public register of licensed persons and registered institutions, and initiating policies on licensing issues. Therefore, the setting up of the competency test is the responsibility of the Licensing Department of the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.18
-
303/567問題
303. 問題
1 分QID79:Which department/division of the SFC supervises the business conduct of licensed corporations and individual licensees on an ongoing basis?
正確
Intermediaries Supervision Department:
(a) supervises the business conduct of licensed corporations and individual licensees on an ongoing basis by conducting on-site reviews and off-site monitoring;
(b) monitors the financial integrity of licensed corporations;
(c) maintains communication with intermediaries and the industry on relevant policy and regulatory issues, and
(d) processes applications for approval, waiver, or modification of various requirements relating to intermediaries.錯誤
Intermediaries Supervision Department:
(a) supervises the business conduct of licensed corporations and individual licensees on an ongoing basis by conducting on-site reviews and off-site monitoring;
(b) monitors the financial integrity of licensed corporations;
(c) maintains communication with intermediaries and the industry on relevant policy and regulatory issues, and
(d) processes applications for approval, waiver, or modification of various requirements relating to intermediaries.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.19
-
304/567問題
304. 問題
1 分QID1177:SFC’s Intermediaries Supervision Department is responsible for:
正確
Intermediaries Supervision Department:
(a) supervises the business conduct of licensed corporations and individual licensees on an ongoing basis, by conducting on-site inspection and off-site monitoring.錯誤
Intermediaries Supervision Department:
(a) supervises the business conduct of licensed corporations and individual licensees on an ongoing basis, by conducting on-site inspection and off-site monitoring.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.19
-
305/567問題
305. 問題
1 分QID1154:Which of the following is NOT a regulatory objective of the SFC?
正確
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency and orderliness of the market;
(b) promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning;
© provide protection to the investing public;
(d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
€ reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
(f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps in relation to the industry.錯誤
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency and orderliness of the market;
(b) promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning;
© provide protection to the investing public;
(d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
€ reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
(f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps in relation to the industry.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
306/567問題
306. 問題
1 分QID908:Which of the following is one of the objectives of the SFO
正確
SFO treats all investors fairly and equally. Regulators should be transparent to promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning.
錯誤
SFO treats all investors fairly and equally. Regulators should be transparent to promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
307/567問題
307. 問題
1 分QID171:The objectives of the SFO are to provide a regulatory framework with which of the following characteristics?
I. Promotes a fair, orderly and transparent market.
II. Is flexible enough to cope with new products and other innovations, and further advances in technological infrastructure.
III. Is administered by a regulator with sufficient powers and discretion whose operations are transparent and who is accountable to the stakeholders through a system of adequate checks and balance.
IV. Is a system that can satisfy PRC mainland legal standards, being compatible with PRC mainland laws and practices and meet local needs.正確
The objectives of the SFO are to provide a regulatory framework which:
(a) promotes a fair, orderly and transparent market;
(b) is flexible enough to cope with new products and other innovations, and further advances in technological infrastructure;
(c) is administered by a regulator with sufficient powers and discretion whose operations are transparent and who is accountable to the stakeholders through a system of adequate
checks and balances.錯誤
The objectives of the SFO are to provide a regulatory framework which:
(a) promotes a fair, orderly and transparent market;
(b) is flexible enough to cope with new products and other innovations, and further advances in technological infrastructure;
(c) is administered by a regulator with sufficient powers and discretion whose operations are transparent and who is accountable to the stakeholders through a system of adequate
checks and balances.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
308/567問題
308. 問題
1 分QID742:Which of the following is one of the objectives of creating the SFO?
正確
The objectives of the SFO are to provide a regulatory framework which:
(a) promotes a fair, orderly and transparent market;
(b) is flexible enough to cope with new products and other innovations, and further advances in technological infrastructure;
(c) is administered by a regulator with sufficient powers and discretion whose operations are transparent and who is accountable to the stakeholders through a system of adequate
checks and balances; and
(d) is on a par with international standards and compatible with international practices, but tailored to meet local needs and circumstances.錯誤
The objectives of the SFO are to provide a regulatory framework which:
(a) promotes a fair, orderly and transparent market;
(b) is flexible enough to cope with new products and other innovations, and further advances in technological infrastructure;
(c) is administered by a regulator with sufficient powers and discretion whose operations are transparent and who is accountable to the stakeholders through a system of adequate
checks and balances; and
(d) is on a par with international standards and compatible with international practices, but tailored to meet local needs and circumstances.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
309/567問題
309. 問題
1 分QID61:Which of the following is a regulatory objective of the SFC?
正確
The regulatory objectives of the SFC are to:
a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency, and orderliness of the market;
b) promote public understanding of the industry;
c) provide protection to the investing public;
d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
e) reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong.
So B is correct.錯誤
The regulatory objectives of the SFC are to:
a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency, and orderliness of the market;
b) promote public understanding of the industry;
c) provide protection to the investing public;
d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
e) reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong.
So B is correct.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
310/567問題
310. 問題
1 分QID58:Which of the following is a regulatory objective of the SFC?
I. Provide protection to the investing public
II. Reduce non-systematic risk in the industry
III. Assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps in relation to the industry.
IV. Assist the HKMA in maintaining the stability of currency in
Hong Kong正確
The regulatory objectives of the SFC are to:
a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency and orderliness of the market;
b) promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning;
c) provide protection to the investing public;
d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
e) reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps in relation to the industry.
So I, III are correct.錯誤
The regulatory objectives of the SFC are to:
a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency and orderliness of the market;
b) promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning;
c) provide protection to the investing public;
d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
e) reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps in relation to the industry.
So I, III are correct.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
311/567問題
311. 問題
1 分QID59:Under the SFO, which of the following are regulatory objectives of the SFC?
I. Promote the public’s understanding of the operation and functioning of the industry
II. Ensure that regulatory standards are identical to international standards
III. Review and authorise new financial products and establishment ordinances
IV. Minimise crime and misconduct in the market正確
The regulatory objectives of the SFC are to:
a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency, and orderliness of the market;
b) promote public understanding of the industry, including its operation and functioning;
c) provide protection to the investing public;
d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
e) reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps concerning the industry.
So I, IV are correct.錯誤
The regulatory objectives of the SFC are to:
a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency, and orderliness of the market;
b) promote public understanding of the industry, including its operation and functioning;
c) provide protection to the investing public;
d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
e) reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps concerning the industry.
So I, IV are correct.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
312/567問題
312. 問題
1 分QID779:Which of the following is NOT a regulatory objective of the SFC?
正確
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency and orderliness of the market;
(b) promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning;
© provide protection to the investing public;
(d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
€ reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
(f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps in relation to the industry.
Providing protection for major shareholders is not one of these objectives.錯誤
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency and orderliness of the market;
(b) promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning;
© provide protection to the investing public;
(d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
€ reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
(f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps in relation to the industry.
Providing protection for major shareholders is not one of these objectives.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
313/567問題
313. 問題
1 分QID1153:The regulatory objectives of the SFC does NOT include:
正確
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency and orderliness of the market;
(b) promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning;
(c) provide protection to the investing public;
(d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
(e) reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
(f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps in relation to the industry.錯誤
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency and orderliness of the market;
(b) promote public’s understanding of the industry including its operation and functioning;
(c) provide protection to the investing public;
(d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
(e) reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
(f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps in relation to the industry.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
314/567問題
314. 問題
1 分QID1152:Which of the followings are the regulatory objectives of the SFC?
I. To promote understanding by the public of the operation and functioning of the securities and futures industry.
II. To provide protection to the investing public.
III. To minimise crime and misconduct in the industry.
IV. To reduce market systemic risks in the industry.正確
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(b) promote understanding by the public of financial services including the operation and functioning of the industry;
(c.) provide protection to the investing public;
(d) minimize crime and misconduct in the industry.錯誤
The objectives of the SFC in relation to the securities and futures industry, as stated in s. 4, SFO, are to:
(b) promote understanding by the public of financial services including the operation and functioning of the industry;
(c.) provide protection to the investing public;
(d) minimize crime and misconduct in the industry.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
315/567問題
315. 問題
1 分QID60:The regulatory objectives of the SFC include:
I. Consumer rights protection
II. Minimise crime and misconduct in the securities and futures industry
III. Promote public understanding of the securities and futures industry
IV. Provide advice on the enforcement of economic policies to the government正確
The regulatory objectives of the SFC are to:
a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency, and orderliness of the market;
b) promote public understanding of the industry, including its operation and functioning;
c) provide protection to the investing public;
d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
e) reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps concerning the industry.
So II, III are correct.錯誤
The regulatory objectives of the SFC are to:
a) maintain and promote the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency, and orderliness of the market;
b) promote public understanding of the industry, including its operation and functioning;
c) provide protection to the investing public;
d) minimise crime and misconduct in the market;
e) reduce systemic risks in the industry; and
f) assist the Financial Secretary in maintaining the financial stability of Hong Kong by taking appropriate steps concerning the industry.
So II, III are correct.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.2
-
316/567問題
316. 問題
1 分QID2721:The main functions of the SFC include:
I. Empowering self-regulatory bodies and professional bodies to form committees
II. Regulating and monitoring intermediaries who engage in regulated activities
III. Supervising and monitoring exchanges, clearing houses and exchange controllers
IV. Promoting investor education and encouraging investors to understand investment products and make informed decisions
正確
Authorizing self-regulatory bodies and professional bodies to set up committees is not the main function of the SFC.
錯誤
Authorizing self-regulatory bodies and professional bodies to set up committees is not the main function of the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.3
-
317/567問題
317. 問題
1 分QID3082:Which of the following are roles of the SFC as per the regulatory framework?
I. Regulating market intermediaries
II. Providing exchange and clearing functions
III. Dealing with investor compensation matters
IV. Supervising licensed corporations and registered institutions正確
The SFC’s roles include regulating market intermediaries and supervising licensed corporations and registered institutions. Providing exchange and clearing functions and dealing with investor compensation matters are roles of other entities such as HKEX and the ICC, respectively.
錯誤
The SFC’s roles include regulating market intermediaries and supervising licensed corporations and registered institutions. Providing exchange and clearing functions and dealing with investor compensation matters are roles of other entities such as HKEX and the ICC, respectively.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.3
-
318/567問題
318. 問題
1 分QID3075:Which of the following statements correctly describes the role of the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) in Hong Kong?
正確
The SFC’s responsibilities include the supervision of licensed corporations and registered institutions, which is part of its role as the principal regulator of the securities industry in Hong Kong. The SFC does not operate trading platforms nor is it the primary operator of the HKFE, and its function is not to facilitate financial transactions for clients.
錯誤
The SFC’s responsibilities include the supervision of licensed corporations and registered institutions, which is part of its role as the principal regulator of the securities industry in Hong Kong. The SFC does not operate trading platforms nor is it the primary operator of the HKFE, and its function is not to facilitate financial transactions for clients.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.3
-
319/567問題
319. 問題
1 分QID2816:Which of the following is not a function of the SFC?
正確
Enforcement of the Listing Rules is the job of the SEHK.
錯誤
Enforcement of the Listing Rules is the job of the SEHK.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.3
-
320/567問題
320. 問題
1 分QID2761:Which of the following statements about the SFC is correct?
正確
The SFC supervise, monitor and regulate the activities of:
(i) recognised exchange, clearing houses, exchange controllers and investor compensation companies or persons carrying on regulated activities; and
(ii) registered institutions that are regulated or to be regulated by the SFC under any relevant provisions.
So, the SFC is responsible for the regulation of all securities and futures activities, including the regulated activities carried out by banks. It is also responsible for regulating the exchange controller.錯誤
The SFC supervise, monitor and regulate the activities of:
(i) recognised exchange, clearing houses, exchange controllers and investor compensation companies or persons carrying on regulated activities; and
(ii) registered institutions that are regulated or to be regulated by the SFC under any relevant provisions.
So, the SFC is responsible for the regulation of all securities and futures activities, including the regulated activities carried out by banks. It is also responsible for regulating the exchange controller.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.3
-
321/567問題
321. 問題
1 分QID1155:Which of the following are the main functions of the SFC?
I. Responsible for front-line supervision.
II. Responsible for regulating the discipline of the exchanges.
III. Oversees other securities intermediaries.
IV. Monitor a variety of approved products.正確
The functions and powers of the SFC are wide and are set out in s. 5, SFO. The principal functions are to:
(b) supervise, monitor and regulate the activities of:
(i) recognized exchange, recognized clearing houses, recognized exchange controllers and recognized investor compensation companies or persons carrying on RAs; and
(ii) registered institutions that are regulated or to be regulated by the SFC under any relevant provisions.錯誤
The functions and powers of the SFC are wide and are set out in s. 5, SFO. The principal functions are to:
(b) supervise, monitor and regulate the activities of:
(i) recognized exchange, recognized clearing houses, recognized exchange controllers and recognized investor compensation companies or persons carrying on RAs; and
(ii) registered institutions that are regulated or to be regulated by the SFC under any relevant provisions.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.3
-
322/567問題
322. 問題
1 分QID1157:Which of the following are powers that the SFC may delegate to others?
I. Promote, encourage and enforce the proper conduct, competence and integrity of persons carrying on regulated activities.
II. Maintain and promote confidence in the securities and futures industry.
III. Cooperate with and provide assistance to other regulators.
IV. Suppress illegal, dishonourable and improper practices in the securities and futures industry.正確
The functions and powers of the SFC are wide and are set out in s. 5, SFO. The principal functions are to:
(c) promote, encourage and enforce the proper conduct, competence and integrity of persons carrying on RAs;
(d) maintain and promote confidence in the securities and futures industry;
(e.) cooperate with and provide assistance to other regulators;
(h) suppress illegal, dishonourable and improper practices in the securities and futures industry.錯誤
The functions and powers of the SFC are wide and are set out in s. 5, SFO. The principal functions are to:
(c) promote, encourage and enforce the proper conduct, competence and integrity of persons carrying on RAs;
(d) maintain and promote confidence in the securities and futures industry;
(e.) cooperate with and provide assistance to other regulators;
(h) suppress illegal, dishonourable and improper practices in the securities and futures industry.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.3
-
323/567問題
323. 問題
1 分QID63:Which of the following are functions and duties of the SFC?
I. Supervise the securities and futures markets in Hong Kong
II. Regulate the securities and futures industries
III. Provide professional assistance to the government
IV. Supervise all settlement banks in Hong Kong正確
The principal functions of the SFC are to:
(a) Ensure fairness, efficiency, and transparency in the market.
(b) Oversee recognised exchange, clearing houses, exchange controllers and investor compensation companies or persons carrying on regulated activities, and registered institutions.
(C) Promote, encourage and enforce the proper conduct, competence and integrity of persons carrying on regulated activities;
(d) Maintain and promote confidence in the industry;
(e) Collaborate with other regulators;
(f) Secure appropriate degree of protection for the investing public;
(g) Promote, encourage and enforce internal control and risk management systems by persons carrying on regulated activities; and
(h) Suppress illegal, dishonourable and improper practices in the industry.
Therefore, I and II are correct.錯誤
The principal functions of the SFC are to:
(a) Ensure fairness, efficiency, and transparency in the market.
(b) Oversee recognised exchange, clearing houses, exchange controllers and investor compensation companies or persons carrying on regulated activities, and registered institutions.
(C) Promote, encourage and enforce the proper conduct, competence and integrity of persons carrying on regulated activities;
(d) Maintain and promote confidence in the industry;
(e) Collaborate with other regulators;
(f) Secure appropriate degree of protection for the investing public;
(g) Promote, encourage and enforce internal control and risk management systems by persons carrying on regulated activities; and
(h) Suppress illegal, dishonourable and improper practices in the industry.
Therefore, I and II are correct.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.3
-
324/567問題
324. 問題
1 分QID62:The principal functions of the SFC include:
I. Supervise all activities conducted by Registered Institutions.
II. Ensure that persons engaged in regulated activities maintain proper conduct, competence, and quality.
III. Promote, encourage, and ensure that those engaged in regulated activities have appropriate internal control and risk management systems.
IV. Maintain market liquidity in the securities and futures markets.正確
The principal functions of the SFC are to:
(a) Ensure fairness, efficiency, and transparency in the market.
(b) Oversee recognised exchange, clearing houses, exchange controllers and investor compensation companies or persons carrying on regulated activities, and registered institutions.
(C) Promote, encourage and enforce the proper conduct, competence and integrity of persons carrying on regulated activities;
(d) Maintain and promote confidence in the industry;
(e) Collaborate with other regulators;
(f) Secure appropriate degree of protection for the investing public;
(g) Promote, encourage and enforce internal control and risk management systems by persons carrying on regulated activities; and
(h) Suppress illegal, dishonourable and improper practices in the industry.
Therefore, II and III are correct.錯誤
The principal functions of the SFC are to:
(a) Ensure fairness, efficiency, and transparency in the market.
(b) Oversee recognised exchange, clearing houses, exchange controllers and investor compensation companies or persons carrying on regulated activities, and registered institutions.
(C) Promote, encourage and enforce the proper conduct, competence and integrity of persons carrying on regulated activities;
(d) Maintain and promote confidence in the industry;
(e) Collaborate with other regulators;
(f) Secure appropriate degree of protection for the investing public;
(g) Promote, encourage and enforce internal control and risk management systems by persons carrying on regulated activities; and
(h) Suppress illegal, dishonourable and improper practices in the industry.
Therefore, II and III are correct.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.3
-
325/567問題
325. 問題
1 分QID1156:The SFC supervises which of the following institutions?
I. Registered Institutions.
II. Licensed corporation.
III. Recognized exchanges.
IV. Recognized clearing houses.正確
The functions and powers of the SFC are wide and are set out in s. 5, SFO. The principal functions are to:
(b) supervise, monitor and regulate the activities of:
(i) recognized exchange, recognized clearing houses, recognized exchange controllers and recognized investor compensation companies or persons carrying on RAs; and
(ii) registered institutions that are regulated or to be regulated by the SFC under any relevant provisions.
Registered institutions are regulated collaborate by the SFC and the HKMA.錯誤
The functions and powers of the SFC are wide and are set out in s. 5, SFO. The principal functions are to:
(b) supervise, monitor and regulate the activities of:
(i) recognized exchange, recognized clearing houses, recognized exchange controllers and recognized investor compensation companies or persons carrying on RAs; and
(ii) registered institutions that are regulated or to be regulated by the SFC under any relevant provisions.
Registered institutions are regulated collaborate by the SFC and the HKMA.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.3
-
326/567問題
326. 問題
1 分QID1159:Which of the following are general duties of the SFC as stated in the SFO?
I. Help maintain Hong Kong’s position as an international financial centre
II. Facilitate innovation in financial products
III. Avoid competition between intermediaries
IV. Act in a transparent manner正確
The SFC has general duties as stated in s. 6, SFO to:
(a) help maintain Hong Kong’s position as an international financial centre;
(b) facilitate innovation in financial products;
(d) act in a transparent manner.錯誤
The SFC has general duties as stated in s. 6, SFO to:
(a) help maintain Hong Kong’s position as an international financial centre;
(b) facilitate innovation in financial products;
(d) act in a transparent manner.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.6
-
327/567問題
327. 問題
1 分QID802:Which of the following are powers that the SFC may NOT delegate to others?
I. Making subsidiary legislations.
II. Establishing committees.
III. Withdraw exchange companies
IV. Intervene in the business operation of registered institutions.正確
The SFO provides that it may not delegate certain functions of the SFC to others.They are detailed in Schedule 2, Part 2, SFO. They include powers:
(a) to make subsidiary legislation;
(b) to establish committees under s. 8, SFO;
(c) to withdraw exchange companies;
(d) to appoint external investigators; and
(e) to institute proceedings in the MMT under s. 252(1) of the SFO.錯誤
The SFO provides that it may not delegate certain functions of the SFC to others.They are detailed in Schedule 2, Part 2, SFO. They include powers:
(a) to make subsidiary legislation;
(b) to establish committees under s. 8, SFO;
(c) to withdraw exchange companies;
(d) to appoint external investigators; and
(e) to institute proceedings in the MMT under s. 252(1) of the SFO.提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.7
-
328/567問題
328. 問題
1 分QID3090:What is the required composition of the board of directors of the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC)?
正確
The board of directors of the SFC must have a majority of non-executive directors who are prominent persons from the industry or the legal and accountancy professions, or other leaders in the securities and futures industry. Therefore, option B is correct.
錯誤
The board of directors of the SFC must have a majority of non-executive directors who are prominent persons from the industry or the legal and accountancy professions, or other leaders in the securities and futures industry. Therefore, option B is correct.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.8
-
329/567問題
329. 問題
1 分QID1160:Which of the following are operating divisions of the SFC?
I. Corporate Finance Division
II. Enforcement Division
III. Investment Product Division
IV. Supervision of Markets Division正確
The Operating divisions are
1. Corporate Finance Division
2. Enforcement Division
3. Investment Products Division
4. Supervision of Markets Division
5. Intermediaries Division錯誤
The Operating divisions are
1. Corporate Finance Division
2. Enforcement Division
3. Investment Products Division
4. Supervision of Markets Division
5. Intermediaries Division提示
Reference Chapter:1.4.9
-
330/567問題
330. 問題
1 分QID21:Which of the following entities is responsible for maintaining the currency stability and the stability of the banking system in Hong Kong?
正確
The HKMA manages the Exchange Fund and the HKSAR’s monetary policy and also supervises the banking system, and is required to maintain currency stability, ensure the safety and stability of the banking system, and promote the efficiency, integrity and development of the financial system.
錯誤
The HKMA manages the Exchange Fund and the HKSAR’s monetary policy and also supervises the banking system, and is required to maintain currency stability, ensure the safety and stability of the banking system, and promote the efficiency, integrity and development of the financial system.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.1
-
331/567問題
331. 問題
1 分QID1179:Which of the following entities is responsible for maintaining the safety and stability of the banking system?
正確
The HKMA is required to maintain currency stability, ensure the safety and stability of the banking system.
錯誤
The HKMA is required to maintain currency stability, ensure the safety and stability of the banking system.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.1
-
332/567問題
332. 問題
1 分QID22:Which of the following are duties of the HKMA?
I. Protect the interest of policyholders
II. Maintain currency stability
III. Promote the efficiency and integrity of the financial system
IV. Ensure the safety and stability of the banking system正確
The HKMA manages the Exchange Fund and the HKSAR’s monetary policy and also supervises the banking system, and is required to maintain currency stability, ensure the safety and stability of the banking system, and promote the efficiency, integrity and development of the financial system. However, protecting the interests of policyholders is not a duty of the HKMA.
錯誤
The HKMA manages the Exchange Fund and the HKSAR’s monetary policy and also supervises the banking system, and is required to maintain currency stability, ensure the safety and stability of the banking system, and promote the efficiency, integrity and development of the financial system. However, protecting the interests of policyholders is not a duty of the HKMA.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.1
-
333/567問題
333. 問題
1 分QID40:What is the most material difference between the Insurance Authority and other regulators?
正確
The IA has powers in relation to the insurance industry similar to those possessed by other financial regulators in Hong Kong.
錯誤
The IA has powers in relation to the insurance industry similar to those possessed by other financial regulators in Hong Kong.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.10
-
334/567問題
334. 問題
1 分QID37:Insurance Authority is responsible for:
I. Authorizing and regulating insurance companies
II. Regulating insurance agents
III. Regulating insurance brokers
IV. Promote self-regulation by the industry正確
The IA has powers in the insurance industry similar to those possessed by other financial regulators in Hong Kong.This includes the power to issue licences for insurance intermediaries.
The Insurance Authority has the following major duties and powers:
(I) The authorisation and regulation of insurers
(II) The regulation of insurance agents
(III) The regulation of insurance brokers錯誤
The IA has powers in the insurance industry similar to those possessed by other financial regulators in Hong Kong.This includes the power to issue licences for insurance intermediaries.
The Insurance Authority has the following major duties and powers:
(I) The authorisation and regulation of insurers
(II) The regulation of insurance agents
(III) The regulation of insurance brokers提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.10
-
335/567問題
335. 問題
1 分QID2860:The duties of the Insurance Authority doesn’t include
正確
The duties of the Insurance Authority includes
1. Regulating and supervising the insurance industry
2. Licensing intermediaries and promote best practice to them.
3. To provide protection to the insurance policy holders.
4. Promote the general stability of the insurance
industry in Hong Kong錯誤
The duties of the Insurance Authority includes
1. Regulating and supervising the insurance industry
2. Licensing intermediaries and promote best practice to them.
3. To provide protection to the insurance policy holders.
4. Promote the general stability of the insurance
industry in Hong Kong提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.10
-
336/567問題
336. 問題
1 分QID38:Which of the following entities should Insurance Agent register with?
正確
Insurance intermediaries in Hong Kong, including both licensed insurance brokers and licensed insurance agents, must be licensed by the Insurance Authority (IA). The IA has powers in the insurance industry similar to those possessed by other financial services regulators in Hong Kong and is responsible for overseeing insurance intermediaries.
錯誤
Insurance intermediaries in Hong Kong, including both licensed insurance brokers and licensed insurance agents, must be licensed by the Insurance Authority (IA). The IA has powers in the insurance industry similar to those possessed by other financial services regulators in Hong Kong and is responsible for overseeing insurance intermediaries.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.10
-
337/567問題
337. 問題
1 分QID1192:Insurance brokers should register with which of the following organizations?
正確
Insurance Brokers should apply for a licence with the Insurance Authority.
錯誤
Insurance Brokers should apply for a licence with the Insurance Authority.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.10
-
338/567問題
338. 問題
1 分QID1190:The Insurance Authority is responsible for:
I. Authorizing and regulating Insurance Companies (Insurer).
II. Regulating Insurance Agents.
III. Regulating Insurance Brokers.
IV. Handling complaints of insurance products.正確
The Insurance Authority is responsible for:
I. Authorizing and regulating Insurance Companies (Insurer).
II. Regulating Insurance Agents.
III. Regulating Insurance Brokers.
IV. Handling complaints of insurance products.錯誤
The Insurance Authority is responsible for:
I. Authorizing and regulating Insurance Companies (Insurer).
II. Regulating Insurance Agents.
III. Regulating Insurance Brokers.
IV. Handling complaints of insurance products.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.10
-
339/567問題
339. 問題
1 分QID1191:Insurance agents should register with which of the following organizations?
正確
Insurance Agents should apply for a licence with the Insurance Authority.
錯誤
Insurance Agents should apply for a licence with the Insurance Authority.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.10
-
340/567問題
340. 問題
1 分QID36:Insurance Brokers should register with which of the following institutions?
正確
Insurance intermediaries in Hong Kong, including both licensed insurance brokers and licensed insurance agents, must be licensed by the Insurance Authority (IA). The IA has powers in the insurance industry similar to those possessed by other financial services regulators in Hong Kong and is responsible for overseeing insurance intermediaries.
錯誤
Insurance intermediaries in Hong Kong, including both licensed insurance brokers and licensed insurance agents, must be licensed by the Insurance Authority (IA). The IA has powers in the insurance industry similar to those possessed by other financial services regulators in Hong Kong and is responsible for overseeing insurance intermediaries.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.10
-
341/567問題
341. 問題
1 分QID1198:The Mandatory Provident Fund Schemes Authority (MPFA) is responsible for which of the following matters relating to Mandatory Provident Fund (MPF) products?
I. Authorisation of the offering documents for the products.
II. Licensing of investment managers of MPF products.
III. overseeing the administration and management of registered schemes and pooled investment funds;
IV. Registration of employer-sponsored MPF schemes.正確
The MPFA has responsibility for:
(a) registering MPF schemes;
(c.) overseeing and making rules and guidelines for the administration and management of
registered schemes and pooled investment funds;
(d) ongoing monitoring of compliance by MPF products with the Mandatory Provident Fund Schemes Ordinance (“MPFSO”);
€ investigating alleged breaches of the provisions of the MPFSO;
(g) dealing with complaints about MPF products and approved trustees, and referring them to the SFC and other regulators for action where necessary.錯誤
The MPFA has responsibility for:
(a) registering MPF schemes;
(c.) overseeing and making rules and guidelines for the administration and management of
registered schemes and pooled investment funds;
(d) ongoing monitoring of compliance by MPF products with the Mandatory Provident Fund Schemes Ordinance (“MPFSO”);
€ investigating alleged breaches of the provisions of the MPFSO;
(g) dealing with complaints about MPF products and approved trustees, and referring them to the SFC and other regulators for action where necessary.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.11
-
342/567問題
342. 問題
1 分QID48:Which of the following activities is Mandatory Provident Fund Schemes Authority (“MPFA”) responsible for ?
正確
One of the responsibilities of the MPFA is to approve trustees and regulate the affairs and activities of such approved trustees.
錯誤
One of the responsibilities of the MPFA is to approve trustees and regulate the affairs and activities of such approved trustees.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.11
-
343/567問題
343. 問題
1 分QID46:Which of the following is a responsibility of the Mandatory Provident Fund Schemes Authority (MPFA)?
正確
One of the responsibilities of the MPFA is to approve trustees and regulate the affairs and activities of such approved trustees.
錯誤
One of the responsibilities of the MPFA is to approve trustees and regulate the affairs and activities of such approved trustees.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.11
-
344/567問題
344. 問題
1 分QID1495:The Mandatory Provident Fund Schemes Authority (MPFA) does NOT have which ONE of the following objectives?
正確
It is not an obligation on the MPFA’s part to ensure that the schemes are operated to maximise the capital or income growth specified in the objectives of the schemes.
錯誤
It is not an obligation on the MPFA’s part to ensure that the schemes are operated to maximise the capital or income growth specified in the objectives of the schemes.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.11
-
345/567問題
345. 問題
1 分QID47:Which of the following are duties and functions of the Mandatory
Provident Fund Schemes Authority (MPFA) in MPF Schemes?
I. Registering MPF schemes
II. Approving Pooled Investment Funds
III. Approving trustees of MPF schemes
IV. Handling complaints related to MPF products and trustees, and referring them to the SFC and other regulators when necessary正確
The MPFA is responsible for:
(a) registering mandatory provident fund schemes;
(b) approving pooled investment funds;
(c) approving trustees and overseeing the activities of such approved trustees;
(d) handling complaints related to MPF products and trustees, and referring them to the SFC and other regulators when necessary.錯誤
The MPFA is responsible for:
(a) registering mandatory provident fund schemes;
(b) approving pooled investment funds;
(c) approving trustees and overseeing the activities of such approved trustees;
(d) handling complaints related to MPF products and trustees, and referring them to the SFC and other regulators when necessary.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.11
-
346/567問題
346. 問題
1 分QID1196:The Mandatory Provident Fund Schemes Authority is responsible for:
I. registering provident fund schemes.
II. approving unit trust funds.
III. overseeing and making rules and guidelines for the administration and management of registered schemes and pooled investment funds.
IV. ongoing monitoring of MPF products’ compliance with the Mandatory Provident Fund Schemes Ordinance.正確
The MPFA has responsibility for:
(a) registering MPF schemes;
(c.) overseeing and making rules and guidelines for the administration and management of registered schemes and pooled investment funds;
(d) ongoing monitoring of compliance by MPF products with the Mandatory Provident Fund Schemes Ordinance (“MPFSO”).錯誤
The MPFA has responsibility for:
(a) registering MPF schemes;
(c.) overseeing and making rules and guidelines for the administration and management of registered schemes and pooled investment funds;
(d) ongoing monitoring of compliance by MPF products with the Mandatory Provident Fund Schemes Ordinance (“MPFSO”).提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.11
-
347/567問題
347. 問題
1 分QID49:Which of the following statements is incorrect?
正確
Certain responsibilities of the MPFA interlink with the particular responsibilities of the SFC, including vetting and authorising MPF products and related marketing materials. IA doesn’t regulate MPF products at all.
錯誤
Certain responsibilities of the MPFA interlink with the particular responsibilities of the SFC, including vetting and authorising MPF products and related marketing materials. IA doesn’t regulate MPF products at all.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.11
-
348/567問題
348. 問題
1 分QID1505:Which of the following duties are performed by the Mandatory Provident Fund Authority (MPFA)?
I. Registering MPF Schemes
II. Approving Pooled Investment Funds.
III. Overseeing and making rules and guidelines for the administration and management of registered schemes and pooled investment funds
IV. Ongoing monitoring of compliance by MPF products with the Mandatory Provident Fund Schemes Ordinance (“MPFSO”)正確
The functions of the MPFA include:
– registering MPF schemes
– the registration procedures of MPF schemes and approval processes of constituent funds and approved pooled investment
funds;
– ongoing monitoring of compliance of MPF products with the MPFSO錯誤
The functions of the MPFA include:
– registering MPF schemes
– the registration procedures of MPF schemes and approval processes of constituent funds and approved pooled investment
funds;
– ongoing monitoring of compliance of MPF products with the MPFSO提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.11
-
349/567問題
349. 問題
1 分QID45:Which of the following are primary functions of the MPFA?
I. Approving fund managers of MPF products
II. Registering and overseeing MPF Schemes
III. Monitoring compliance with the Mandatory Provident Fund
Schemes Ordinance (MPFSO)
IV. Authorising MPF products and related marketing materials正確
The MPFA is responsible for registering and overseeing MPF Schemes and monitoring compliance with the MPFSO. The SFC is responsible for approving the fund managers of MPF scheme investment products and authorising MPF products and related marketing materials.
錯誤
The MPFA is responsible for registering and overseeing MPF Schemes and monitoring compliance with the MPFSO. The SFC is responsible for approving the fund managers of MPF scheme investment products and authorising MPF products and related marketing materials.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.11
-
350/567問題
350. 問題
1 分QID1497:Which of the following is not a general principles followed by the
MPFA?正確
It is not an obligation on the MPFA’s part to ensure that the schemes are operated to maximise the capital or income growth specified in the objectives of the schemes, or to advise on, or ensure, the employers’ and scheme members’ choice of the best schemes/funds to achieve their objectives.
錯誤
It is not an obligation on the MPFA’s part to ensure that the schemes are operated to maximise the capital or income growth specified in the objectives of the schemes, or to advise on, or ensure, the employers’ and scheme members’ choice of the best schemes/funds to achieve their objectives.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.11
-
351/567問題
351. 問題
1 分QID52:Which of the following institutions is responsible for investigations into breaches of the SFC Code on MPF Products?
正確
SFC is responsible for investigating alleged breaches of the provisions of the SFC Code on MPF Products and any relevant ordinances, and taking enforcement action
錯誤
SFC is responsible for investigating alleged breaches of the provisions of the SFC Code on MPF Products and any relevant ordinances, and taking enforcement action
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.14
-
352/567問題
352. 問題
1 分QID50:Which of the following spheres of the MPF schemes has linkage with the SFC?
I. The SFC vets and authorizes MPF products
II. The SFC vets and authorizes marketing materials of investment products of MPF Schemes.
III. The SFC approves Pooled Investment Funds.
IV. The SFC approves trustees of MPF Schemes正確
Certain responsibilities of the MPFA interlink with the particular responsibilities of the SFC, including vetting and authorising MPF products and related marketing materials.The MPFA, not the SFC, is responsible for approving Pooled Investment Funds and trustees of MPF Schemes. Therefore, options I and II are correct, while options III and IV are not the responsibilities of the SFC in relation to MPF schemes.
錯誤
Certain responsibilities of the MPFA interlink with the particular responsibilities of the SFC, including vetting and authorising MPF products and related marketing materials.The MPFA, not the SFC, is responsible for approving Pooled Investment Funds and trustees of MPF Schemes. Therefore, options I and II are correct, while options III and IV are not the responsibilities of the SFC in relation to MPF schemes.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.14
-
353/567問題
353. 問題
1 分QID2774:Which organisation authorises the advertisement of MPF scheme products?
正確
Advertisements for MPF scheme products are authorised by the SFC.
錯誤
Advertisements for MPF scheme products are authorised by the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.14
-
354/567問題
354. 問題
1 分QID1573:MPF Intermediaries are regulated by?
正確
MPFA is the authority responsible for registering MPF intermediaries, issuing guidelines on compliance with statutory requirements, and imposing disciplinary sanctions for non-compliance.
The Monetary Authority (MA), the Insurance Authority (IA) and the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) are given the statutory role of frontline regulators to supervise and investigate MPF intermediaries whose core business is in the banking, insurance and securities sectors respectively.
MPFA relies on these regulators to supervise MPF intermediaries under their respective regimes.
MPF intermediaries who carry on MPF sales and marketing activities as their secondary line of business (in addition to their primary line of business in the banking, insurance and/or securities sectors) will be supervised by the MA, the IA and the SFC respectively.錯誤
MPFA is the authority responsible for registering MPF intermediaries, issuing guidelines on compliance with statutory requirements, and imposing disciplinary sanctions for non-compliance.
The Monetary Authority (MA), the Insurance Authority (IA) and the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) are given the statutory role of frontline regulators to supervise and investigate MPF intermediaries whose core business is in the banking, insurance and securities sectors respectively.
MPFA relies on these regulators to supervise MPF intermediaries under their respective regimes.
MPF intermediaries who carry on MPF sales and marketing activities as their secondary line of business (in addition to their primary line of business in the banking, insurance and/or securities sectors) will be supervised by the MA, the IA and the SFC respectively.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.14
-
355/567問題
355. 問題
1 分QID1201:Which of the following responsibilities between the SFC and the MPF schemes are interlinked?
I. Vetting and authorising MPF products and related marketing materials.
II. Registering and approving investment managers.
III. Investigating alleged breaches of the provisions of the SFC Code on MPF Products and any relevant ordinances, and taking enforcement action.
IV. Regulate the sales process of sales representatives selling MPF schemes.正確
Certain responsibilities of the MPFA interlink with the particular responsibilities of the SFC:
(a) vetting and authorizing MPF products and related marketing materials in accordance with the provisions of the SFC Code on MPF Products and the relevant ordinances (including the SFO);
(b) registering and approving investment managers and continued monitoring of their conduct in the investment management of MPF products;
(d) investigating alleged breaches of the provisions of the SFC Code on MPF Products and any relevant ordinances, and taking enforcement action.錯誤
Certain responsibilities of the MPFA interlink with the particular responsibilities of the SFC:
(a) vetting and authorizing MPF products and related marketing materials in accordance with the provisions of the SFC Code on MPF Products and the relevant ordinances (including the SFO);
(b) registering and approving investment managers and continued monitoring of their conduct in the investment management of MPF products;
(d) investigating alleged breaches of the provisions of the SFC Code on MPF Products and any relevant ordinances, and taking enforcement action.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.14
-
356/567問題
356. 問題
1 分QID1199:Mr. Ko is an investment manager; he wishes to manage a fund under the Kaohsiung Bank Group’s MPF schemes. He needs to be licensed by which of the following?
正確
Certain responsibilities of the MPFA interlink with the particular responsibilities of the SFC:
(b) registering and approving investment managers and continued monitoring of their conduct in the investment management of MPF products.錯誤
Certain responsibilities of the MPFA interlink with the particular responsibilities of the SFC:
(b) registering and approving investment managers and continued monitoring of their conduct in the investment management of MPF products.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.14
-
357/567問題
357. 問題
1 分QID1200:Which of the following are SFC’s duties towards the MPF Schemes?
I. Vetting and authorising MPF products and related marketing materials in accordance with the provisions of the SFC Code on MPF Products and the relevant ordinances (including the SFO).
II. Registering and approving investment managers and continued monitoring of their conduct in the investment management of MPF products.
III. Investigating alleged breaches of the provisions of the SFC Code on MPF Products and any relevant ordinances, and taking enforcement action.
IV. Supervising the selling process of the sales representatives selling MPF schemes.正確
Certain responsibilities of the MPFA interlink with the particular responsibilities of the SFC:
(a) vetting and authorizing MPF products and related marketing materials in accordance with the provisions of the SFC Code on MPF Products and the relevant ordinances (including the SFO);
(b) registering and approving investment managers and continued monitoring of their conduct in the investment management of MPF products;
(d) investigating alleged breaches of the provisions of the SFC Code on MPF Products and any relevant ordinances, and taking enforcement action.錯誤
Certain responsibilities of the MPFA interlink with the particular responsibilities of the SFC:
(a) vetting and authorizing MPF products and related marketing materials in accordance with the provisions of the SFC Code on MPF Products and the relevant ordinances (including the SFO);
(b) registering and approving investment managers and continued monitoring of their conduct in the investment management of MPF products;
(d) investigating alleged breaches of the provisions of the SFC Code on MPF Products and any relevant ordinances, and taking enforcement action.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.14
-
358/567問題
358. 問題
1 分QID51:Which of the following matters is the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) responsible for relating to Mandatory Provident Fund (MPF) products?
I. Authorisation of MPF products and related marketing materials
II. Approving investment managers engaged in the investment management of MPF products
III. Registering and overseeing MPF Schemes
IV. Registration of employer-sponsored MPF schemes for employers正確
Some responsibilities of the MPFA interlink with the specific duties of the SFC, including:
(a) authorising MPF products and related marketing materials
(b) registering and approving investment managers engaged in the investment management of MPF products.However,The MPFA, not the SFC, handles the registration and oversight of MPF schemes.
錯誤
Some responsibilities of the MPFA interlink with the specific duties of the SFC, including:
(a) authorising MPF products and related marketing materials
(b) registering and approving investment managers engaged in the investment management of MPF products.However,The MPFA, not the SFC, handles the registration and oversight of MPF schemes.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.14
-
359/567問題
359. 問題
1 分QID23:British Construction Bank is an AFI regulated by the HKMA. If it plans to conduct Type 9 Regulated Activity (Asset Management) in the near future, how should it proceed?
正確
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity.
錯誤
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
360/567問題
360. 問題
1 分QID1183:If an authorised financial institution would like to conduct regulated actives under the SFO, which organization should it register with?
正確
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, AFIs, which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-RA.
錯誤
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, AFIs, which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-RA.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
361/567問題
361. 問題
1 分QID1182:The British Construction bank is a licensed bank under the HKMA and plans to provide securities trading services for its clients, it should:
正確
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, AFIs, which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-RA.
錯誤
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, AFIs, which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-RA.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
362/567問題
362. 問題
1 分QID24:If an AFI plans to conduct regulated activities as defined by the SFO, which of the following entities should it register with ?
正確
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity.
錯誤
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
363/567問題
363. 問題
1 分QID26:British Construction Bank is an authorised financial institution. Amid the downfall of the Hong Kong banking sector, it would like to sell fund products of other companies to clients to generate revenue. Where should British Construction Bank apply for a license?
正確
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out
on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.錯誤
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out
on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
364/567問題
364. 問題
1 分QID28:Which entity is the frontline regulator of registered institution that conducts regulated activity as defined by the SFO?
正確
As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the HKMA takes the leading role in vetting applications for AFIs’ registration and supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including conducting on-site inspections.
錯誤
As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the HKMA takes the leading role in vetting applications for AFIs’ registration and supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including conducting on-site inspections.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
365/567問題
365. 問題
1 分QID1180:Which of the following organizations are supervised, monitored and regulated by the HKMA?
I. The Banking Authority
II. Registered Institutions
III. Licensed Corporation
IV. Authorised Financial Institutions正確
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, AFIs, which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-RA.
錯誤
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, AFIs, which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-RA.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
366/567問題
366. 問題
1 分QID30:Which of the following is the regulator of Registered Institutions?
正確
As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the HKMA takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out
on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.錯誤
As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the HKMA takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out
on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
367/567問題
367. 問題
1 分QID32:Which of the following descriptions are correct?
I. All banks in Hong Kong are supervised by the SFC.
II. The SFO applies to some of the activities conducted by registered institutions.
III. A memorandum of understanding (“MOU”) has been signed between the SFC and the HKMA to minimize regulatory overlaps.
IV. The Insurance Authority is the major regulator of the insurance industry in Hong Kong.正確
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. Clearly, the HKMA and the SFC must work closely together in relation to any SFC-regulated activities that are carried out by registered institutions. To this end, a memorandum of understanding (“MOU”) has been signed between the two regulators, setting out their roles and responsibilities so as to minimise overlaps under the regulatory regime.
The Insurance Authority is the major regulator of the insurance industry in Hong Kong.錯誤
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. Clearly, the HKMA and the SFC must work closely together in relation to any SFC-regulated activities that are carried out by registered institutions. To this end, a memorandum of understanding (“MOU”) has been signed between the two regulators, setting out their roles and responsibilities so as to minimise overlaps under the regulatory regime.
The Insurance Authority is the major regulator of the insurance industry in Hong Kong.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
368/567問題
368. 問題
1 分QID2471:Which institution should banks apply for a license or register if they want to engage in futures trading business?
正確
Banks should register from the SFC rather than applying for a license if they want to engage in futures trading business. Futures trading is a Type 2 regulated activity.
錯誤
Banks should register from the SFC rather than applying for a license if they want to engage in futures trading business. Futures trading is a Type 2 regulated activity.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
369/567問題
369. 問題
1 分QID341:A person engaging in any activity regulated by the SFO, which includes asset management, will need to be licensed by the
正確
Any person that wish to conduct a regulated activity must be licensed by the SFC.
錯誤
Any person that wish to conduct a regulated activity must be licensed by the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
370/567問題
370. 問題
1 分QID31:Which of the following is the regulator of Authorised Financial
Institutions?正確
As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the HKMA takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.
If AFIs are not registered with the SFC,they will not be regulated by the SFC.錯誤
As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the HKMA takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.
If AFIs are not registered with the SFC,they will not be regulated by the SFC.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
371/567問題
371. 問題
1 分QID1181:What are the two regulatory authorities primarily involved in regulating the asset management industry
I. SFC
II. HKMA
III. SEHK
IV. HKEX正確
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, AFIs, which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-RA.
錯誤
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, AFIs, which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-RA.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
372/567問題
372. 問題
1 分QID809:What is the difference between Licensed Corporations and Registered Institutions?
正確
AFIs, which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to
carry out an SFC-RA. As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-RAs, including carrying out on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.錯誤
AFIs, which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to
carry out an SFC-RA. As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-RAs, including carrying out on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
373/567問題
373. 問題
1 分QID1494:What is the primary function of Registered Institution in the Asset Management Business?
正確
Many AFIs participate in the fund management industry as distributors of CISs products. Accordingly, the HKMA, in its capacity as the banking regulatory authority, is concerned with the asset management industry insofar as it affects AFIs engaged in the regulated activity of asset management, i.e. registered institutions.
錯誤
Many AFIs participate in the fund management industry as distributors of CISs products. Accordingly, the HKMA, in its capacity as the banking regulatory authority, is concerned with the asset management industry insofar as it affects AFIs engaged in the regulated activity of asset management, i.e. registered institutions.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
374/567問題
374. 問題
1 分QID33:British Construction Bank is an AFI regulated by the HKMA. Which of the following entities is responsible for supervising the regulated activities it conducts under the SFO?
正確
British Construction Bank, as an AFI regulated by the HKMA, must register with the SFC as a registered institution to conduct SFC-regulated activities. These activities are jointly supervised by the HKMA and the SFC to ensure regulatory compliance. To this end, an MOU has been signed between the two regulators, setting out their roles and responsibilities so as to minimize overlaps under the regulatory regime.
錯誤
British Construction Bank, as an AFI regulated by the HKMA, must register with the SFC as a registered institution to conduct SFC-regulated activities. These activities are jointly supervised by the HKMA and the SFC to ensure regulatory compliance. To this end, an MOU has been signed between the two regulators, setting out their roles and responsibilities so as to minimize overlaps under the regulatory regime.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
375/567問題
375. 問題
1 分QID29:Which of the following descriptions about Authorised Financial Institutions (AFI) are true?
I. All Registered Institutions are banks.
II. If the AFIs are conducting the regulated activities as defined by the SFO, the AFIs should register with the SFC.
III. SFC is responsible for licensing AFIs for all businesses
IV. The HKMA may refer cases of suspected malpractice by registered institutions in respect of the SFC-regulated activities to the SFC正確
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which
are regulated by the HKMA and include banks (but not only limited to banks), have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity.
The HKMA may refer cases of suspected malpractice by registered institutions in respect of the SFC-regulated activities to the SFC, which may directly review those institutions.錯誤
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which
are regulated by the HKMA and include banks (but not only limited to banks), have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity.
The HKMA may refer cases of suspected malpractice by registered institutions in respect of the SFC-regulated activities to the SFC, which may directly review those institutions.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
376/567問題
376. 問題
1 分QID1184:British Construction Bank is and AFI regulated by the HKMA, if it plans to conduct Type 9 Regulated Activity in the near future, how should it proceed?
正確
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, AFIs, which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-RA.
錯誤
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, AFIs, which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-RA.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
377/567問題
377. 問題
1 分QID1185:Which entity is the frontline regulator(s) of registered institutions that conducts regulated activities?
正確
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC asregistered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. As the frontline
regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out onsite inspections.錯誤
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC asregistered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. As the frontline
regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out onsite inspections.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
378/567問題
378. 問題
1 分QID1158:Who is responsible for the supervision of registered institutions?
正確
HKMA is the frontline regulator of registered institutions.
錯誤
HKMA is the frontline regulator of registered institutions.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.3
-
379/567問題
379. 問題
1 分QID1186:The HKMA may refer cases of suspected malpractices by registered institutions in respect of the SFC-regulated activities to the:
正確
The HKMA may refer cases of suspected malpractice by registered institutions in respect of the SFC-RAs to the SFC, which may directly review those institutions.
錯誤
The HKMA may refer cases of suspected malpractice by registered institutions in respect of the SFC-RAs to the SFC, which may directly review those institutions.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.4
-
380/567問題
380. 問題
1 分QID55:Which of the following ordinances are administered and enforced by the Registrar of Companies?
I. Bankruptcy Ordinance
II. Money Lenders Ordinance
III. SFO Part IVA (some of the provisions relating to open-ended fund companies)
IV. Trustee Ordinance正確
The Registrar of Companies administers CO, Companies (Winding-Up and Miscellaneous Provisions) Ordinance; Limited Partnerships Ordinance, Limited Partnership Fund Ordinance, Trustee Ordinance; Registered Trustees Incorporation Ordinance; Money Lenders Ordinance; Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorist Financing Ordinance (for trust and company service providers); SFO Part IVA (some of the provisions relating to open-ended fund companies); and Miscellaneous Incorporation Ordinances.
Therefore, options II, III, and IV are correct.錯誤
The Registrar of Companies administers CO, Companies (Winding-Up and Miscellaneous Provisions) Ordinance; Limited Partnerships Ordinance, Limited Partnership Fund Ordinance, Trustee Ordinance; Registered Trustees Incorporation Ordinance; Money Lenders Ordinance; Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorist Financing Ordinance (for trust and company service providers); SFO Part IVA (some of the provisions relating to open-ended fund companies); and Miscellaneous Incorporation Ordinances.
Therefore, options II, III, and IV are correct.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.5
-
381/567問題
381. 問題
1 分QID1187:The Registrar of Companies administers and enforces which of the following?
I. the Companies Ordinance(‘CO’)
II. the Limited Partnerships Ordinance
III. the Trustee Ordinance
IV. the Registered Trustees Incorporation Ordinance正確
The Registrar of Companies administers and enforces certain aspects of the:
(a) NCO;
(c.) Limited Partnerships Ordinance;
(d) Trustee Ordinance;
(e.) Registered Trustees Incorporation Ordinance.錯誤
The Registrar of Companies administers and enforces certain aspects of the:
(a) NCO;
(c.) Limited Partnerships Ordinance;
(d) Trustee Ordinance;
(e.) Registered Trustees Incorporation Ordinance.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.5
-
382/567問題
382. 問題
1 分QID2805:Which of the following is the responsibility of the Companies Registry?
I. Keep and make available companies’ returns for public inspection
II. Strike off companies that fail to file returns or do not carry on business
III. Directly supervise companies
IV. Recover returns from companies that fail to file on time正確
The Companies Registry is responsible
I. Keep and make the company’s returns for public inspection
II. Strike off companies for failure to file returns or not carry on business
III. Recover returns from companies that fail to file on timeThe Companies Registry does not directly regulate companies.
錯誤
The Companies Registry is responsible
I. Keep and make the company’s returns for public inspection
II. Strike off companies for failure to file returns or not carry on business
III. Recover returns from companies that fail to file on timeThe Companies Registry does not directly regulate companies.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.6
-
383/567問題
383. 問題
1 分QID56:The Registrar of Companies:
I. Has no direct links with the SFC in regulatory areas
II. Maintains and makes available for public inspection financial returns registered by companies
III. Does not regulate companies directly
IV. Administers some of the provisions of the SFO正確
The Registrar of Companies administers parts of SFO.
There are no direct links between the SFC and the Companies Registry in regulatory areas, although the two agencies maintain an active liaison on issues of common interest.
The Companies Registry maintains and makes available for public inspection financial and other returns, charges registered by companies and so on.
The Registrar of Companies does not directly regulate companies, limited partnerships, trustees or money lenders; such functions are assumed by different bodies.錯誤
The Registrar of Companies administers parts of SFO.
There are no direct links between the SFC and the Companies Registry in regulatory areas, although the two agencies maintain an active liaison on issues of common interest.
The Companies Registry maintains and makes available for public inspection financial and other returns, charges registered by companies and so on.
The Registrar of Companies does not directly regulate companies, limited partnerships, trustees or money lenders; such functions are assumed by different bodies.提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.8
-
384/567問題
384. 問題
1 分QID35:Which of the following entities is responsible for authorising and supervising insurance companies?
正確
The Insurance Authority is concerned with the regulation of insurance companies and insurance intermediaries.
錯誤
The Insurance Authority is concerned with the regulation of insurance companies and insurance intermediaries.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.5.9
-
385/567問題
385. 問題
1 分QID92:Which of the following descriptions about the HKEX is correct?
I. The HKEX is a listed company on the SEHK.
II. The HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC.
III. The SEHK, HKFE, and the three associated clearing houses are subsidiaries of the HKEX.
IV. The HKEX is responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants.
English Answer A: I, II, III
English Answer B: I, IV
English Answer C: II, III
English Answer D: II, III, IV正確
The HKEX is a listed company on the SEHK. The SEHK, HKFE and the three associated clearing houses are wholly owned subsidiaries of the HKEX. The HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC. However, the HKEX is not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants; this role is performed by the SFC.
錯誤
The HKEX is a listed company on the SEHK. The SEHK, HKFE and the three associated clearing houses are wholly owned subsidiaries of the HKEX. The HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC. However, the HKEX is not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants; this role is performed by the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.
-
386/567問題
386. 問題
1 分QID1204:Which of the following organizations are recognized clearing houses under the SFO?
I. Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited
II. The SEHK Options Clearing House Limited
III. HKFE Clearing Corporation Limited
IV. The HKEX正確
On 6 March 2000, the SEHK, HKFE and the three associated clearing houses Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited, The SEHK Options Clearing House Limited and HKFE Clearing Corporation Limited became wholly owned subsidiaries of HKEX.
錯誤
On 6 March 2000, the SEHK, HKFE and the three associated clearing houses Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited, The SEHK Options Clearing House Limited and HKFE Clearing Corporation Limited became wholly owned subsidiaries of HKEX.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.1
-
387/567問題
387. 問題
1 分QID1203:How many stock exchanges are there in Hong Kong?
正確
Only the SEHK is the securities exchange. HKFE is a futures exchange, not securities exchange.
錯誤
Only the SEHK is the securities exchange. HKFE is a futures exchange, not securities exchange.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.1
-
388/567問題
388. 問題
1 分QID1202:Which of the following is NOT a clearing house under the HKEX?
正確
HKEX is a listed company on the SEHK. On 6 March 2000, the SEHK, HKFE and the three associated clearing houses Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited, The SEHK Options Clearing House Limited and HKFE Clearing Corporation Limited became wholly owned subsidiaries of HKEX.
錯誤
HKEX is a listed company on the SEHK. On 6 March 2000, the SEHK, HKFE and the three associated clearing houses Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited, The SEHK Options Clearing House Limited and HKFE Clearing Corporation Limited became wholly owned subsidiaries of HKEX.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.1
-
389/567問題
389. 問題
1 分QID514:Which of the following agencies are the 3 major clearing houses in Hong Kong?
I. Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited (HKSCC).
II. The SEHK Options Clearing House Limited (SEOCH).
III. HKFE Clearing Corporation Limited (HKCC).
IV. Hong Kong OTC Clear Limited.正確
Upon merger and demutualisation, the two exchanges and three
clearing houses (HKSCC, SEOCH and HKCC) became the wholly owned subsidiaries of HKEX and “participantship” of the exchanges and clearing houses was introduced. They became the three major clearing houses in Hong Kong.錯誤
Upon merger and demutualisation, the two exchanges and three
clearing houses (HKSCC, SEOCH and HKCC) became the wholly owned subsidiaries of HKEX and “participantship” of the exchanges and clearing houses was introduced. They became the three major clearing houses in Hong Kong.提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.1
-
390/567問題
390. 問題
1 分QID1205:Which of the following is a recognised exchange controller under the SFO?
正確
HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC under s. 59, SFO. The SEHK and HKFE are recognised under s. 19, SFO as exchange companies that may operate a stock market and a futures market in Hong Kong respectively. The three clearing houses obtain their recognition under s. 37, SFO. A recognised exchange controller may control a recognised exchange company or clearing house.
錯誤
HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC under s. 59, SFO. The SEHK and HKFE are recognised under s. 19, SFO as exchange companies that may operate a stock market and a futures market in Hong Kong respectively. The three clearing houses obtain their recognition under s. 37, SFO. A recognised exchange controller may control a recognised exchange company or clearing house.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.2
-
391/567問題
391. 問題
1 分QID100:Which of the following securities and futures exchanges are currently in Hong Kong?
I. Stock Exchange of Hong Kong
II. Hong Kong Futures Exchange Limited
III. Hong Kong Options Exchange
IV. Hong Kong Bonds Exchange正確
The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong and the Hong Kong Futures Exchange Limited are recognised under Section 19 of the Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO)as exchange companies that may operate a stock and a futures market in Hong Kong.
錯誤
The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong and the Hong Kong Futures Exchange Limited are recognised under Section 19 of the Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO)as exchange companies that may operate a stock and a futures market in Hong Kong.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.2
-
392/567問題
392. 問題
1 分QID905:Which of the following correctly describes the HKEX?
正確
HKEX is not the venue for buying and selling Hong Kong stocks. HKEX is an exchange controller. HKEX’s subsidiary SEHK is the venue for buying and selling Hong Kong stocks. The SFC is responsible for licensing and registration of intermediaries. Stamp duty is a source of income of the government of the HKSAR.
錯誤
HKEX is not the venue for buying and selling Hong Kong stocks. HKEX is an exchange controller. HKEX’s subsidiary SEHK is the venue for buying and selling Hong Kong stocks. The SFC is responsible for licensing and registration of intermediaries. Stamp duty is a source of income of the government of the HKSAR.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.2
-
393/567問題
393. 問題
1 分QID101:Which of the following is an exchange controller in Hong Kong
正確
HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC under Section 59 of the Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO).A recognised exchange controller may control a recognised exchange company or clearing house.
錯誤
HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC under Section 59 of the Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO).A recognised exchange controller may control a recognised exchange company or clearing house.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.2
-
394/567問題
394. 問題
1 分QID1206:Which of the following are recognized exchange companies under the SFO?
I. HKEX
II. SEHK
III. HKFE
IV. HKSCC正確
HKEX is an exchange controller recognized by the SFC under s. 59, SFO. The SEHK and HKFE are recognized under s. 19, SFO as exchange companies that may operate a stock market and a futures market in Hong Kong respectively.
錯誤
HKEX is an exchange controller recognized by the SFC under s. 59, SFO. The SEHK and HKFE are recognized under s. 19, SFO as exchange companies that may operate a stock market and a futures market in Hong Kong respectively.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.2
-
395/567問題
395. 問題
1 分QID99:Which entity is recognized by the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) as an exchange controller in Hong Kong?
正確
HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC under Section 59 of the Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO).A recognised exchange controller may control a recognised exchange company or clearing house.
錯誤
HKEX is an exchange controller recognised by the SFC under Section 59 of the Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO).A recognised exchange controller may control a recognised exchange company or clearing house.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.2
-
396/567問題
396. 問題
1 分QID1207:The duties of the HKEX, as the exchange controller, include which of the following?
I. Ensuring an orderly and fair market in securities and futures contracts traded on or through the SEHK and HKFE.
II. Ensuring that risks are managed prudently, to act in the interests of the public, having particular regard to the interests of the investing public.
III. Being responsible for front-line prudential and regulation of market participants.
IV. Not being responsible for front-line prudential and regulation of market participants.正確
HKEX is responsible for ensuring an orderly and fair market in securities and futures contracts traded on or through the SEHK and HKFE, respectively. HKEX is required to ensure that risks are managed prudently, to act in the interests of the public, having particular regard to the interests of the investing public, and to ensure that where such interests conflict with any other interests the former shall prevail.
錯誤
HKEX is responsible for ensuring an orderly and fair market in securities and futures contracts traded on or through the SEHK and HKFE, respectively. HKEX is required to ensure that risks are managed prudently, to act in the interests of the public, having particular regard to the interests of the investing public, and to ensure that where such interests conflict with any other interests the former shall prevail.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.3
-
397/567問題
397. 問題
1 分QID733:The HKEX is responsible for regulating which of the following entities and matters?
I. Listed Companies
II. SEHK
III. HKFE
IV. Investors who participate in securities trading.正確
HKEX is responsible for ensuring an orderly and fair market in securities and futures contracts traded on or through the SEHK and HKFE, respectively. HKEX is required to ensure that risks are managed prudently, to act in the interests of the public, having
particular regard to the interests of the investing public, and to ensure that where such interests conflict with any other interests the former shall prevail. The SEHK is also responsible for administering the Listing Rules.錯誤
HKEX is responsible for ensuring an orderly and fair market in securities and futures contracts traded on or through the SEHK and HKFE, respectively. HKEX is required to ensure that risks are managed prudently, to act in the interests of the public, having
particular regard to the interests of the investing public, and to ensure that where such interests conflict with any other interests the former shall prevail. The SEHK is also responsible for administering the Listing Rules.提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.3
-
398/567問題
398. 問題
1 分QID1208:How is the board of HKEX formed?
正確
The board of HKEX is a mix of directors appointed by the Government (the majority) and those elected by the shareholders; the board elects the Chairman and appoints the Chief Executive. The Chairman of HKEX must be approved by the Chief Executive of the Hong Kong SAR, while the Chief Executive of HKEX has to be approved by the SFC.
錯誤
The board of HKEX is a mix of directors appointed by the Government (the majority) and those elected by the shareholders; the board elects the Chairman and appoints the Chief Executive. The Chairman of HKEX must be approved by the Chief Executive of the Hong Kong SAR, while the Chief Executive of HKEX has to be approved by the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.4
-
399/567問題
399. 問題
1 分QID104:Which of the following entity is responsible for monitoring the exchanges and clearing houses in Hong Kong?
正確
The SFC supervises and monitors the activities of HKEX, the exchange companies and the clearing houses, approves their rules and amendments to the rules, approves the fees they charge, and administers and enforces the applicable legislation. It also carries out regular reviews of these activities.
錯誤
The SFC supervises and monitors the activities of HKEX, the exchange companies and the clearing houses, approves their rules and amendments to the rules, approves the fees they charge, and administers and enforces the applicable legislation. It also carries out regular reviews of these activities.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.5
-
400/567問題
400. 問題
1 分QID3106:Which statement accurately reflects the role of the SFC in Hong Kong’s financial market?
正確
The SFC’s role includes supervising and regulating exchanges and clearing houses, as part of its broader responsibilities in the financial market.
錯誤
The SFC’s role includes supervising and regulating exchanges and clearing houses, as part of its broader responsibilities in the financial market.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.5
-
401/567問題
401. 問題
1 分QID106:Which of the following entity is responsible for the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules?
正確
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants, which is carried out by the SFC.
錯誤
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants, which is carried out by the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.6
-
402/567問題
402. 問題
1 分QID788:Which of the following regulators in Hong Kong assumes responsibility for front-line regulation and discipline of participants of the securities and futures industry?
正確
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants, which is carried out by the SFC.
錯誤
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants, which is carried out by the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.6
-
403/567問題
403. 問題
1 分QID105:Which of the following organization is responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants?
正確
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants, which is carried out by the SFC.
錯誤
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants, which is carried out by the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.6
-
404/567問題
404. 問題
1 分QID1209:Which of the following organizations is responsible for front line conduct of market participants in the securities and futures business?
正確
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants, which is carried out by the SFC.
錯誤
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants, which is carried out by the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.6
-
405/567問題
405. 問題
1 分QID1490:Which of the following is not regulated by the the SFC?
正確
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own
listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses
are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants,
which is carried out by the SFC.錯誤
Except in relation to the management of business risk, and the enforcement of their own
listing, trading, clearing and settlement rules, HKEX, the exchanges and the clearing houses
are not responsible for front-line prudential and conduct regulation of market participants,
which is carried out by the SFC.提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.6
-
406/567問題
406. 問題
1 分QID2751:Which of the following descriptions about the HKEX is incorrect?
正確
HKEX is not responsible for front-line prudential regulation of market participants. Such task is the responsibility of the SFC.
錯誤
HKEX is not responsible for front-line prudential regulation of market participants. Such task is the responsibility of the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.6.6
-
407/567問題
407. 問題
1 分QID188:Which of the following description about the single licence regime is correct?
正確
Although there are ten types of regulated activity, the SFC will grant to a person only one licence (or registration) which will enable the holder to undertake one or more of the ten regulated activities. This is normally referred to as the “single licence regime”.
錯誤
Although there are ten types of regulated activity, the SFC will grant to a person only one licence (or registration) which will enable the holder to undertake one or more of the ten regulated activities. This is normally referred to as the “single licence regime”.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
408/567問題
408. 問題
1 分QID1662:Registered Institutions are exempted from registering for which of the following regulated activities?
正確
An AFI carrying out Type 3 or Type 8 regulated activity is exempted from the registration requirement. So Registered Institutions are exempted from registering for:
Type 3: leveraged foreign exchange trading
Type 8: securities margin financing錯誤
An AFI carrying out Type 3 or Type 8 regulated activity is exempted from the registration requirement. So Registered Institutions are exempted from registering for:
Type 3: leveraged foreign exchange trading
Type 8: securities margin financing提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
409/567問題
409. 問題
1 分QID909:Which of the following individuals are more likely to be affected by the Licensing and registration part of the SFO?
I. Licensed Corporation
II. AFIs that is preparing to conduct regulated activities in the near future
III. Executive officers of a Registered Institution
IV. Professional Investors正確
Professional Investors do not need to be licensed. AFIs will need to be registered in order to conduct regulated activities.
錯誤
Professional Investors do not need to be licensed. AFIs will need to be registered in order to conduct regulated activities.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
410/567問題
410. 問題
1 分QID226:Which of the following entities will require registration or licensing when conducting regulated activities as defined by the SFO?
I. Registered Institution
II. Licensed Corporation
III. Money Lender
IV. Trust Companies正確
Part V, SFO provides for the implementation of the licensing regime, including:
(a) the setting up of a single licensing system to cover the 12 specified types of RA and the licensing of corporations (“licensed corporations”) to conduct one or more RAs subject to any conditions the SFC may wish to impose;
(b) allowing licensed persons conducting some RAs to undertake certain others, e.g. a Type 1 licence or registration covers Type 4, Type 6 and Type 9 RAs as well if the conducting of those activities is wholly incidental to the conducting of the Type 1 RA;
(c.) the registration of AFIs to engage in one or more of the 12 types of RA (“registeredinstitutions”) ; however, an AFI carrying out Type 3 or Type 8 RAis exempted from the registration requirement.
Under the SFO, both Registered Institutions and Licensed Corporations must be registered or licensed to conduct regulated activities. Money Lenders and Trust Companies are not required to be registered or licensed under the SFO unless they conduct regulated activities.錯誤
Part V, SFO provides for the implementation of the licensing regime, including:
(a) the setting up of a single licensing system to cover the 12 specified types of RA and the licensing of corporations (“licensed corporations”) to conduct one or more RAs subject to any conditions the SFC may wish to impose;
(b) allowing licensed persons conducting some RAs to undertake certain others, e.g. a Type 1 licence or registration covers Type 4, Type 6 and Type 9 RAs as well if the conducting of those activities is wholly incidental to the conducting of the Type 1 RA;
(c.) the registration of AFIs to engage in one or more of the 12 types of RA (“registeredinstitutions”) ; however, an AFI carrying out Type 3 or Type 8 RAis exempted from the registration requirement.
Under the SFO, both Registered Institutions and Licensed Corporations must be registered or licensed to conduct regulated activities. Money Lenders and Trust Companies are not required to be registered or licensed under the SFO unless they conduct regulated activities.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
411/567問題
411. 問題
1 分QID233:Individuals engaged in asset management require
正確
Part V, SFO provides for the implementation of the licensing regime, including:
(i) requiring an individual engaging in a regulated activity for a licensed corporation (as his principal) to be licensed (licensed representative);
(ii) permitting an individual to engage in a regulated activity for a registered institution provided that his name is entered in the register maintained by the HKMA as engaged by the registered institution in respect of that regulated activity;
(iii) approving persons who, in addition to being licensed as representatives, carry out supervisory functions for a licensed corporation and are nominated as responsible officers by the licensed corporation.
Asset management is a regulated activity. Therefore, if an individual wants to engage in the asset management business, he or she needs to obtain at least a licensed representative license; the responsible officer must also get a responsible officer’s license.錯誤
Part V, SFO provides for the implementation of the licensing regime, including:
(i) requiring an individual engaging in a regulated activity for a licensed corporation (as his principal) to be licensed (licensed representative);
(ii) permitting an individual to engage in a regulated activity for a registered institution provided that his name is entered in the register maintained by the HKMA as engaged by the registered institution in respect of that regulated activity;
(iii) approving persons who, in addition to being licensed as representatives, carry out supervisory functions for a licensed corporation and are nominated as responsible officers by the licensed corporation.
Asset management is a regulated activity. Therefore, if an individual wants to engage in the asset management business, he or she needs to obtain at least a licensed representative license; the responsible officer must also get a responsible officer’s license.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
412/567問題
412. 問題
1 分QID187:Although there are ten types of regulated activity, the SFC will grant to a person only one licence (or registration) which will enable the holder to undertake one or more of the ten regulated activities. This is normally referred to as the
正確
Although there are ten types of regulated activity, the SFC will grant to a person only one licence (or registration) which will enable the holder to undertake one or more of the ten regulated activities. This is normally referred to as the “single licence regime”.
錯誤
Although there are ten types of regulated activity, the SFC will grant to a person only one licence (or registration) which will enable the holder to undertake one or more of the ten regulated activities. This is normally referred to as the “single licence regime”.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
413/567問題
413. 問題
1 分QID2362:Kaohsiung Securities holds type 1 license which can conduct regulated activities wholly incidental to type 1 activities including:
I. Type 4 – advising on securities
II. Type 5 – advising on futures contract
III. Type 6 – advising on institutional financing
IV. Type 9 – providing asset management services正確
(d) allowing licensed persons conducting some regulated activities to conduct certain others, e.g. a Type 1 licence or registration covers Type 4, Type 6 and Type 9 regulated activities as well if the conducting of those activities is wholly incidental to the conducting of the Type 1 regulated activity. It also covers Type 8 regulated activity.
Kaohsiung Securities holds type 1 license which can conduct regulated activities wholly incidental to type 1 activities including:
Type 4 – advising on securities
Type 6 – advising on institutional financing
Type 8 – providing securities margin financing
Type 9 – providing asset management services錯誤
(d) allowing licensed persons conducting some regulated activities to conduct certain others, e.g. a Type 1 licence or registration covers Type 4, Type 6 and Type 9 regulated activities as well if the conducting of those activities is wholly incidental to the conducting of the Type 1 regulated activity. It also covers Type 8 regulated activity.
Kaohsiung Securities holds type 1 license which can conduct regulated activities wholly incidental to type 1 activities including:
Type 4 – advising on securities
Type 6 – advising on institutional financing
Type 8 – providing securities margin financing
Type 9 – providing asset management services提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
414/567問題
414. 問題
1 分QID1212:The system that covers the 12specified types of regulated activities and the licensing of corporations (“licensed corporations”) to conduct one or more regulated activities subject to any conditions the SFC may wish to impose is known as the:
正確
The setting up of a single licensing system to cover the ten specified types of RA (see section 7.4 below) and the licensing of corporations (“licensed corporations”) to conduct one or more RAs subject to any conditions the SFC may wish to impose.
錯誤
The setting up of a single licensing system to cover the ten specified types of RA (see section 7.4 below) and the licensing of corporations (“licensed corporations”) to conduct one or more RAs subject to any conditions the SFC may wish to impose.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
415/567問題
415. 問題
1 分QID114:Which intermediaries are regulated and require licensing or registration by the SFC?
I. Independent Financial Advisor
II. Investment Bank
III. Trustee
IV. Insurance Agent正確
Corporations or authorised financial institutions engaged in one or more regulated activities must be licensed or registered with the SFC.
Independent financial advisors primarily advise on corporate finance. Investment banks are professional institutions specializing in corporate financing, capital market transactions, and asset management, and therefore, they need to be licensed or registered.錯誤
Corporations or authorised financial institutions engaged in one or more regulated activities must be licensed or registered with the SFC.
Independent financial advisors primarily advise on corporate finance. Investment banks are professional institutions specializing in corporate financing, capital market transactions, and asset management, and therefore, they need to be licensed or registered.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
416/567問題
416. 問題
1 分QID1218:Which of the following personnel or organizations should be licensed or registered when they are conducting regulated activities classified by the SFO?
I. Frontline staff of the intermediary
II. Responsible officers/ Executive officers of the intermediary
III. The major shareholders of the intermediary
IV. The intermediary正確
Individuals engaged in regulated activities as intermediaries, responsible officers of intermediaries, and intermediaries carrying out regulated activities are required to obtain a license.
錯誤
Individuals engaged in regulated activities as intermediaries, responsible officers of intermediaries, and intermediaries carrying out regulated activities are required to obtain a license.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
417/567問題
417. 問題
1 分QID185:Which of the following entities should apply for a licence or registering with the SFC for Asset Management Services?
I. A Licensed Corporation managing an unauthorised CISII. A Registered Institution managing an authorised CIS
III. A trustee safe keeping asset for a CIS
IV. A Licensed Corporation managing an authorised CIS
正確
Regardless of the CIS is being authorised by the SFC or not, as long as the licenced corporation is managing it, the corporation who manage the CIS should be licensed by the SFC. Activities that require an asset management licence by the SFC include:
1. Discretionary management of Securities and/or Futures Portfolio
2. Management of CIS (Regardless of being authorised by the SFC or not)
錯誤
Regardless of the CIS is being authorised by the SFC or not, as long as the licenced corporation is managing it, the corporation who manage the CIS should be licensed by the SFC. Activities that require an asset management licence by the SFC include:
1. Discretionary management of Securities and/or Futures Portfolio
2. Management of CIS (Regardless of being authorised by the SFC or not)
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
418/567問題
418. 問題
1 分QID186:Which of the following descriptions about the single license regime is correct?
正確
Although there are ten types of regulated activity, the SFC will grant to a person only one licence (or registration) which will enable the holder to undertake one or more of the ten regulated activities. This is normally referred to as the “single licence regime”.
錯誤
Although there are ten types of regulated activity, the SFC will grant to a person only one licence (or registration) which will enable the holder to undertake one or more of the ten regulated activities. This is normally referred to as the “single licence regime”.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
419/567問題
419. 問題
1 分QID2361:The licensing and registration requirements of the Securities and Futures Ordinance may apply to?
I. Staffs of licensed corporations
II. Staffs of registered agents
III. Banks conducting regulated activities
IV. Professional investors正確
The licensing and registration requirements of the Securities and Futures Ordinance apply to
I. Licensed CorporationII. Employees of licensed corporations (licensed representatives and responsible officers)
III. Registered institution (i.e. bank conducting regulated activities)IV. Staff of the registered institution (Executive officers and relevant individuals)
錯誤
The licensing and registration requirements of the Securities and Futures Ordinance apply to
I. Licensed CorporationII. Employees of licensed corporations (licensed representatives and responsible officers)
III. Registered institution (i.e. bank conducting regulated activities)IV. Staff of the registered institution (Executive officers and relevant individuals)
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
420/567問題
420. 問題
1 分QID1210:Part V of the SFO provides for the implementation of which of the following licensing regime?
正確
Part V, SFO provides for the implementation of the licensing regime, including:
(a) the setting up of a single licensing system to cover the ten specified types of RA (see section 7.4 below) and the licensing of corporations (“licensed corporations”) to conduct one or more RAs subject to any conditions the SFC may wish to impose.錯誤
Part V, SFO provides for the implementation of the licensing regime, including:
(a) the setting up of a single licensing system to cover the ten specified types of RA (see section 7.4 below) and the licensing of corporations (“licensed corporations”) to conduct one or more RAs subject to any conditions the SFC may wish to impose.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
421/567問題
421. 問題
1 分QID230:British Construction Bank is an authorised financial institution. Amid the downfall of the Hong Kong banking sector, it would like start an asset management business and sell CIS fund products it manages to clients to generate revenue. Which type license of regulated activity should British Construction Bank apply for to conduct such activities?
正確
Part V, SFO provides for the implementation of the licensing regime, including:
(c.) the registration of AFIs to engage in one or more of the 12 types of RA (“registeredinstitutions”) .
As an authorised financial institution, British Construction Bank must be registered with the SFC to conduct any SFC Regulated Activities. For managing funds and offering CIS fund products to clients, a Type 9 (asset management) license is required.錯誤
Part V, SFO provides for the implementation of the licensing regime, including:
(c.) the registration of AFIs to engage in one or more of the 12 types of RA (“registeredinstitutions”) .
As an authorised financial institution, British Construction Bank must be registered with the SFC to conduct any SFC Regulated Activities. For managing funds and offering CIS fund products to clients, a Type 9 (asset management) license is required.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.1
-
422/567問題
422. 問題
1 分QID1221:Which of the following restrictions about responsible officers are correct?
I. A licensed corporation should appoint not less than two responsible officers.
II. At least one of the responsible officers should be the executive director of the licensed corporation.
III. All executive directors should be responsible officers.
IV. For each regulated activity, at least one responsible officer available at all times to supervise the business of the regulated activity for which it is licensed, and who is based in Hong Kong (s. 118(1)(a)(ii), SFO).正確
Each licensed corporation is required to:
(a) appoint not less than two responsible officers, at least one of whom must be an executive director (see Note 1 below) (s. 125, SFO);
(b) ensure that every individual executive director of the licensed corporation is approved as a responsible officer (s. 125, SFO); and
(c.) ensure that it has, for each RA, at least one responsible officer available at all times to supervise the business of the RA for which it is licensed, and who is based in Hong Kong (s. 118(1)(a)(ii), SFO) (see Note 2 below).錯誤
Each licensed corporation is required to:
(a) appoint not less than two responsible officers, at least one of whom must be an executive director (see Note 1 below) (s. 125, SFO);
(b) ensure that every individual executive director of the licensed corporation is approved as a responsible officer (s. 125, SFO); and
(c.) ensure that it has, for each RA, at least one responsible officer available at all times to supervise the business of the RA for which it is licensed, and who is based in Hong Kong (s. 118(1)(a)(ii), SFO) (see Note 2 below).提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.10
-
423/567問題
423. 問題
1 分QID239:Under the Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO), which of the following conditions apply to responsible officers of a licensed corporation?
I. Every responsible officer other than a designated compliance officer must be an executive director.
II. There must be at least two responsible officers for every regulated activity engaged in by a licensed corporation.
III. There must be at least one responsible officer present at all times to supervise the regulated activity of a licensed corporation.
IV. The designated compliance officer must be a responsible officer.正確
Each licensed corporation is required to:
(a) appoint not less than two responsible officers, at least one of whom must be an executivedirector;
(b) ensure that every individual executive director of the licensed corporation is approved as a responsible officer; and
(c) ensure that it has, for each RA, at least one responsible officer available at all times to supervise the business of the RA for which it is licensed, and who is based in Hong Kong.錯誤
Each licensed corporation is required to:
(a) appoint not less than two responsible officers, at least one of whom must be an executivedirector;
(b) ensure that every individual executive director of the licensed corporation is approved as a responsible officer; and
(c) ensure that it has, for each RA, at least one responsible officer available at all times to supervise the business of the RA for which it is licensed, and who is based in Hong Kong.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.10
-
424/567問題
424. 問題
1 分QID242: A licensed corporation must have
正確
every licensed corporation must have, for each regulated activity for which it is licensed, at least two responsible officers approved by the SFC as such; and at least one of them shall be an executive director of the licensed corporation.
錯誤
every licensed corporation must have, for each regulated activity for which it is licensed, at least two responsible officers approved by the SFC as such; and at least one of them shall be an executive director of the licensed corporation.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.10
-
425/567問題
425. 問題
1 分QID2677:With regards to responsible officers of a licensed corporation, which of the following is correct?
正確
Responsible Officers of a Lincened Corporation may or may not be directors. Its not required that only INED can become a responsible officer of a Licenced Corporation. Only Registered Institutions are required to employ Executive Officers. Each Licenced Corporation must have at least two Responsible Officers.
錯誤
Responsible Officers of a Lincened Corporation may or may not be directors. Its not required that only INED can become a responsible officer of a Licenced Corporation. Only Registered Institutions are required to employ Executive Officers. Each Licenced Corporation must have at least two Responsible Officers.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.10
-
426/567問題
426. 問題
1 分QID1003:Which of the following descriptions about RO is correct?
正確
Licensed corporations should ensure that it has, for each RA, at least one responsible officer available at all times to supervise the business of the RA for which it is licensed, and who is based in Hong Kong.
錯誤
Licensed corporations should ensure that it has, for each RA, at least one responsible officer available at all times to supervise the business of the RA for which it is licensed, and who is based in Hong Kong.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.10
-
427/567問題
427. 問題
1 分QID237:A licensed corporation or registered institution should have
I. at least 2 RO and 1 Executive Director as RO
II. at all times there must be at least 1 executive officer available to supervise the business of the regulated activity
III. at least 1 RO, including 1 an Executive Director as RO
IV. at all times there must be at least 2 executive officer available to supervise the business of the regulated activity正確
Each licensed corporation is required to:
(a) appoint not less than two responsible officers, at least one of whom must be an executivedirector;
(b) ensure that every individual executive director of the licensed corporation is approved as a responsible officer; and
(c) ensure that it has, for each RA, at least one responsible officer available at all times to supervise the business of the RA for which it is licensed, and who is based in Hong Kong.錯誤
Each licensed corporation is required to:
(a) appoint not less than two responsible officers, at least one of whom must be an executivedirector;
(b) ensure that every individual executive director of the licensed corporation is approved as a responsible officer; and
(c) ensure that it has, for each RA, at least one responsible officer available at all times to supervise the business of the RA for which it is licensed, and who is based in Hong Kong.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.10
-
428/567問題
428. 問題
1 分QID236:Which of the following descriptions about the responsible officer of a licensed corporation are CORRECT?
I. Every executive director of a licensed corporation must be
approved by the SFC as a responsible officer.
II. Every licensed corporation must have, for each of the regulated activity for which it is licensed, at least two responsible officers approved by the SFC as such; and at least one of them shall be an executive director of the licensed corporation.
III. Any licensed corporation must carry out various regulated activities according to the license it was issued with; at least one person must be approved by the SFC as a responsible officer for the regulated activity the licensed corporation was issued a license to carry out, and at least one responsible officer must be established as the executive director of the licensed corporation.
IV. If a licensed corporation is licensed to carry out a number of various types of regulated activities, the responsible officer for each activity may not overlap.正確
Each licensed corporation is required to:
(a) appoint not less than two responsible officers, at least one of whom must be an executivedirector;
(b) ensure that every individual executive director of the licensed corporation is approved as a responsible officer; and
(c) ensure that it has, for each RA, at least one responsible officer available at all times to supervise the business of the RA for which it is licensed, and who is based in Hong Kong.錯誤
Each licensed corporation is required to:
(a) appoint not less than two responsible officers, at least one of whom must be an executivedirector;
(b) ensure that every individual executive director of the licensed corporation is approved as a responsible officer; and
(c) ensure that it has, for each RA, at least one responsible officer available at all times to supervise the business of the RA for which it is licensed, and who is based in Hong Kong.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.10
-
429/567問題
429. 問題
1 分QID238:Which of the following descriptions about a registered institution’s
executive office are is/are CORRECT?
I. A registered institution shall appoint at least 2 executive
officers in respect of each type of regulated activity, and there must be at least 1 executive officer available to supervise the business of the regulated activity at all times.
II. A registered institution shall appoint at least 1 executive officer in respect of each type of regulated activity, and there must be at least 1 executive officer available to supervise the business of the regulated activity at all times.
III. All executive officers of a registered institution must be the directors of the registered institution and must be approved by the SFC as responsible officers.
IV. If a registered institution is licensed to carry out many types of regulated activities, the executive officer for each regulated activity must not overlap.正確
There must be at least two executive officers appointed by a registered institution in respect of each type of regulated activity, and at all times there must be at least one executive officer available to supervise the business of the regulated activity.
錯誤
There must be at least two executive officers appointed by a registered institution in respect of each type of regulated activity, and at all times there must be at least one executive officer available to supervise the business of the regulated activity.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.13
-
430/567問題
430. 問題
1 分QID1222:At least how many executive officers should a registered institution have at all times to supervise the business of the RA concerned.
正確
At least two executive officers must be appointed in respect of each type of RA, and at all times there must be at least one executive officer available to supervise the business of the RA concerned.
錯誤
At least two executive officers must be appointed in respect of each type of RA, and at all times there must be at least one executive officer available to supervise the business of the RA concerned.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.13
-
431/567問題
431. 問題
1 分QID241:Why do licensed corporations need to determine the identity of substantial shareholder?
正確
The status of substantial shareholder has special relevance to the application of the licensing regime. A person may not become or continue to be a substantial shareholder of a licensed corporation without first being approved by the SFC.
錯誤
The status of substantial shareholder has special relevance to the application of the licensing regime. A person may not become or continue to be a substantial shareholder of a licensed corporation without first being approved by the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.14
-
432/567問題
432. 問題
1 分QID240:A substantial shareholder of a licensed corporation needs to be approved by the
正確
The status of substantial shareholder has special relevance to the application of the licensing regime. A person may not become or continue to be a substantial shareholder of a licensed corporation without first being approved by the SFC as such (s. 131 and s. 6, Schedule 1, SFO).
錯誤
The status of substantial shareholder has special relevance to the application of the licensing regime. A person may not become or continue to be a substantial shareholder of a licensed corporation without first being approved by the SFC as such (s. 131 and s. 6, Schedule 1, SFO).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.14
-
433/567問題
433. 問題
1 分QID2783:Mr. Ko owns 45% of the voting rights of Kaohsiung Enterprises. Recently Mr. Ko intends to increase his holding of shares of Kaohsiung Enterprises by 10% while Kaohsiung Enterprise holds 15% shares of Kaohsiung Securities, a licensed corporation. Should Mr. Ko obtain SFC’s approval before increasing his Kaohsiung shares holdings?
正確
Since Kaohsiung Enterprises controls more than 10% of Kaohsiung Securities, Kaohsiung Enterprises is the substantial shareholder of Kaohsiung Securities. Mr. Ko controls more than 35% shares of Kaohsiung Enterprises, so he indirectly becomes a substantial shareholder of Kaohsiung Securities.
SFC’s approval is only required if a non-substantial shareholder becomes a substantial shareholder. As Mr. Ko has been a substantial shareholder of Kaohsiung Securities, there is no need for the approval of the SFC.
錯誤
Since Kaohsiung Enterprises controls more than 10% of Kaohsiung Securities, Kaohsiung Enterprises is the substantial shareholder of Kaohsiung Securities. Mr. Ko controls more than 35% shares of Kaohsiung Enterprises, so he indirectly becomes a substantial shareholder of Kaohsiung Securities.
SFC’s approval is only required if a non-substantial shareholder becomes a substantial shareholder. As Mr. Ko has been a substantial shareholder of Kaohsiung Securities, there is no need for the approval of the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.14
-
434/567問題
434. 問題
1 分QID1004:Black Flower Oil has acquired 15% of shares of a licenced corporation, Millionaire Securities, in the past month. Until now, Black Flower Oil and Millionaire Securities have made no notification to the SFC about such acquisition. Is there anything wrong?
正確
One must be approved by the SFC prior to becoming a substantial shareholder of a licenced corporation. Otherwise, it is against the SFO. Anyone with 10% of more of shares in a Licenced Corporation will be considered as a substantial shareholder.
錯誤
One must be approved by the SFC prior to becoming a substantial shareholder of a licenced corporation. Otherwise, it is against the SFO. Anyone with 10% of more of shares in a Licenced Corporation will be considered as a substantial shareholder.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.15
-
435/567問題
435. 問題
1 分QID243:Which of the following is/are substantial shareholders of, Millionaire Securities, a licensed corporation?
I. Mr. Ip, who has a 11% stake of Millionaire Securities.
II. Ms. Chan, who has 20% of the voting power of Millionaire
Securities.
III. Mr. Mok, who was granted the authority to manage the investments of his seriously-ill spouse, Ms. Eu. Ms. Eu has a
30% stake of Millionaire Securities.
IV. Ms. Lau, who inherited her family business, Black Flower Oil. She has a 35% stake of Black Flower Oil and the company holds a 15% stake of Millionaire Securities.正確
A substantial shareholder of a corporation refer to a person who alone or together with his associates:
(a) has an interest of more than 10% of the total number of issued shares of the corporation;
(b) directly or indirectly has more than 10% of the voting power of the corporation at a general meeting; or
© is able to exercise 35% or more of the voting power of another corporation at a general meeting which in turn has more than 10% of the voting power of the corporation at a general meeting.
All of the individuals mentioned in this question comply with one or more of the criteria set for someone to become a substantial shareholder.錯誤
A substantial shareholder of a corporation refer to a person who alone or together with his associates:
(a) has an interest of more than 10% of the total number of issued shares of the corporation;
(b) directly or indirectly has more than 10% of the voting power of the corporation at a general meeting; or
© is able to exercise 35% or more of the voting power of another corporation at a general meeting which in turn has more than 10% of the voting power of the corporation at a general meeting.
All of the individuals mentioned in this question comply with one or more of the criteria set for someone to become a substantial shareholder.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.15
-
436/567問題
436. 問題
1 分QID2664:Miss Mok is a shareholder of a licensed corporation. Since the licesed corporation is buying back its shares, Miss Mok holdings in the company has increased to over 10% which in turn makes her a substantial shareholder. Miss Mok is only aware of this after two weeks, what can she do?
正確
She should notify the SFC in writing within 3 days of becoming aware of such incident.
錯誤
She should notify the SFC in writing within 3 days of becoming aware of such incident.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.18
-
437/567問題
437. 問題
1 分QID189:According to the SFO, an intermediary could mean
I. A Registered Institution
II. A Licensed Corporation
III. A Trust Company
IV. An Authorised Financial Institution正確
Only corporations may become intermediaries. A corporation that obtains a licence will be regarded as a “licensed corporation” unless it is an AFI, in which case it will be regarded as a “registered institution”. Together they are referred to as “intermediaries”.
錯誤
Only corporations may become intermediaries. A corporation that obtains a licence will be regarded as a “licensed corporation” unless it is an AFI, in which case it will be regarded as a “registered institution”. Together they are referred to as “intermediaries”.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.2
-
438/567問題
438. 問題
1 分QID1223:In terms of Type 4 regulated activities, which of the following persons may NOT be exempted and must apply for a license or register to carry out regulated activities?
正確
There are certain persons some of whose activities might otherwise fit the descriptions of Ras listed in Part 1, Schedule 5, SFO, but for the fact that these are specifically excluded from the
definitions of RAs given in Part 2 of the Schedule. Such persons will not need licensing in respect of those activities. They include:
(a) professional accountants, solicitors and counsel conducting Type 4, Type 5, Type 6 or Type 9 Ras that are wholly incidental to their professions;
(d) persons licensed or registered to conduct Type 1 RA who carry out Type 4, Type 6 or Type 9 Ras solely for the purposes of their Type 1 RA (the “wholly incidental” exemption).錯誤
There are certain persons some of whose activities might otherwise fit the descriptions of Ras listed in Part 1, Schedule 5, SFO, but for the fact that these are specifically excluded from the
definitions of RAs given in Part 2 of the Schedule. Such persons will not need licensing in respect of those activities. They include:
(a) professional accountants, solicitors and counsel conducting Type 4, Type 5, Type 6 or Type 9 Ras that are wholly incidental to their professions;
(d) persons licensed or registered to conduct Type 1 RA who carry out Type 4, Type 6 or Type 9 Ras solely for the purposes of their Type 1 RA (the “wholly incidental” exemption).提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
439/567問題
439. 問題
1 分QID1575:Do trust companies that act as trustee for CIS need to apply for license?
正確
When acting strictly in their core capacity as mentioned (e.g. a custodian taking custody of fund assets, or a lawyer advising on fund structure), Other intermediaries involved in the asset management industry include trustees, custodians and professionals such as lawyers, accountants and investment advisers are not engaging in any activity regulated by the SFO.
錯誤
When acting strictly in their core capacity as mentioned (e.g. a custodian taking custody of fund assets, or a lawyer advising on fund structure), Other intermediaries involved in the asset management industry include trustees, custodians and professionals such as lawyers, accountants and investment advisers are not engaging in any activity regulated by the SFO.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
440/567問題
440. 問題
1 分QID2735:In addition to buying and selling securities for clients, Monopoly Securities also provides discretionary account management services and securities margin financing services for clients’ securities accounts. Monopoly Securities can meet regulatory requirements through which of the following combinations of licenses?
I. Type 1 RA Licence
II. Type 9 RA Licence
III. Type 1 RA Licence + Type 9 RA Licence
IV. Type 1 RA Licence + Type 8 RA Licence + Type 9 RA Licence
正確
As securities discretionary management services and securities margin financing services are wholly incidental to securities trading services. Therefore, Monopoly Securities does not need to have a license for type 9 regulated activities (asset management) and type 8 regulated activities (securities margin financing). But it’s perfectly okay to have them as well.
However, a licensed corporation holding a Type 9 regulated activity license only is not permitted to conduct securities trading activities, so this is a wrong answer.
錯誤
As securities discretionary management services and securities margin financing services are wholly incidental to securities trading services. Therefore, Monopoly Securities does not need to have a license for type 9 regulated activities (asset management) and type 8 regulated activities (securities margin financing). But it’s perfectly okay to have them as well.
However, a licensed corporation holding a Type 9 regulated activity license only is not permitted to conduct securities trading activities, so this is a wrong answer.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
441/567問題
441. 問題
1 分QID244:According to the exemption provisions of the SFO, Professional Accountants can conduct regulated activates under which of the following circumstances?
正確
There are certain persons, some of whose activities might otherwise fit the descriptions of regulated activities listed in Part 1, Schedule 5, SFO, but for the fact that these are specifically excluded from the definitions of regulated activities given in Part 2 of the Schedule. Such persons will not need licensing in respect of those activities. They include:
(a) professional accountants, solicitors and counsel conducting Type 4, Type 5, Type 6 and Type 9 regulated activities that are wholly incidental to their professions (see section 1.9 below).錯誤
There are certain persons, some of whose activities might otherwise fit the descriptions of regulated activities listed in Part 1, Schedule 5, SFO, but for the fact that these are specifically excluded from the definitions of regulated activities given in Part 2 of the Schedule. Such persons will not need licensing in respect of those activities. They include:
(a) professional accountants, solicitors and counsel conducting Type 4, Type 5, Type 6 and Type 9 regulated activities that are wholly incidental to their professions (see section 1.9 below).提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
442/567問題
442. 問題
1 分QID353:Mr Wan is a registered representative of type 1 regulated activity of British Construction Bank, a registered institution. Mr Wan is constantly looking out for the portfolios of his retired customers and advises them on stock trading and other asset management activities, these activities are wholly incidental to his type 1 activity. In this case, should Mr Wan apply for a registration or license for the type 9 activities he conducts?
正確
Part V SFO allows licensed persons conducting some regulated activities to conduct certain others, e.g. a Type 1 licence or registration covers Type 4, Type 6 and Type 9 regulated
activities as well if the conducting of those activities is wholly incidental to the conducting of the Type 1 regulated activity.錯誤
Part V SFO allows licensed persons conducting some regulated activities to conduct certain others, e.g. a Type 1 licence or registration covers Type 4, Type 6 and Type 9 regulated
activities as well if the conducting of those activities is wholly incidental to the conducting of the Type 1 regulated activity.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
443/567問題
443. 問題
1 分QID913:Under which of the circumstances is additional licenses not required?
正確
Option A does not say it is a wholly-owned subsidiary;
Option B is to provide futures contract trading services, which is not included in the excluded activities;
Option C holds a Category 8 activity license and does not have exempted activities;
The answer is D.錯誤
Option A does not say it is a wholly-owned subsidiary;
Option B is to provide futures contract trading services, which is not included in the excluded activities;
Option C holds a Category 8 activity license and does not have exempted activities;
The answer is D.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
444/567問題
444. 問題
1 分QID1216:Kaohsiung Trust Company is not required to obtain a license to carry out regulated activities for which of the following?
正確
Trust companies conducting Type 4, Type 5, Type 6 or Type 9 Ras wholly incidental to the discharge of their trustee duties do not need to apply for a license. There is no mention of wholly incidental conduct here, but professional conduct, so A, B, and D require a Securities and Futures Commission license. Real estate does not belong to securities and futures and is not regulated by the Securities and Futures Ordinance.. Real estate are not securities and futures and not regulated by the SFO>
錯誤
Trust companies conducting Type 4, Type 5, Type 6 or Type 9 Ras wholly incidental to the discharge of their trustee duties do not need to apply for a license. There is no mention of wholly incidental conduct here, but professional conduct, so A, B, and D require a Securities and Futures Commission license. Real estate does not belong to securities and futures and is not regulated by the Securities and Futures Ordinance.. Real estate are not securities and futures and not regulated by the SFO>
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
445/567問題
445. 問題
1 分QID2472:Which of the following institution has to apply for an additional license or registration with respect to the Type 2 regulated activity?
正確
Institutions which provide their fully owned subsidiaries with futures trading advice don’t need any license.
For institutions holding a license for Type 9 regulated activities to engage in futures trading as a result of discretionary investment for their clients, they don’t need any additional license or registration as well since futures trading activities is fully accompanied by discretionary activities.
For institutions holding a license for Type 1 regulated activities to trade an ETF which is listed on the SEHK and only trades futures on behalf of their clients, since the target traded is listed ETFs rather than futures, naturally, there is no need to obtain a license or registration with respect to Type 2 regulated activities.
For institutions holding a license for Type 1 regulated activities to engage in futures trading as a result of discretionary investment for their clients, they need an additional license or registration since futures trading activities is not fully accompanied by Type 1 regulated activities.錯誤
Institutions which provide their fully owned subsidiaries with futures trading advice don’t need any license.
For institutions holding a license for Type 9 regulated activities to engage in futures trading as a result of discretionary investment for their clients, they don’t need any additional license or registration as well since futures trading activities is fully accompanied by discretionary activities.
For institutions holding a license for Type 1 regulated activities to trade an ETF which is listed on the SEHK and only trades futures on behalf of their clients, since the target traded is listed ETFs rather than futures, naturally, there is no need to obtain a license or registration with respect to Type 2 regulated activities.
For institutions holding a license for Type 1 regulated activities to engage in futures trading as a result of discretionary investment for their clients, they need an additional license or registration since futures trading activities is not fully accompanied by Type 1 regulated activities.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
446/567問題
446. 問題
1 分QID338:Mr Ko is a client of Kaohsiung Securities, a licensed corporation that carries out type 1 and type 8 activities. Mr Ko frequently trades securities on margin with the accommodation provide by Kaohsiung Securities. Mr Ko is suddenly in need of extra capital. Can Kaohsiung securities provide additional accommodation to Mr Ko?
正確
persons licensed or registered to conduct Type 1 RA who may provide financial accommodation (Type 8 RA) to facilitate acquisitions or holdings of securities by those persons for clients.
錯誤
persons licensed or registered to conduct Type 1 RA who may provide financial accommodation (Type 8 RA) to facilitate acquisitions or holdings of securities by those persons for clients.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
447/567問題
447. 問題
1 分QID746:Which of the following regulated activities can be carried out by holding a Type 1 regulated activity license?
I. Type 4 activity wholly incidental to Type 1
II. Type 5 activity wholly incidental to Type 1
III. Type 6 activity wholly incidental to Type 1
IV. Type 9 activity wholly incidental to Type 1正確
Regulated activities 4, 6 or 9 will be permitted if wholly incidental to Type 1.
錯誤
Regulated activities 4, 6 or 9 will be permitted if wholly incidental to Type 1.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
448/567問題
448. 問題
1 分QID345:Which of the following persons are excluded from the definition of “securities or futures management”?
I. corporations that carry on securities or futures contracts management solely for their wholly owned subsidiaries, their holding companies which hold all their issued shares, or other wholly owned subsidiaries of the latter
II. persons licensed to deal in securities and/or futures contracts
(i.e. licensed for Type 1 and/or Type 2 regulated activity), who carry out securities or futures contracts management as an activity wholly incidental to the licensed activity
III. Solicitors, counsel (barristers), professional accountants and trustees who provide securities or futures contracts management services wholly incidental to their professional practices.
IV. Auditors and professionals who provide securities or futures contracts management services.正確
Part V, SFO provides for the implementation of the licensing regime, including:
(a) allowing licensed persons conducting some regulated activities to conduct certain others, e.g. a Type 1 licence or registration covers Type 4, Type 6 and Type 9 regulated activities as well if the conducting of those activities is wholly incidental to the conducting of the Type 1 regulated activity;
(b) professional accountants, solicitors and counsel conducting Type 4, Type 5, Type 6 and Type 9 regulated activities that are wholly incidental to their professions and also;
(c.) corporations carrying out Type 4, Type 5, Type 6 and Type 9 regulated activities solely for their wholly owned subsidiaries, holding companies holding all their issued shares or other wholly owned subsidiaries of the holding company.錯誤
Part V, SFO provides for the implementation of the licensing regime, including:
(a) allowing licensed persons conducting some regulated activities to conduct certain others, e.g. a Type 1 licence or registration covers Type 4, Type 6 and Type 9 regulated activities as well if the conducting of those activities is wholly incidental to the conducting of the Type 1 regulated activity;
(b) professional accountants, solicitors and counsel conducting Type 4, Type 5, Type 6 and Type 9 regulated activities that are wholly incidental to their professions and also;
(c.) corporations carrying out Type 4, Type 5, Type 6 and Type 9 regulated activities solely for their wholly owned subsidiaries, holding companies holding all their issued shares or other wholly owned subsidiaries of the holding company.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
449/567問題
449. 問題
1 分QID349:Under the “Securities and Futures Ordinance”, which of the following licensed or registered persons providing asset management services do not need to obtain an additional license for their regulated activities?
I. Securities margin financing activities conducted by a licensed corporation.
II. Securities trading activities conducted by a registered institution.
III. Futures contract trading activities conducted by a licensed corporation.
IV. Opinions provided by registered personnel on securities trading activities.正確
Persons licensed or registered to conduct Type 9 regulated activity who carry out Type1, Type 2, Type 4 and Type 5 regulated activities solely for the purposes of their Type 9 regulated activity will not need licensing in respect of those activities.
錯誤
Persons licensed or registered to conduct Type 9 regulated activity who carry out Type1, Type 2, Type 4 and Type 5 regulated activities solely for the purposes of their Type 9 regulated activity will not need licensing in respect of those activities.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
450/567問題
450. 問題
1 分QID1608:Kaohsiung Securities trades Hong Kong stocks for clients. It carries a type 1 licence and is also an exchange participant. It recently wishes to providing financing to clients for their purchase of stocks in return for clients’ stocks as collaterals, does it need an extra licence?
正確
There are certain persons some of whose activities might otherwise fit the descriptions of Ras listed in Part 1, Schedule 5, SFO, but for the fact that these are specifically excluded from the definitions of RAs given in Part 2 of the Schedule. Such persons will not need licensing in respect of those activities. They include:
(e.) persons licensed or registered to conduct Type 1 RA who may provide financial accommodation (Type 8 RA) to facilitate acquisitions or holdings of securities by those persons for clients.
Therefore, answer A is correct.錯誤
There are certain persons some of whose activities might otherwise fit the descriptions of Ras listed in Part 1, Schedule 5, SFO, but for the fact that these are specifically excluded from the definitions of RAs given in Part 2 of the Schedule. Such persons will not need licensing in respect of those activities. They include:
(e.) persons licensed or registered to conduct Type 1 RA who may provide financial accommodation (Type 8 RA) to facilitate acquisitions or holdings of securities by those persons for clients.
Therefore, answer A is correct.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
451/567問題
451. 問題
1 分QID2861:If a company is licensed to run Type 1 actvity is running Type 9 activity, is there a problem?
正確
If the conductino of Type 9 Activity is wholly incidental to its Type 1 Activity, its not illegal. They are persons specifically excluded from the definition of securities or futures contracts management
錯誤
If the conductino of Type 9 Activity is wholly incidental to its Type 1 Activity, its not illegal. They are persons specifically excluded from the definition of securities or futures contracts management
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
452/567問題
452. 問題
1 分QID799:Trust companies can be exempted from licensing if they conduct which of the following regulated activities wholly incidental to their trustee duties?
I. Dealing in securities
II. Advising on securities
III. Advising on futures contracts
IV. Asset management正確
There are certain persons some of whose activities might otherwise fit the descriptions of regulated activities listed in Part 1, Schedule 5, SFO, but for the fact that these are specifically excluded from the definitions of regulated activities given in Part 2 of the Schedule. Such persons will not need licensing in respect of those activities. They include:
– trust companies conducting Type 4, Type 5, Type 6 and Type 9 regulated activities wholly incidental to the discharge of their trustee duties.錯誤
There are certain persons some of whose activities might otherwise fit the descriptions of regulated activities listed in Part 1, Schedule 5, SFO, but for the fact that these are specifically excluded from the definitions of regulated activities given in Part 2 of the Schedule. Such persons will not need licensing in respect of those activities. They include:
– trust companies conducting Type 4, Type 5, Type 6 and Type 9 regulated activities wholly incidental to the discharge of their trustee duties.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
453/567問題
453. 問題
1 分QID2473:Kaohsiung Securities holds a license for Type 2 regulated activities. In which of the following condition should they obtain a license for Type 5 regulated activities when delivering advice?
正確
Providing advice regarding futures trading with friends and charging a fee independently proves that it’s not solely associated with Type 2 regulated activities. Therefore, it is needed to obtain an additional license for Type 5 regulated activities.
錯誤
Providing advice regarding futures trading with friends and charging a fee independently proves that it’s not solely associated with Type 2 regulated activities. Therefore, it is needed to obtain an additional license for Type 5 regulated activities.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
454/567問題
454. 問題
1 分QID2682:If a solicitor is conducting a Type 4 acitivity, should he/she apply for a licence?
正確
As long as its wholly incidental to his/her professional capacity, solicitors are not require to apply for a licence for conducting Type 4,5,6,9 activities.
錯誤
As long as its wholly incidental to his/her professional capacity, solicitors are not require to apply for a licence for conducting Type 4,5,6,9 activities.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.21
-
455/567問題
455. 問題
1 分QID1224:A company can apply for a temporary licence under the SFO if they can satisfy which of the following conditions?
I. A company that principally carries on its business overseas.
II. A company that conducts certain specified SFC regulated activities (including Type 1 and Type 4 regulated activities) in Hong Kong.
III. A company that conducts certain specified SFC regulated activities (including Type 2 and Type 5 regulated activities) in Hong Kong.
IV. The total period for which temporary licences can be held by the same person may not exceed six months over a 24-month period.正確
The SFC may grant a temporary licence for a period not exceeding three months, subject to conditions, to a corporation which principally carries on its business overseas, allowing it to conduct one or more than one RA (other than Type 3, Type 7, Type 8 and Type 9 Ras) in Hong Kong. Representatives of licensed and temporarily licensed corporations may be given temporary licences for a period not exceeding three months for the same purpose. The total period for which temporary licences can be held by the same person may not exceed six months over a 24-month period.
錯誤
The SFC may grant a temporary licence for a period not exceeding three months, subject to conditions, to a corporation which principally carries on its business overseas, allowing it to conduct one or more than one RA (other than Type 3, Type 7, Type 8 and Type 9 Ras) in Hong Kong. Representatives of licensed and temporarily licensed corporations may be given temporary licences for a period not exceeding three months for the same purpose. The total period for which temporary licences can be held by the same person may not exceed six months over a 24-month period.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.22
-
456/567問題
456. 問題
1 分QID1664:British Construction Securities is a foreign company, it has to conduct a series of securities transactions for clients in Hong Kong. These transactions will happen in a course of 2 months, these activities are all Type 1 activities. Should British Construction Securities apply for a license or registration in Hong Kong.
正確
The SFC may grant a temporary licence for a period not exceeding three months, subject to
conditions, to a corporation which principally carries on its business overseas, allowing it to
conduct one or more than one RA (other than Type 3, Type 7, Type 8 and Type 9 RAs) in Hong
Kong.
Because the activity period is less than 3 months, British Construction Securities should obtain a short-term license.錯誤
The SFC may grant a temporary licence for a period not exceeding three months, subject to
conditions, to a corporation which principally carries on its business overseas, allowing it to
conduct one or more than one RA (other than Type 3, Type 7, Type 8 and Type 9 RAs) in Hong
Kong.
Because the activity period is less than 3 months, British Construction Securities should obtain a short-term license.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.22
-
457/567問題
457. 問題
1 分QID247:British Construction Securities is a securities broker of the UK. It wishes to conduct a series of bond dealing in Hong Kong on behalf of a client for a period of less than 3 months. Should British Construction Securities register or apply for a licence?
正確
The Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) may grant a temporary licence, subject to conditions, to a corporation which principally carries on its business overseas, allowing it to conduct one or more than one regulated activity (other than Type 3 and Type 7 to Type 9 regulated activities) in Hong Kong.
Therefore, if British Construction Securities wishes to come to Hong Kong to carry out a series of bond transactions for its clients, it can apply to the SFC for a temporary licence for Type 1 regulated activities.
錯誤
The Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) may grant a temporary licence, subject to conditions, to a corporation which principally carries on its business overseas, allowing it to conduct one or more than one regulated activity (other than Type 3 and Type 7 to Type 9 regulated activities) in Hong Kong.
Therefore, if British Construction Securities wishes to come to Hong Kong to carry out a series of bond transactions for its clients, it can apply to the SFC for a temporary licence for Type 1 regulated activities.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.22
-
458/567問題
458. 問題
1 分QID173:Kaohsiung Finance is the subsidiary of an overseas bank and operates mainly overseas. Recently, the company was appointed by Vita Milk, a listed company in Hong Kong, to provide advice on corporate finance activities such as takeovers and mergers. What is the most appropriate manner for Kaohsiung Finance to deal with the matter?
正確
The SFC may grant a temporary licence for a period not exceeding three months, subject to conditions, to a corporation which principally carries on its business overseas, allowing it to
conduct one or more than one regulated activity (other than Type 3 and Type 7 to Type 9 regulated activities) in Hong Kong. Representatives of licensed and temporary licensed corporations may be given temporary licences for a period not exceeding three months for the same purpose. The total period for which temporary licences can be held by the same person may not exceed six months over a 24-month period.錯誤
The SFC may grant a temporary licence for a period not exceeding three months, subject to conditions, to a corporation which principally carries on its business overseas, allowing it to
conduct one or more than one regulated activity (other than Type 3 and Type 7 to Type 9 regulated activities) in Hong Kong. Representatives of licensed and temporary licensed corporations may be given temporary licences for a period not exceeding three months for the same purpose. The total period for which temporary licences can be held by the same person may not exceed six months over a 24-month period.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.22
-
459/567問題
459. 問題
1 分QID2582:Which of the following company can apply for a temporary licence?
正確
The SFC has the right to grant a temporary license for a period not exceeding three months to a company who is based outside Hong Kong and the total period allowed should not exceed 6 months within 24 months.
錯誤
The SFC has the right to grant a temporary license for a period not exceeding three months to a company who is based outside Hong Kong and the total period allowed should not exceed 6 months within 24 months.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.22
-
460/567問題
460. 問題
1 分QID2681:Which of the following description is correct regarding temporary licence?
正確
Temporary Licence can last at most 3 months, its applicable to companies and individuals operating outside of Hong Kong. The validity of a Temporary Licence cannot surpass 6 months within 24 months. It will not be granted to companies operating in Hong Kong.
錯誤
Temporary Licence can last at most 3 months, its applicable to companies and individuals operating outside of Hong Kong. The validity of a Temporary Licence cannot surpass 6 months within 24 months. It will not be granted to companies operating in Hong Kong.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.22
-
461/567問題
461. 問題
1 分QID999:Mr Liu has advertised himself in multiple newspapers in Hong Kong. He claimed to be a futures contracts expert and can assist clients in dealing with foreign futures contracts. As a matter of fact, Mr Liu was not licenced by or registered with the SFC. Had he done anything wrong?
正確
To advertise oneself as operating a regulated activity is the same as operating a regulated activity. Conducting a regulated activity without licence or registration is against the SFO.
錯誤
To advertise oneself as operating a regulated activity is the same as operating a regulated activity. Conducting a regulated activity without licence or registration is against the SFO.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.24
-
462/567問題
462. 問題
1 分QID231:Conducting asset management activities without holding a valid SFC licence is a?
正確
The SFC licenses and supervises intermediaries engaged in asset management (Type 9 regulated activity) as well as others engaged in providing advisory services in the industry (Type 4 and Type 5 regulated activities).
In other words, engaging in asset management requires obtaining a license from the SFC. Engaging in asset management without a license will violate the Securities and Futures Ordinance and is illegal.錯誤
The SFC licenses and supervises intermediaries engaged in asset management (Type 9 regulated activity) as well as others engaged in providing advisory services in the industry (Type 4 and Type 5 regulated activities).
In other words, engaging in asset management requires obtaining a license from the SFC. Engaging in asset management without a license will violate the Securities and Futures Ordinance and is illegal.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.3
-
463/567問題
463. 問題
1 分QID1213:Which of the following are regulated activities under the SFO?
I. Type 7: Providing ATS
II. Type 8: SMF
III. Type 9: futures portfolio management
IV. Type 10: providing credit rating services正確
Type 7: providing ATS;
Type 8: SMF;
Type 9: asset management; and
Type 10: providing credit rating services.錯誤
Type 7: providing ATS;
Type 8: SMF;
Type 9: asset management; and
Type 10: providing credit rating services.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.4
-
464/567問題
464. 問題
1 分QID180:“Asset Management” is a type of which of the following regulated activity?
正確
There are ten distinct types of regulated activity (see Schedule 5, SFO):
Type 9: asset management.錯誤
There are ten distinct types of regulated activity (see Schedule 5, SFO):
Type 9: asset management.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.4
-
465/567問題
465. 問題
1 分QID181:Which of the followings is not a regulated activities as defined by the SFO?
正確
There are ten distinct types of regulated activity (see Schedule 5, SFO):
Type 3: leveraged foregin exchange trading
Type 9: asset management.
Therefor,The correct number for option C is 9.錯誤
There are ten distinct types of regulated activity (see Schedule 5, SFO):
Type 3: leveraged foregin exchange trading
Type 9: asset management.
Therefor,The correct number for option C is 9.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.4
-
466/567問題
466. 問題
1 分QID333:Which of the following activities is not a case of Type 2 or Type 5 Activities?
正確
Any activities that are not conducted on behalf of others cannot be a regulated activity.
錯誤
Any activities that are not conducted on behalf of others cannot be a regulated activity.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.4
-
467/567問題
467. 問題
1 分QID183:Registration or licensing is required for which of the following activities in accordance with the Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO)?
正確
Part V specifies that any person who carries on or holds himself out as carrying on the business of a “regulated activity” commits an offence unless that person is appropriately licensed by or registered with the SFC, or that person/activity fits within an applicable exemption.
There are ten distinct types of regulated activity (see Schedule 5, SFO):
Type 7: providing automated trading services.錯誤
Part V specifies that any person who carries on or holds himself out as carrying on the business of a “regulated activity” commits an offence unless that person is appropriately licensed by or registered with the SFC, or that person/activity fits within an applicable exemption.
There are ten distinct types of regulated activity (see Schedule 5, SFO):
Type 7: providing automated trading services.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.4
-
468/567問題
468. 問題
1 分QID1215:Which of the following is NOT a regulated activity under the SFO?
正確
Type 3 is leveraged foreign exchange trading.
錯誤
Type 3 is leveraged foreign exchange trading.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.4
-
469/567問題
469. 問題
1 分QID2587:Does inducing or attempting to induce another person to acquire a futures contract need a license?
正確
Induces or attempting to induce another person to enter into, acquire or dispose of a futures
contract is one of the definitions of dealing in futures contracts, thus, a type 2 regulated activity license is required. Answer D is only partly correct. If that person accepts benefits from that friend or family member, it would make the activity a regulated activity.錯誤
Induces or attempting to induce another person to enter into, acquire or dispose of a futures
contract is one of the definitions of dealing in futures contracts, thus, a type 2 regulated activity license is required. Answer D is only partly correct. If that person accepts benefits from that friend or family member, it would make the activity a regulated activity.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.4
-
470/567問題
470. 問題
1 分QID224:Yellow River Investment Limited is a company which conducts type 9 Regulated activity as defined by the SFO, which of the following entities should be licensed by the SFC?
I. Yellow River Investment Limited
II. The Executive Directors of Yellow River Trading
III. Staff that conducts type 9 activity
IV. All Staff of Yellow River Investment Limited正確
Assets management is type 9 regulated activity; therefore, carrying out this kind of activity requires a licence. An Executive Director of a company must be a responsible officer, and responsible officer needs to be licensed; therefore, the Executive Directors of Yellow River Trading must carry a licence.
錯誤
Assets management is type 9 regulated activity; therefore, carrying out this kind of activity requires a licence. An Executive Director of a company must be a responsible officer, and responsible officer needs to be licensed; therefore, the Executive Directors of Yellow River Trading must carry a licence.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.5
-
471/567問題
471. 問題
1 分QID27:Which of the following descriptions about intermediaries are correct?
I. Licensed Corporations are licensed by and supervised by the SFC.
II. Authorised Financial Institutions must register with the SFC in order to conduct regulated activities.
III. Registered Institutions need to comply with some of the codes and guidelines issued by the SFC.
IV. Registered Institutions need to be registered with the company registry.正確
The SFC licenses corporations that conduct one or more regulated activities (“licensed corporations”).
AFIs (including banks) authorised and regulated by the HKMA and conducting SFC-regulated activities must be registered with the SFC as “Registered Institutions.” They are jointly regulated by the HKMA and the SFC, with the HKMA being the front-line regulator that will apply all SFC regulatory criteria, including fitness and properness and business
conduct, other than capital adequacy, the handling of client money, and the audit requirements in supervising them.錯誤
The SFC licenses corporations that conduct one or more regulated activities (“licensed corporations”).
AFIs (including banks) authorised and regulated by the HKMA and conducting SFC-regulated activities must be registered with the SFC as “Registered Institutions.” They are jointly regulated by the HKMA and the SFC, with the HKMA being the front-line regulator that will apply all SFC regulatory criteria, including fitness and properness and business
conduct, other than capital adequacy, the handling of client money, and the audit requirements in supervising them.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.6
-
472/567問題
472. 問題
1 分QID176:Which of the following institutions is required to become a “registered institution”?
正確
The provisions of the SFO have different applications to the following different classes of person:
(b) “registered institution”, which refers to authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”) directly supervised by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (“HKMA”) and registered with the SFC.錯誤
The provisions of the SFO have different applications to the following different classes of person:
(b) “registered institution”, which refers to authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”) directly supervised by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (“HKMA”) and registered with the SFC.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.6
-
473/567問題
473. 問題
1 分QID228:If an AFI wishes to conduct regulated activities as defined by the SFO, which of the following entities should it approach for registration?
正確
AFIs (including banks) that are authorised and regulated by the HKMA and conduct the SFC regulated activities must be registered with the SFC as “Registered Institutions”, such status having been set up as a special category because of the special features of AFIs.
錯誤
AFIs (including banks) that are authorised and regulated by the HKMA and conduct the SFC regulated activities must be registered with the SFC as “Registered Institutions”, such status having been set up as a special category because of the special features of AFIs.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.6
-
474/567問題
474. 問題
1 分QID25:British Construction Bank is an authorised financial institution (AFI). Due to the rapid development of the securities markets, the company plans to provide securities trading services to its customer. How should the company proceed?
正確
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.
錯誤
Under the SFO and the Banking Ordinance, authorised financial institutions (“AFIs”), which are regulated by the HKMA and include banks, have to be registered with the SFC as registered institutions if they wish to carry out an SFC-regulated activity. As the frontline regulator of AFIs is the HKMA, the latter takes the leading role in vetting applications for such registration and in supervising their SFC-regulated activities, including carrying out on-site inspections. The HKMA applies all SFC criteria, such as the “fit and proper” criteria, in supervising AFIs registered with the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.6
-
475/567問題
475. 問題
1 分QID232:Which entity is primarily responsible for the regulation of an authorized financial institution that intends to carry out one or more regulated activities under the SFO?
正確
AFIs (including banks) that are authorised and regulated by the HKMA and conduct the SFC regulated activities must be registered with the SFC as “Registered Institutions”, such status having been set up as a special category because of the special features of AFIs. They are jointly regulated by the HKMA and the SFC, with the HKMA being the front-line regulator that will apply all SFC regulatory criteria, including fitness and properness and business conduct, other than capital adequacy, the handling of client money and the audit requirements in supervising them.
錯誤
AFIs (including banks) that are authorised and regulated by the HKMA and conduct the SFC regulated activities must be registered with the SFC as “Registered Institutions”, such status having been set up as a special category because of the special features of AFIs. They are jointly regulated by the HKMA and the SFC, with the HKMA being the front-line regulator that will apply all SFC regulatory criteria, including fitness and properness and business conduct, other than capital adequacy, the handling of client money and the audit requirements in supervising them.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.6
-
476/567問題
476. 問題
1 分QID1570:Do AFI’s who are trying to conduct regulated activities need to be licensed or registered?
正確
The position is slightly different for AFIs (such as banks) which are also regulated by the HKMA. Where an AFI wishes to engage in one or more regulated activities, it needs to be registered with the SFC.
錯誤
The position is slightly different for AFIs (such as banks) which are also regulated by the HKMA. Where an AFI wishes to engage in one or more regulated activities, it needs to be registered with the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.6
-
477/567問題
477. 問題
1 分QID1217:Are registered institutions required to comply with the SFC’s regulatory criteria, including Fitness and Properness and Business Conduct?
正確
AFIs (including banks) are jointly regulated by the
HKMA and the SFC, with the HKMA being the front-line regulator that will apply all SFC regulatory criteria, including fitness and properness and business conduct, other than capital
adequacy, the handling of client money and the audit requirements in supervising them.錯誤
AFIs (including banks) are jointly regulated by the
HKMA and the SFC, with the HKMA being the front-line regulator that will apply all SFC regulatory criteria, including fitness and properness and business conduct, other than capital
adequacy, the handling of client money and the audit requirements in supervising them.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.6 and 1.9.21
-
478/567問題
478. 問題
1 分QID248:Mr Ko has been an executive director of a licensed corporation -Kaohsiung Securities for a long time. Recently, Mr Ko has ceased to become an INED of Kaohsiung. When should he or Kaohsiung report the event to the SFC?
正確
Where a person becomes or ceases to be a director of a licensed corporation, both the person and the corporation shall, within 7 business days thereafter, notify the Commission in writing of the name and address of the person and of the nature of the position which he occupies or has ceased to occupy (as the case may be).
錯誤
Where a person becomes or ceases to be a director of a licensed corporation, both the person and the corporation shall, within 7 business days thereafter, notify the Commission in writing of the name and address of the person and of the nature of the position which he occupies or has ceased to occupy (as the case may be).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.8
-
479/567問題
479. 問題
1 分QID2770:If a licensed representative ceases to be employed, within how many days can the licensed representative be transferred to another licensed corporation?
正確
If the licensed representative’s employment is terminated, the licensed representative may transfer to another licensed corporation within 180 days.
錯誤
If the licensed representative’s employment is terminated, the licensed representative may transfer to another licensed corporation within 180 days.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.8
-
480/567問題
480. 問題
1 分QID2769:If the licensed representative’s employment is terminated, within how many business days should the licensed corporation notify the SFC?
正確
If the licensed representative ceases to be employed, the licensed corporation shall notify the SFC within 7 business days.
錯誤
If the licensed representative ceases to be employed, the licensed corporation shall notify the SFC within 7 business days.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.8
-
481/567問題
481. 問題
1 分QID234:If a licensed representative ceased to be employed with his accredited licensed corporation, which of the following statements CORRECTLY describes the transfer of representative’s accreditation?
I. Both the representative and the corporation must notify the
SFC within 7 days after the cessation.
II. The licensed representative is allowed to transfer his accreditation to another licensed corporation within 180 days upon cessation.
III. If the licensed representative fails to transfer his accreditation to another licensed corporation after 180 days, his license is deemed to have been revoked upon cessation.
IV. The licensed representative may appeal against the termination
of his appointment and have his license restored.正確
If a licensed representative ceases to be employed with his accredited licensed corporation, both the representative and the corporation must notify the SFC within seven business days
after the cessation. The licensed representative is allowed 180 days for transfer of his accreditation to another licensed corporation, failing which his licence is deemed to have
been revoked upon such cessation.錯誤
If a licensed representative ceases to be employed with his accredited licensed corporation, both the representative and the corporation must notify the SFC within seven business days
after the cessation. The licensed representative is allowed 180 days for transfer of his accreditation to another licensed corporation, failing which his licence is deemed to have
been revoked upon such cessation.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.8
-
482/567問題
482. 問題
1 分QID229:If a registered representative wishes to become a responsible officer, it should
I. Obtain nomination from the SFC to become a RO
II. Obtain nomination from his principal to become an RO
III. Obtain approval of the SFC to become an RO
IV. Obtain approval of his principal to become an RO正確
A responsible officer is a licensed representative who
(ii) is nominated by the licensed corporation as a responsible officer, and
(iii) is approved by the SFC as a responsible officer.錯誤
A responsible officer is a licensed representative who
(ii) is nominated by the licensed corporation as a responsible officer, and
(iii) is approved by the SFC as a responsible officer.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.9
-
483/567問題
483. 問題
1 分QID1220:A responsible officer of regulated activities carried out by a licensed corporation needs to be:
I. nominated by the licensed corporation.
II. approved by the SFC.
III. approved by the HKMA.
IV. approved by the HKEX.正確
A responsible officer is a licensed representative who:
(a) actively participates in or supervises a RA;
(b) is nominated by the licensed corporation as a responsible officer; and
(c.) is approved by the SFC as a responsible officer.錯誤
A responsible officer is a licensed representative who:
(a) actively participates in or supervises a RA;
(b) is nominated by the licensed corporation as a responsible officer; and
(c.) is approved by the SFC as a responsible officer.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.9
-
484/567問題
484. 問題
1 分QID1219:A responsible officer is a licensed representative; his duties include:
I. being nominated by the licensed corporation as a responsible officer.
II. being approved by the SFC as a responsible officer.
III. being approved by the HKMA as a responsible officer.
IV. actively participating in or supervising a regulated activity.正確
A responsible officer is a licensed representative who:
(a) actively participates in or supervises a RA;
(b) is nominated by the licensed corporation as a responsible officer; and
(c.) is approved by the SFC as a responsible officer.錯誤
A responsible officer is a licensed representative who:
(a) actively participates in or supervises a RA;
(b) is nominated by the licensed corporation as a responsible officer; and
(c.) is approved by the SFC as a responsible officer.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.9
-
485/567問題
485. 問題
1 分QID862:Which of the following statements correctly describes responsible officers?
正確
A responsible officer is a licensed representative who (i) actively participates in or supervises a regulated activity, (ii) is nominated by the licensed corporation as a responsible officer, and (iii) is approved by the SFC as a responsible officer. The definition of
responsible officer as given here is not stated in the SFO but has been provided by the SFC.錯誤
A responsible officer is a licensed representative who (i) actively participates in or supervises a regulated activity, (ii) is nominated by the licensed corporation as a responsible officer, and (iii) is approved by the SFC as a responsible officer. The definition of
responsible officer as given here is not stated in the SFO but has been provided by the SFC.提示
Reference Chapter:1.7.9
-
486/567問題
486. 問題
1 分QID3:The SFO is applicable to the primary business of which of the following individuals?
I. Fund Managers
II. Money Lenders
III. The Hong Kong Mortgage Corporation
IV. Professional Options Trader正確
The SFO is not applicable to money lenders and The Hong Kong Mortgage Corporation, as these operations are unrelated to securities and futures. Despite the fact that money lending is an integral part of the financial markets, money lending itself is not related to securities and futures.
The primary business of The Hong Kong Mortgage Corporation is administering the mortgage insurance program which by itself is not related to securities and futures.錯誤
The SFO is not applicable to money lenders and The Hong Kong Mortgage Corporation, as these operations are unrelated to securities and futures. Despite the fact that money lending is an integral part of the financial markets, money lending itself is not related to securities and futures.
The primary business of The Hong Kong Mortgage Corporation is administering the mortgage insurance program which by itself is not related to securities and futures.提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.1
-
487/567問題
487. 問題
1 分QID656:What is the relationship between the SFC and trustees/custodians of authorised funds?
正確
Trustees/custodians are unusual in the SFC’s regulatory regime as their activities are not “regulated activities” under the SFO, and they are not therefore required to be licensed by or registered with the SFC. However, the SFC does exercise a degree of regulatory oversight through requirements placed on the users of trustees/custodians, such as authorised CISs: for a CIS to obtain authorisation, it must have a trustee/custodian which is acceptable to the SFC.
錯誤
Trustees/custodians are unusual in the SFC’s regulatory regime as their activities are not “regulated activities” under the SFO, and they are not therefore required to be licensed by or registered with the SFC. However, the SFC does exercise a degree of regulatory oversight through requirements placed on the users of trustees/custodians, such as authorised CISs: for a CIS to obtain authorisation, it must have a trustee/custodian which is acceptable to the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.10
-
488/567問題
488. 問題
1 分QID806:In terms of Type 1 regulated activity (namely securities trading), persons licensed or registered may include which of the following individuals and institutions?
I. Stock exchange participants, whether it engages in activities on the SEHK or outside it.
II. An AFI registered with the SFC for this activity.
III. A portfolio manager who is licensed (as a securities dealer) for Type 1 regulated activity.
IV. A securities introducing agent.正確
The categories of persons conducting Type 1 regulated activity include:
(a) a participant of the SEHK, whether it engages in activities on the SEHK or outside it;
(b) another securities dealer carrying out dealing in securities in Hong Kong;
(c.) a licensed representative of the above;
(d) an AFI registered with the SFC for this activity (and its staff who deal with the public and are on a register maintained by the HKMA as engaged in such activity);
(e.) a portfolio manager who is licensed (as a securities dealer) for Type 1 regulated activity; and
(f) a securities introducing agent.錯誤
The categories of persons conducting Type 1 regulated activity include:
(a) a participant of the SEHK, whether it engages in activities on the SEHK or outside it;
(b) another securities dealer carrying out dealing in securities in Hong Kong;
(c.) a licensed representative of the above;
(d) an AFI registered with the SFC for this activity (and its staff who deal with the public and are on a register maintained by the HKMA as engaged in such activity);
(e.) a portfolio manager who is licensed (as a securities dealer) for Type 1 regulated activity; and
(f) a securities introducing agent.提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.12
-
489/567問題
489. 問題
1 分QID329:Mr Wan wishes to set up a company. The company will help Mr Wan’s friend, Mr Ko who resides in Japan to deal in foreign securities. The company will charge a symbolic commission. Should the company apply for a licence with the SFC?
正確
Dealing in securities for the purposes of the SFC licensing regime will include dealing in securities traded on the SEHK and other securities, where the activity is conducted in Hong Kong.
錯誤
Dealing in securities for the purposes of the SFC licensing regime will include dealing in securities traded on the SEHK and other securities, where the activity is conducted in Hong Kong.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.12
-
490/567問題
490. 問題
1 分QID330:Mr Ko is an asset manager working for Kaohsiung Securities, A licensed corporation. Mr Ko has managed a number of CIS, mostly bond funds. Mr Wan is a seasoned investor who has invested in funds that were managed by Mr Ko for a long time. He trusted Mr Ko and ask if Mr Ko can handle his personal investment which includes securities and futures. Mr Ko does not have enough time to manage Mr Wan’s portfolio and thus refer Stock broker from another company Mr Ip to handle Mr Wan’s request. Mr Wan then invests heavily with Mr Ip and has generated a substantial amount of commission for Mr Ip. Mr Ip thus promised to pay Mr Ko some introductory fee and Mr Ko agreed to it. Should Mr Ko apply for a licence for Type 1 regulated activity in this case?
正確
One of the categories of persons conducting Type 1 regulated activity according to the SFC includes:
(f) a securities introducing agent.錯誤
One of the categories of persons conducting Type 1 regulated activity according to the SFC includes:
(f) a securities introducing agent.提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.12
-
491/567問題
491. 問題
1 分QID1225:Which of the following persons or institutions are very likely to be licensed or registered to carry out Type 1 regulated activity?
I. Exchange Participants.
II. Registered Institutions.
III. A brokerage firm in Hong Kong.
IV. A securities introducing agent.正確
To conclude this initial definition section, the categories of persons conducting Type 1 RA
include:
(a) a participant of the SEHK, whether it engages in activities on the SEHK or outside it;
(d) an AFI registered with the SFC for this activity (and its staff who deal with the public and are on a register maintained by the HKMA as engaged in such activity);
(e.) a portfolio manager who is licensed (as a securities dealer) for Type 1 RA; and
(f) a securities introducing agent.錯誤
To conclude this initial definition section, the categories of persons conducting Type 1 RA
include:
(a) a participant of the SEHK, whether it engages in activities on the SEHK or outside it;
(d) an AFI registered with the SFC for this activity (and its staff who deal with the public and are on a register maintained by the HKMA as engaged in such activity);
(e.) a portfolio manager who is licensed (as a securities dealer) for Type 1 RA; and
(f) a securities introducing agent.提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.12
-
492/567問題
492. 問題
1 分QID2377:Which of the following activity is required to register for Type 1 license?
正確
Providing advice for clients on real estate investment and buying insurance are not regulated activities. Introducing clients to open an account at securities company, and earning money belongs to introducing agents, which is required to register for Type 1 licence. Providing advice for clients on suggestions to trade futures, and earning money belongs to Type 5 activities.
錯誤
Providing advice for clients on real estate investment and buying insurance are not regulated activities. Introducing clients to open an account at securities company, and earning money belongs to introducing agents, which is required to register for Type 1 licence. Providing advice for clients on suggestions to trade futures, and earning money belongs to Type 5 activities.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.16
-
493/567問題
493. 問題
1 分QID810:M.D. Yu is a seasoned and successful investor. She always brags about her investment track record to her friends. Her friends have provided M.D. Yu with “Tea Money” (Cash for sundry expenses) and have asked M.D. Yu to refer her stock broker to them, allowing them to replicate M.D. Yu’s success. If M.D. Yu agrees to this practice, should M.D. Yu apply for a licence for these activities?
正確
M.D. Yu should apply for a Type 1 License because she is acting as a securities introducing agent by referring her friends to her stock broker. This activity falls under Type 1 regulated activity (dealing in securities) as per the Securities and Futures Ordinance. Therefore, she needs a Type 1 License to legally conduct these activities.
錯誤
M.D. Yu should apply for a Type 1 License because she is acting as a securities introducing agent by referring her friends to her stock broker. This activity falls under Type 1 regulated activity (dealing in securities) as per the Securities and Futures Ordinance. Therefore, she needs a Type 1 License to legally conduct these activities.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.16
-
494/567問題
494. 問題
1 分QID2858:Is a licence required for holding securities for clients?
正確
A licence is not required for holding securities for clients since its not a regulated activity.
錯誤
A licence is not required for holding securities for clients since its not a regulated activity.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.2
-
495/567問題
495. 問題
1 分QID327:The definition of “securities” is extensive and includes
I. Shares, Bonds, Debentures
II. Interests, rights in collective investment schemes
III. Ownership of investment linked Insurance schemes
IV. Interest in any CISs正確
Securities are defined in Schedule 1, SFO, to cover a wide range of instruments. Option III (Investment linked Insurance Scheme) is not covered by this definition.
錯誤
Securities are defined in Schedule 1, SFO, to cover a wide range of instruments. Option III (Investment linked Insurance Scheme) is not covered by this definition.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.3
-
496/567問題
496. 問題
1 分QID2428:According to the Securities and Futures Ordinance, which of the following is not securities?
正確
Options and their warrants are normally considered as derivatives. So futures options do not belong to securities.
錯誤
Options and their warrants are normally considered as derivatives. So futures options do not belong to securities.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.3
-
497/567問題
497. 問題
1 分QID325:Which of the following are not examples of securities?
I. Shares in a private company
II. Shares in a public company
III. Interests in CISs that are either registered mandatory
provident fund schemes under MPFSO, occupational
retirement schemes under ORSO
IV. Contracts of insurance in relation to any class of insurance
business under the Insurance Companies Ordinance (“ICO”).正確
Securities are defined in Schedule 1, SFO, to cover a wide range of instruments. Options I, III and IV are not covered by this definition.
錯誤
Securities are defined in Schedule 1, SFO, to cover a wide range of instruments. Options I, III and IV are not covered by this definition.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.3
-
498/567問題
498. 問題
1 分QID970:Which of the following are examples of security?
I. Listed Stocks
II. Equity Warrants
III. Derivative Warrants
IV. Bonds正確
A security is a tradable financial asset. The term commonly refers to any form of financial instrument including stocks, bonds and warrants.
錯誤
A security is a tradable financial asset. The term commonly refers to any form of financial instrument including stocks, bonds and warrants.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.3
-
499/567問題
499. 問題
1 分QID326:Which of the following are defined as Securities under s. 392, SFO as securities?
I. CISs
II. Bonds
III. Stocks
IV. Other interests prescribed by the Financial Secretary正確
Securities are defined in Schedule 1, SFO, to cover a wide range of instruments, including:
(a) shares, stocks, debentures, loan stocks, funds, bonds or notes;
(d) interests in CISs;
(f) interests, rights or property which are prescribed by the Financial Secretary under s. 392, SFO as securities.錯誤
Securities are defined in Schedule 1, SFO, to cover a wide range of instruments, including:
(a) shares, stocks, debentures, loan stocks, funds, bonds or notes;
(d) interests in CISs;
(f) interests, rights or property which are prescribed by the Financial Secretary under s. 392, SFO as securities.提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.3
-
500/567問題
500. 問題
1 分QID2363:Providing advice on which of the following transactions does not require a license from the SFC?
正確
Foreign collective investment schemes, regardless of whether they are recognized by the SFC, are securities; non-listed private bonds are also securities, and providing advice on securities requires a Type 4 regulated activity license;
Overseas futures are also futures, and providing advice on futures contracts requires a Type 5 regulated activity license;
Advising on unlisted real estate private companies is not a regulated activity and therefore does not require a license from the SFC.
It should be noted that shares of private companies are not securities, so providing advice on shares of private companies is not a regulated activity, and therefore does not need to apply for a SFC license.錯誤
Foreign collective investment schemes, regardless of whether they are recognized by the SFC, are securities; non-listed private bonds are also securities, and providing advice on securities requires a Type 4 regulated activity license;
Overseas futures are also futures, and providing advice on futures contracts requires a Type 5 regulated activity license;
Advising on unlisted real estate private companies is not a regulated activity and therefore does not require a license from the SFC.
It should be noted that shares of private companies are not securities, so providing advice on shares of private companies is not a regulated activity, and therefore does not need to apply for a SFC license.提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.3
-
501/567問題
501. 問題
1 分QID328:According to the Securities and Futures Ordinance, the definitions of securities include which of the following?
I. Stock options.
II. Stock futures.
III. All structured products.
IV. Interests in Collective Investment Schemes (CISs).正確
Securities are defined in Schedule 1, SFO, to cover a wide range of instruments, including:
(a) shares, stocks, debentures, loan stocks, funds, bonds or notes;
(d) interests in CISs.錯誤
Securities are defined in Schedule 1, SFO, to cover a wide range of instruments, including:
(a) shares, stocks, debentures, loan stocks, funds, bonds or notes;
(d) interests in CISs.提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.3
-
502/567問題
502. 問題
1 分QID1227:Which of the following entities can prescribe other arrangements on security by notice under s. 392 SFO?
正確
Interests, rights or property which are prescribed by the Financial Secretary under s. 392, SFO as securities.
錯誤
Interests, rights or property which are prescribed by the Financial Secretary under s. 392, SFO as securities.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.3
-
503/567問題
503. 問題
1 分QID222:Which of the following agencies or individuals may prescribe, by notice in the Gazette, new financial products as being (or not being) securities or futures contracts?
正確
Powers are given to the Financial Secretary to prescribe, by notice in the Gazette:
(a) new financial products as being (or not being) securities or futures contracts, and new financial arrangements as CISs, thus capturing new products in the regulatory net as appropriate (ss. 392 and 393, SFO)錯誤
Powers are given to the Financial Secretary to prescribe, by notice in the Gazette:
(a) new financial products as being (or not being) securities or futures contracts, and new financial arrangements as CISs, thus capturing new products in the regulatory net as appropriate (ss. 392 and 393, SFO)提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.3
-
504/567問題
504. 問題
1 分QID347:Which of the following types of interests in Collective Investment
Schemes (CISs) are not considered as securities?
I. A registered Mandatory Provident Fund scheme under the MPFSO or its constituent fund.
II. An occupational retirement scheme under the ORSO
III. A contract of insurance in relation to any class of insurance business under the Insurance Companies Ordinance.
IV. Real estate investments management as stipulated in the Securities and Futures Ordinance.正確
The definition of asset management speaking of managing
“securities”, is specifically includes interests in any CIS; but does not include any interest in a CIS that is:
(a) a registered Mandatory Provident Fund scheme under the MPFSO or its constituent fund;
(b) an occupational retirement scheme under the ORSO; or
© a contract of insurance in relation to any class of insurance business under the Insurance Ordinance.錯誤
The definition of asset management speaking of managing
“securities”, is specifically includes interests in any CIS; but does not include any interest in a CIS that is:
(a) a registered Mandatory Provident Fund scheme under the MPFSO or its constituent fund;
(b) an occupational retirement scheme under the ORSO; or
© a contract of insurance in relation to any class of insurance business under the Insurance Ordinance.提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.3
-
505/567問題
505. 問題
1 分QID221:What are the powers of the Financial Secretary in relation to securities?
正確
The Financial Secretary may prescribe new financial arrangements as CISs and new financial products as securities or futures contracts by issuing a notice in the Gazette, as per the powers granted under sections 392 and 393 of the SFO. This enables the inclusion of new products in the regulatory framework as appropriate.
錯誤
The Financial Secretary may prescribe new financial arrangements as CISs and new financial products as securities or futures contracts by issuing a notice in the Gazette, as per the powers granted under sections 392 and 393 of the SFO. This enables the inclusion of new products in the regulatory framework as appropriate.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.3
-
506/567問題
506. 問題
1 分QID2689:Under the Securities and Futures Ordinance, soliciting others to buy securities is classified as which type of regulated activity?
正確
Soliciting others to buy securities is defined as “dealing in securities,” which is a Type 1 Regulated Activity as per the Securities and Futures Ordinance. This includes making or offering to make an agreement, or inducing or attempting to induce another person to enter into an agreement for acquiring, disposing of, subscribing for, or underwriting securities.
錯誤
Soliciting others to buy securities is defined as “dealing in securities,” which is a Type 1 Regulated Activity as per the Securities and Futures Ordinance. This includes making or offering to make an agreement, or inducing or attempting to induce another person to enter into an agreement for acquiring, disposing of, subscribing for, or underwriting securities.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.8.9
-
507/567問題
507. 問題
1 分QID1229:Applicants for licences or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements. The main categories of the fit and proper requirements as stated in the SFO include:
I. the net worth and financial status of the applicant.
II. The educational or other qualifications or experience (having regard to the nature of the functions to be performed).
III. The ability to carry on the regulated activity competently, honestly and fairly.
IV. The reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity.正確
Both corporate (including officers e.g. directors, managers etc.) and individual applicants for licences or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements. There are four main categories of these fit and proper requirements (s. 129, SFO):
(a) financial status or solvency;
(b) educational or other qualifications or experience (having regard to the nature of the functions to be performed);
(c.) ability to carry on the RA competently, honestly and fairly; and
(d) reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity.錯誤
Both corporate (including officers e.g. directors, managers etc.) and individual applicants for licences or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements. There are four main categories of these fit and proper requirements (s. 129, SFO):
(a) financial status or solvency;
(b) educational or other qualifications or experience (having regard to the nature of the functions to be performed);
(c.) ability to carry on the RA competently, honestly and fairly; and
(d) reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity.提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.1
-
508/567問題
508. 問題
1 分QID2367:Mr. Wan got fined because of a public fight in Singapore last month. Mr. Wan is registering for a license now. He didn’t report this crime to avoid the hassle. Is there any wrong doing with Mr. Wan?
正確
Mr. Wan’s concealment of information from the SFC was a violation of the Securities and Futures Ordinance.
The Code of Conduct applies to licensed or registered persons.錯誤
Mr. Wan’s concealment of information from the SFC was a violation of the Securities and Futures Ordinance.
The Code of Conduct applies to licensed or registered persons.提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.1
-
509/567問題
509. 問題
1 分QID251:The fit and proper guidelines will judge a person’s fitness and properness by his/her,
I. financial status or solvency
II. Historic investment performance
III. Educational or other qualifications or experience, ability to carry on the regulated activity competently, honestly and fairly; and
IV. Reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity正確
The corporate (including its officers e.g. directors, managers, etc.) and individual applicants for licensing or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements stated in the Fit and Proper Guidelines. These relate to:
(a) financial status or solvency;
(b) educational or other qualifications or experience;
© ability to carry on the regulated activity competently, honestly and fairly; and
(d) reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity.錯誤
The corporate (including its officers e.g. directors, managers, etc.) and individual applicants for licensing or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements stated in the Fit and Proper Guidelines. These relate to:
(a) financial status or solvency;
(b) educational or other qualifications or experience;
© ability to carry on the regulated activity competently, honestly and fairly; and
(d) reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity.提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.1
-
510/567問題
510. 問題
1 分QID249:The fit and proper criteria for SFC licensing of corporations and individuals include matters relating to
I. Financial status or solvency
II. Competence
III. Capability
IV. Character.正確
The corporate (including its officers e.g. directors, managers, etc.) and individual applicants for licensing or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements stated in the Fit and Proper Guidelines. These relate to:
(a) financial status or solvency;
(b) educational or other qualifications or experience;
© ability to carry on the regulated activity competently, honestly and fairly; and
(d) reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity.錯誤
The corporate (including its officers e.g. directors, managers, etc.) and individual applicants for licensing or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements stated in the Fit and Proper Guidelines. These relate to:
(a) financial status or solvency;
(b) educational or other qualifications or experience;
© ability to carry on the regulated activity competently, honestly and fairly; and
(d) reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity.提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.1
-
511/567問題
511. 問題
1 分QID250:The fit and proper guidelines will judge a persons fit and properness by his/her,
I. financial status or solvency
II. historic investment profitability
III. academic attainment and competencies
IV. reputation and integrity正確
The corporate (including its officers e.g. directors, managers, etc.) and individual applicants for licensing or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements stated in the Fit and Proper Guidelines. These relate to:
(a) financial status or solvency;
(b) educational or other qualifications or experience;
© ability to carry on the regulated activity competently, honestly and fairly; and
(d) reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity.錯誤
The corporate (including its officers e.g. directors, managers, etc.) and individual applicants for licensing or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements stated in the Fit and Proper Guidelines. These relate to:
(a) financial status or solvency;
(b) educational or other qualifications or experience;
© ability to carry on the regulated activity competently, honestly and fairly; and
(d) reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity.提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.1
-
512/567問題
512. 問題
1 分QID2819:The fit and proper guidelines are less considered when processing applications for licences or registrations
正確
Factors to be considered in the Fit and Proper Guidelines:
1. The applicant’s financial situation
2. Whether the applicant has the ability to carry out the regulated activity competently and fairly
3. The character of the applicant
4. Applicant’s academic qualificationsHowever, applicants do not necessarily need a bachelor’s degree or above to meet the requirements, so it is the best out of the 4 options.
錯誤
Factors to be considered in the Fit and Proper Guidelines:
1. The applicant’s financial situation
2. Whether the applicant has the ability to carry out the regulated activity competently and fairly
3. The character of the applicant
4. Applicant’s academic qualificationsHowever, applicants do not necessarily need a bachelor’s degree or above to meet the requirements, so it is the best out of the 4 options.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.1
-
513/567問題
513. 問題
1 分QID2583:Which of the following will the SFC consider in the case of licensing a Type 1 representative?
i. Industry experience and/or educational level
ii. Must have 3 years of work experience in a Type 1 intermediary
iii. Whether or not he/she has been the management of an insolvent corporation
iv. Investment experience正確
Normally, passes in the subjects of [Chinese subject and Mathematics] or [English subject and Mathematics] in the High School Examination is the minimum educational level requirement for become a licensed representative, may or may not with the aid of a certain years of work experience in the industry. Also, if one has been the management of an insolvent corporation recently, it may hold him/her back from obtaining the license. However, you do not need the experience of participating in a type 1 firm as a staff member nor the experience in investment.
錯誤
Normally, passes in the subjects of [Chinese subject and Mathematics] or [English subject and Mathematics] in the High School Examination is the minimum educational level requirement for become a licensed representative, may or may not with the aid of a certain years of work experience in the industry. Also, if one has been the management of an insolvent corporation recently, it may hold him/her back from obtaining the license. However, you do not need the experience of participating in a type 1 firm as a staff member nor the experience in investment.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.1
-
514/567問題
514. 問題
1 分QID758:The Fit and proper guidelines of the SFO are more likely to apply to which of the following individuals or entities?
I. Company that’s applying for a license or registration.
II. Representative of company that’s applying for a license or registration.
III. Executive Director of company that’s applying for a license or registration.
IV. Professional Investor正確
The corporate (including its officers e.g. directors, managers, etc.) and individual applicants for licensing or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements stated in the Fit and Proper Guidelines. These requirements apply to applicants and to licensed and registered persons on an ongoing basis. Compliance with the requirements will be monitored by the HKMA in the case of AFIs and their executive officers and staff, and by the SFC in the case of others.
錯誤
The corporate (including its officers e.g. directors, managers, etc.) and individual applicants for licensing or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements stated in the Fit and Proper Guidelines. These requirements apply to applicants and to licensed and registered persons on an ongoing basis. Compliance with the requirements will be monitored by the HKMA in the case of AFIs and their executive officers and staff, and by the SFC in the case of others.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.1
-
515/567問題
515. 問題
1 分QID3098:Which of the following criteria must an individual satisfy when applying for a license with the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC)?
I. Meeting the fitness and properness criteria.
II. Demonstrating a basic knowledge of relevant business laws.
III. Being of good character.
IV. Having not been disqualified by the court from acting as a director.正確
An individual applying for a license with the SFC must meet the fitness and properness criteria, which includes being of good financial status, having the necessary qualifications or experience, being able to carry on the regulated activity competently, honestly, and fairly, and having a good reputation, character, reliability, and financial integrity. This encompasses a basic knowledge of relevant business laws, being of good character, and not having been disqualified by the court from acting as a director.
錯誤
An individual applying for a license with the SFC must meet the fitness and properness criteria, which includes being of good financial status, having the necessary qualifications or experience, being able to carry on the regulated activity competently, honestly, and fairly, and having a good reputation, character, reliability, and financial integrity. This encompasses a basic knowledge of relevant business laws, being of good character, and not having been disqualified by the court from acting as a director.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.1
-
516/567問題
516. 問題
1 分QID3097:Which of the following are ongoing obligations of a licensee under the Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO)?
I. Adhering to the Fit and Proper Guidelines.
II. Following the Guidelines on Competence.
III. Complying with the Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training (CPT). IV. Regularly attending informal industry networking events.正確
Licensees are required to adhere to the Fit and Proper Guidelines, follow the Guidelines on Competence, and comply with the Guidelines on CPT as part of their ongoing obligations under the SFO. Attending informal industry networking events is not a formal ongoing obligation.
錯誤
Licensees are required to adhere to the Fit and Proper Guidelines, follow the Guidelines on Competence, and comply with the Guidelines on CPT as part of their ongoing obligations under the SFO. Attending informal industry networking events is not a formal ongoing obligation.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.1
-
517/567問題
517. 問題
1 分QID1005:In considering the licence application or registration of Type 2 applicants, the SFC will consider which of the following?
I. The academic qualification of the applicants
II. The applicants’ character
III. The applicant’s experience in the industry
IV. The applicants’ financial status正確
The corporate (including its officers e.g. directors, managers, etc.) and individual applicants for licensing or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements stated in the Fit and Proper Guidelines. These relate to:
(a) financial status or solvency;
(b) educational or other qualifications or experience (having regard to the nature of the functions to be performed);
© ability to carry on the regulated activity competently, honestly and fairly; and
(d) reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity.錯誤
The corporate (including its officers e.g. directors, managers, etc.) and individual applicants for licensing or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements stated in the Fit and Proper Guidelines. These relate to:
(a) financial status or solvency;
(b) educational or other qualifications or experience (having regard to the nature of the functions to be performed);
© ability to carry on the regulated activity competently, honestly and fairly; and
(d) reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity.提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.1
-
518/567問題
518. 問題
1 分QID225:Registered Institutions should ensure that their employees who conduct regulated activities are
正確
The corporate (including its officers e.g. directors, managers, etc.) and individual applicants for licensing or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements stated in the Fit and Proper Guidelines. Thus, employees of registered institutions responsible for or conducting regulated activities are expected to comply with the SFC’s Fit and Proper Guidelines to ensure they are suitable for their roles, as monitored by the HKMA.
錯誤
The corporate (including its officers e.g. directors, managers, etc.) and individual applicants for licensing or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements stated in the Fit and Proper Guidelines. Thus, employees of registered institutions responsible for or conducting regulated activities are expected to comply with the SFC’s Fit and Proper Guidelines to ensure they are suitable for their roles, as monitored by the HKMA.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.1
-
519/567問題
519. 問題
1 分QID1665:SFC will not considered which of the following traits of an applicant’s when assessing the fit and properness of the applicant?
正確
SFC will not considered an applicant’s profitability while assessing its fit and properness.
錯誤
SFC will not considered an applicant’s profitability while assessing its fit and properness.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.1
-
520/567問題
520. 問題
1 分QID1230:Which of the following are categories of the fitness and properness requirements set by the SFO?
I. Net worth
II. Educational or other qualifications or experience
III. Ability to carry on the regulated activity competently, honestly and fairly
IV. Reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity正確
Both corporate (including officers e.g. directors, managers etc.) and individual applicants for licences or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements. There are four main categories of these fit and proper requirements (s. 129, SFO):
(a) financial status or solvency;
(b) educational or other qualifications or experience (having regard to the nature of the functions to be performed);
(c.) ability to carry on the RA competently, honestly and fairly; and
(d) reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity.錯誤
Both corporate (including officers e.g. directors, managers etc.) and individual applicants for licences or registration have to satisfy fitness and properness requirements. There are four main categories of these fit and proper requirements (s. 129, SFO):
(a) financial status or solvency;
(b) educational or other qualifications or experience (having regard to the nature of the functions to be performed);
(c.) ability to carry on the RA competently, honestly and fairly; and
(d) reputation, character, reliability and financial integrity.提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.1
-
521/567問題
521. 問題
1 分QID1235:The Guidelines on CPT set out the SFC’s requirements that the conduct and arrangements of CPT programmes are responsibilities of which of the following organizations or persons?
正確
The Guidelines on CPT set out the SFC’s requirements that, among other things,:
(a) corporations should conduct or arrange CPT programmes best suited for their staff to enhance their industry knowledge, skills and professionalism錯誤
The Guidelines on CPT set out the SFC’s requirements that, among other things,:
(a) corporations should conduct or arrange CPT programmes best suited for their staff to enhance their industry knowledge, skills and professionalism提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.15
-
522/567問題
522. 問題
1 分QID3093:Which of the following statements accurately reflect the CPT requirements for individual practitioners in Hong Kong?
I. Licensed representatives must undertake a minimum of twelve CPT hours per calendar year.
II. Responsible officers must complete at least two additional CPT hours related to regulatory compliance.
III. Each individual practitioner must complete at least five CPT hours on topics directly relevant to their licensed RAs. IV. New practitioners are required to complete two CPT hours on ethics within the first six months of practice.正確
Responsible officers are required to undertake a minimum of twelve CPT hours per calendar year, with two additional hours related to regulatory compliance. Each individual practitioner must complete at least five CPT hours on topics directly relevant to their licensed RAs. Licensed representatives are required to undertake a minimum of ten CPT hours, not twelve, and new practitioners must complete two CPT hours on ethics within 12 months, not six.
錯誤
Responsible officers are required to undertake a minimum of twelve CPT hours per calendar year, with two additional hours related to regulatory compliance. Each individual practitioner must complete at least five CPT hours on topics directly relevant to their licensed RAs. Licensed representatives are required to undertake a minimum of ten CPT hours, not twelve, and new practitioners must complete two CPT hours on ethics within 12 months, not six.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.16
-
523/567問題
523. 問題
1 分QID3094:Has Mr. Lee, a responsible officer, fulfilled the CPT requirements for the calendar year if he completed eight CPT hours on business management and four hours on themacro and micro economic analysis?
正確
Mr. Lee has not fulfilled the CPT requirements for the calendar year because, as a responsible officer, he is required to complete at least two CPT hours on topics relating to ethics or compliance. While he completed twelve hours in total, none were specifically on ethics or compliance.
錯誤
Mr. Lee has not fulfilled the CPT requirements for the calendar year because, as a responsible officer, he is required to complete at least two CPT hours on topics relating to ethics or compliance. While he completed twelve hours in total, none were specifically on ethics or compliance.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.16
-
524/567問題
524. 問題
1 分QID3092:Which of the following is a correct statement about the CPT requirements for individual practitioners in Hong Kong?
正確
Each individual practitioner must complete no less than two CPT hours on topics relating to ethics or compliance per calendar year. This statement is correct and reflects the CPT requirements as outlined.
錯誤
Each individual practitioner must complete no less than two CPT hours on topics relating to ethics or compliance per calendar year. This statement is correct and reflects the CPT requirements as outlined.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.16
-
525/567問題
525. 問題
1 分QID3091:How many Continuous Professional Training (CPT) hours must a licensed representative undertake per calendar year?
正確
A licensed representative is required to undertake a minimum of ten CPT hours per calendar year, regardless of the number and types of Regulated Activities they engage in.
錯誤
A licensed representative is required to undertake a minimum of ten CPT hours per calendar year, regardless of the number and types of Regulated Activities they engage in.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.16
-
526/567問題
526. 問題
1 分QID2916:According to the SFC’s “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”, how many hours of continuous training must a licensed representative or relevant person attend each calendar year?
正確
According to the SFC’s “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”, a licensed representative or relevant person must attend at least 10 hours of continuous training each calendar year.
錯誤
According to the SFC’s “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”, a licensed representative or relevant person must attend at least 10 hours of continuous training each calendar year.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.16
-
527/567問題
527. 問題
1 分QID2917:How many hours of continuous professional training related to professional ethics must a new individual practitioner complete within 12 months?
正確
According to the “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training” of the Securities and Futures Commission, new individual practitioners must complete 2 hours of continuous professional training related to professional ethics within 12 months.
錯誤
According to the “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training” of the Securities and Futures Commission, new individual practitioners must complete 2 hours of continuous professional training related to professional ethics within 12 months.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.16
-
528/567問題
528. 問題
1 分QID257:Mr Ko is a licensed representative of a licensed corporation -Kaohsiung Securities and conduct type 9 activities as a representative. According to the CPT requirement of the SFC, what kind of requirements should Mr Ko satisfy to be fit and proper?
正確
Under the SFC’s Guidelines on CPT: a licensed representative or relevant individual must undertake a minimum of ten CPT hours per calendar year (regardless of the number and types of regulated activities he or she engages in) while a responsible officer or executive officer must undertake a minimum of twelve CPT hours per calendar year (in which the two additional CPT hours should be related to regulatory compliance). So Mr Ko should ensure that he has at least 10 hours of CPT per year.
錯誤
Under the SFC’s Guidelines on CPT: a licensed representative or relevant individual must undertake a minimum of ten CPT hours per calendar year (regardless of the number and types of regulated activities he or she engages in) while a responsible officer or executive officer must undertake a minimum of twelve CPT hours per calendar year (in which the two additional CPT hours should be related to regulatory compliance). So Mr Ko should ensure that he has at least 10 hours of CPT per year.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.16
-
529/567問題
529. 問題
1 分QID1236:The SFC requires every individual licensee to undertake a minimum of how many CPT hours?
正確
A licensed representative or relevant individual must undertake a minimum of ten CPT hours per calendar year (regardless of the number and types of RAs he or she engages in).
錯誤
A licensed representative or relevant individual must undertake a minimum of ten CPT hours per calendar year (regardless of the number and types of RAs he or she engages in).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.16
-
530/567問題
530. 問題
1 分QID2866:Licenced Representatives and Relevant Individuals must ensure that they have more than how many hours of CPT per year?
正確
Licenced Representatives and Relevant Individuals must ensure that they have more than 10 hours of CPT per year?
錯誤
Licenced Representatives and Relevant Individuals must ensure that they have more than 10 hours of CPT per year?
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.16
-
531/567問題
531. 問題
1 分QID2867:RO and EO must ensure that they have more than how many hours of CPT per year?
正確
RO and EO must ensure that they have more than 12 hours of CPT per year. (The 2 extra hours should be related to regulator compliance).
錯誤
RO and EO must ensure that they have more than 12 hours of CPT per year. (The 2 extra hours should be related to regulator compliance).
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.16
-
532/567問題
532. 問題
1 分QID2868:Licenced Representatives and Relevant Individuals must ensure that they have more than how many hours of CPT per year directly related to their regulated activity?
正確
Licenced Representatives and Relevant Individuals must ensure that they have more than 5 hours of CPT directly related to their regulated activity.
錯誤
Licenced Representatives and Relevant Individuals must ensure that they have more than 5 hours of CPT directly related to their regulated activity.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.16
-
533/567問題
533. 問題
1 分QID2918:According to the “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training” of the Securities and Futures Commission, how many hours of continuous training must a responsible officer or executive officer attend each calendar year?
正確
According to the “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training” of the Securities and Futures Commission, a responsible officer or executive officer must attend at least 12 hours of continuous training each calendar year.
錯誤
According to the “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training” of the Securities and Futures Commission, a responsible officer or executive officer must attend at least 12 hours of continuous training each calendar year.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.16
-
534/567問題
534. 問題
1 分QID2869:RO and EO must ensure that they have more than how many hours of CPT per year directly related to their regulated activity?
正確
RO and EO must ensure that they have more than 5 hours of CPT directly related to their regulated activity.
錯誤
RO and EO must ensure that they have more than 5 hours of CPT directly related to their regulated activity.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.16
-
535/567問題
535. 問題
1 分QID3096:Which of the following activities could count towards Continuous Professional Training (CPT) for a licensed representative?
I. Participating in an online learning course about securities regulation.
II. Publishing a research paper on financial market trends.
III. Delivering a speech at a financial services conference.
IV. Regularly updating a personal blog with financial analysis.正確
Activities I, II, and III are structured learning activities that involve interaction with others or contribute to the industry’s knowledge base and are therefore considered CPT. Updating a personal blog, while educational, is not structured or verified as professional training.
錯誤
Activities I, II, and III are structured learning activities that involve interaction with others or contribute to the industry’s knowledge base and are therefore considered CPT. Updating a personal blog, while educational, is not structured or verified as professional training.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.17
-
536/567問題
536. 問題
1 分QID1666:Which of the following are not an acceptable method of CPT?
正確
Reading Financial Publications is not an acceptable form of acquiring CPT hours.
錯誤
Reading Financial Publications is not an acceptable form of acquiring CPT hours.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.17
-
537/567問題
537. 問題
1 分QID3095:Which of the following activities would be considered as Continuous Professional Training (CPT) for a licensed representative?
正確
CPT involves structured learning activities such as attending workshops, courses, or seminars. Reading financial newspapers and journals or undertaking normal work activities do not count as CPT because they do not involve interaction with other persons or may not be structured learning activities.
錯誤
CPT involves structured learning activities such as attending workshops, courses, or seminars. Reading financial newspapers and journals or undertaking normal work activities do not count as CPT because they do not involve interaction with other persons or may not be structured learning activities.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.17
-
538/567問題
538. 問題
1 分QID1577:Which of the following form of activity is not a prescribed method of attaining CPT hours under the Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training?
正確
CPT may be achieved through attending courses, workshops, lectures and seminars; distance learning; self-study with submission of assignments to recognised institutions; research; publications; speeches and so on.
錯誤
CPT may be achieved through attending courses, workshops, lectures and seminars; distance learning; self-study with submission of assignments to recognised institutions; research; publications; speeches and so on.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.17
-
539/567問題
539. 問題
1 分QID3099:Mr. Chan, a licensed representative, has attended a seminar on the latest developments in securities regulation and completed an online course on ethical practices in financial services. Which of these activities can be counted towards his CPT requirement?
正確
Both attending a seminar on securities regulation and completing an online course on ethical practices are structured learning activities that involve interaction with others or contribute to the industry’s knowledge base, and therefore both can be counted towards Mr. Chan’s CPT requirement.
錯誤
Both attending a seminar on securities regulation and completing an online course on ethical practices are structured learning activities that involve interaction with others or contribute to the industry’s knowledge base, and therefore both can be counted towards Mr. Chan’s CPT requirement.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.17
-
540/567問題
540. 問題
1 分QID3100:Ms. Wong, a compliance officer, is planning her CPT activities for the year. Which of the following activities should she include to meet the CPT requirements?
I. Attending a workshop on anti-money laundering.
II. Reading daily updates on financial markets.
III. Participating in a roundtable discussion on regulatory changes.
IV. Conducting internal training sessions on compliance standards.正確
CPT may be achieved through attending courses, workshops, lectures and seminars; distance learning with submission of assignments; self-study or online learning courses; industry research; publication of papers; delivery of speeches and so on. Making option I, III, IV is correct. However, reading financial journals, newspapers and other technical publications, and undertaking normal work and activities which do not involve interaction with other persons will not count as CPT. Making option II is incorrect.
錯誤
CPT may be achieved through attending courses, workshops, lectures and seminars; distance learning with submission of assignments; self-study or online learning courses; industry research; publication of papers; delivery of speeches and so on. Making option I, III, IV is correct. However, reading financial journals, newspapers and other technical publications, and undertaking normal work and activities which do not involve interaction with other persons will not count as CPT. Making option II is incorrect.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.17
-
541/567問題
541. 問題
1 分QID3102:Which of the following additional topics are relevant for Continuous Professional Training (CPT) purposes specifically for responsible officers, beyond the general topics for all licensees?
I. Business management
II. Risk management and control strategies
III. General principles of law
IV. Macroeconomic and microeconomic analysis正確
Responsible officers are required to undertake CPT on additional topics beyond those for licensees generally, which include business management, risk management and control strategies, and both macroeconomic and microeconomic analysis. General principles of law are a topic for all licensees and not an additional requirement for responsible officers.
錯誤
Responsible officers are required to undertake CPT on additional topics beyond those for licensees generally, which include business management, risk management and control strategies, and both macroeconomic and microeconomic analysis. General principles of law are a topic for all licensees and not an additional requirement for responsible officers.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.18
-
542/567問題
542. 問題
1 分QID2921:According to “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”, which of the following topics is not included in the continuous training for Responsible Officers?
正確
According to “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”, the topics related to the continuous training for Responsible Officers include business management, risk management and monitoring strategies, general management and supervision skills, macro and micro economic analysis, and financial reporting and quantitative analysis, etc., but do not include basic economic analysis, which is a topic for general Licensed Persons.
錯誤
According to “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”, the topics related to the continuous training for Responsible Officers include business management, risk management and monitoring strategies, general management and supervision skills, macro and micro economic analysis, and financial reporting and quantitative analysis, etc., but do not include basic economic analysis, which is a topic for general Licensed Persons.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.18
-
543/567問題
543. 問題
1 分QID2923:In the “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”, which areas do general licensed persons need to undergo continuous training in?
正確
According to “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”, the relevant topics for the continuous training of general licensed persons include environment, social and governance, fintech, cybersecurity, etc.
錯誤
According to “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”, the relevant topics for the continuous training of general licensed persons include environment, social and governance, fintech, cybersecurity, etc.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.18
-
544/567問題
544. 問題
1 分QID2920:According to the “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”, which of the following is not included in the continuous training related topics for general licensed persons?
正確
According to the “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”, the continuous training related topics for general licensed persons include applicable compliance guidelines, legal regulations and regulatory standards, market developments, newly launched financial products and risk management systems, and cybersecurity, etc., but do not include risk management and monitoring strategies, which is a topic for responsible officers.
錯誤
According to the “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”, the continuous training related topics for general licensed persons include applicable compliance guidelines, legal regulations and regulatory standards, market developments, newly launched financial products and risk management systems, and cybersecurity, etc., but do not include risk management and monitoring strategies, which is a topic for responsible officers.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.18
-
545/567問題
545. 問題
1 分QID3101:Which of the following is NOT a topic relevant for Continuous Professional Training (CPT) purposes for licensees generally?
正確
International trade laws are not listed as a relevant topic for CPT purposes for licensees generally. The topics mentioned for CPT include basic accounting theories, cybersecurity, and ESG, among others.
錯誤
International trade laws are not listed as a relevant topic for CPT purposes for licensees generally. The topics mentioned for CPT include basic accounting theories, cybersecurity, and ESG, among others.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.18
-
546/567問題
546. 問題
1 分QID3105:Which entities may initiate disciplinary proceedings against individuals for non-compliance with the Guidelines on CPT?
I. The SFC
II. The HKMA
III. The Securities and Exchange Commission
IV. Registered institutions正確
The SFC may initiate disciplinary proceedings against responsible officers and licensed representatives of licensed corporations, while the HKMA may do so against executive officers and relevant individuals of registered institutions for non-compliance with the Guidelines on CPT.
錯誤
The SFC may initiate disciplinary proceedings against responsible officers and licensed representatives of licensed corporations, while the HKMA may do so against executive officers and relevant individuals of registered institutions for non-compliance with the Guidelines on CPT.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.22
-
547/567問題
547. 問題
1 分QID3110:A licensed representative at a brokerage firm neglected to complete any CPT for the year and did not maintain records of previous CPT activities. What action is most likely to be taken by the SFC?
正確
Neglecting to complete CPT and failing to maintain records can lead to disciplinary proceedings by the SFC against the licensed representative.
錯誤
Neglecting to complete CPT and failing to maintain records can lead to disciplinary proceedings by the SFC against the licensed representative.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.22
-
548/567問題
548. 問題
1 分QID3109:Which of the following individuals are subject to the Guidelines on CPT?
I. Responsible officers of licensed corporations
II. Executive officers of registered institutions
III. Licensed representatives of licensed corporations
IV. Individuals registered by the HKMA performing regulated activities正確
Responsible officers and licensed representatives of licensed corporations, executive officers, and relevant individuals of registered institutions, including those registered by the HKMA performing regulated activities, are all subject to the Guidelines on CPT.
錯誤
Responsible officers and licensed representatives of licensed corporations, executive officers, and relevant individuals of registered institutions, including those registered by the HKMA performing regulated activities, are all subject to the Guidelines on CPT.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.22
-
549/567問題
549. 問題
1 分QID2922:What could be the consequences if certain individuals do not comply with the “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”?
正確
If certain individuals do not comply with the “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”, including maintaining appropriate records, their fit and proper qualifications for licensing or registration may be questioned, and it may trigger disciplinary action by the Securities and Futures Commission or the Monetary Authority.
錯誤
If certain individuals do not comply with the “Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training”, including maintaining appropriate records, their fit and proper qualifications for licensing or registration may be questioned, and it may trigger disciplinary action by the Securities and Futures Commission or the Monetary Authority.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.22
-
550/567問題
550. 問題
1 分QID3111:Which of the following actions can cast doubt on the fitness and properness of a licensed representative?
I. Failing to comply with the Guidelines on CPT
II. Keeping meticulous records of CPT
III. Undergoing disciplinary proceedings by the SFC
IV. Regularly attending SFC briefings正確
Failing to comply with the Guidelines on CPT and undergoing disciplinary proceedings by the SFC can cast doubt on the fitness and properness of a licensed representative. Keeping meticulous records and attending briefings are actions that would likely support their fitness and properness.
錯誤
Failing to comply with the Guidelines on CPT and undergoing disciplinary proceedings by the SFC can cast doubt on the fitness and properness of a licensed representative. Keeping meticulous records and attending briefings are actions that would likely support their fitness and properness.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.22
-
551/567問題
551. 問題
1 分QID3107:Which of the following are objectives of the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC)?
I. To maintain and promote market fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency, and orderliness
II. To provide banking services
III. To promote public understanding of the securities and futures industry
IV. To protect the investing public正確
The objectives of the SFC include maintaining and promoting the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency, and orderliness of the market, promoting public understanding of the securities and futures industry, and protecting the investing public. Providing banking services is not an objective of the SFC.
錯誤
The objectives of the SFC include maintaining and promoting the fairness, efficiency, competitiveness, transparency, and orderliness of the market, promoting public understanding of the securities and futures industry, and protecting the investing public. Providing banking services is not an objective of the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.22
-
552/567問題
552. 問題
1 分QID3108:In which scenario might the SFC consider a licensed representative unfit and improper?
正確
Failure to keep appropriate records of CPT can cast doubt on the fitness and properness of a licensed representative, potentially leading to disciplinary proceedings by the SFC.
錯誤
Failure to keep appropriate records of CPT can cast doubt on the fitness and properness of a licensed representative, potentially leading to disciplinary proceedings by the SFC.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.22
-
553/567問題
553. 問題
1 分QID3104:What may be the consequence for a licensed corporation’s responsible officers and licensed representatives if they fail to comply with the Guidelines on Continuous Professional Training (CPT)?
正確
Failure to comply with the Guidelines on CPT, including keeping appropriate records, may lead to disciplinary proceedings by the SFC against responsible officers and licensed representatives of licensed corporations.
錯誤
Failure to comply with the Guidelines on CPT, including keeping appropriate records, may lead to disciplinary proceedings by the SFC against responsible officers and licensed representatives of licensed corporations.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.22
-
554/567問題
554. 問題
1 分QID2806:What is the minimum age for a licensed representative?
正確
The minimum age to become a licensed representative is 18.
錯誤
The minimum age to become a licensed representative is 18.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.4
-
555/567問題
555. 問題
1 分QID1231:An individual applicant should meet age requirements (i.e. 18 years for representatives or equivalents) and competence qualifications as listed in the Fit and Proper Guidelines and amplified in the Guidelines on Competence. The competence tests include which of the following?
I. A relevant person’s experience.
II. A relevant person’s educational qualifications.
III. A relevant person’s past performance in the industry.
IV. A relevant person has not breached any codes or guidelines promulgated by the SFC or other regulators.正確
An individual applicant should meet age requirements (i.e. 18 years for representatives or equivalents) and competence qualifications as listed in the Fit and Proper Guidelines and amplified in the Guidelines on Competence. The competence tests involve experience and educational qualifications.
錯誤
An individual applicant should meet age requirements (i.e. 18 years for representatives or equivalents) and competence qualifications as listed in the Fit and Proper Guidelines and amplified in the Guidelines on Competence. The competence tests involve experience and educational qualifications.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.4&5
-
556/567問題
556. 問題
1 分QID861:The SFC will not take which of the following into consideration when measuring an applicants’ competence and integrity?
正確
An individual applicant should meet age requirements (i.e. 18 years for representatives or equivalents) and competence qualifications as listed in the Fit and Proper Guidelines and amplified in the Guidelines on Competence. The competence tests involve experience and educational qualifications. They don’t include investment track records.
錯誤
An individual applicant should meet age requirements (i.e. 18 years for representatives or equivalents) and competence qualifications as listed in the Fit and Proper Guidelines and amplified in the Guidelines on Competence. The competence tests involve experience and educational qualifications. They don’t include investment track records.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.5
-
557/567問題
557. 問題
1 分QID1232:Which of the following are part of the competence and capability tests of the SFC and HKMA?
I. Experience.
II. Educational qualifications.
III. Performance in the Industry.
IV. An undischarged or recently discharged bankrupt, be currently involved in bankruptcy or similar proceedings or have failed to meet any judgment debt.正確
The competence tests involve experience and educational qualifications.
錯誤
The competence tests involve experience and educational qualifications.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.5
-
558/567問題
558. 問題
1 分QID252:Mr Wan would like to become a licenced representative and conduct securities dealing business. He has already acquired a pass in the Paper 1, Paper 7 and Paper 8 of the Licencing Exam. Which of the following experience of Mr Wan may not have an adverse effect
正確
Option 1, 3 and 4 will adversely affect Mr. Wan to become a licensed representative given the following:
Individual applicants for licensing or registration should satisfy the SFC (or the HKMA as appropriate) that he:
(a) is of good character;
(b) has not breached any codes or guidelines promulgated by the SFC or other regulators;
(c) has not been subject to disciplinary action by professional associations;
(d) has not been disqualified by the court from acting as a director, as detailed in the Fit and Proper Guidelines; and
€ has not been a director or substantial shareholder of, or been involved in managing, an insolvent corporation.錯誤
Option 1, 3 and 4 will adversely affect Mr. Wan to become a licensed representative given the following:
Individual applicants for licensing or registration should satisfy the SFC (or the HKMA as appropriate) that he:
(a) is of good character;
(b) has not breached any codes or guidelines promulgated by the SFC or other regulators;
(c) has not been subject to disciplinary action by professional associations;
(d) has not been disqualified by the court from acting as a director, as detailed in the Fit and Proper Guidelines; and
€ has not been a director or substantial shareholder of, or been involved in managing, an insolvent corporation.提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.6
-
559/567問題
559. 問題
1 分QID1233:Which of the following criteria does the SFC NOT taken into account of when considering an applicant’s character and integrity?
正確
An individual applicant should satisfy the SFC (or the HKMA as appropriate) that he:
(b) has not breached any codes or guidelines promulgated by the SFC or other regulators;
(c) has not been subject to disciplinary action by professional associations;
(d) has not been disqualified by the court from acting as a director, as detailed in the Fit and Proper Guidelines; and
(e) has not been a director or substantial shareholder of, or been involved in managing, an insolvent corporation.
Therefore, only D is not considered by theSFC.錯誤
An individual applicant should satisfy the SFC (or the HKMA as appropriate) that he:
(b) has not breached any codes or guidelines promulgated by the SFC or other regulators;
(c) has not been subject to disciplinary action by professional associations;
(d) has not been disqualified by the court from acting as a director, as detailed in the Fit and Proper Guidelines; and
(e) has not been a director or substantial shareholder of, or been involved in managing, an insolvent corporation.
Therefore, only D is not considered by theSFC.提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.6
-
560/567問題
560. 問題
1 分QID253:Kaohsiung Securities is a licensed corporation that conduct asset management businesses. Recently Kaohsiung Securities is having civil litigations overseas which might adversely affects its financial well being. Should Kaohsiung contact the SFC regarding such events?
正確
An intermediary should:
(a) be able to comply with the capital requirements: for licensed corporations, the FRR; for registered institutions, the HKMA’s capital adequacy requirements; and
(b) not be subject to bankruptcy proceedings or have failed to meet a judgment debt.
In this case, if the Kaohsiung Securities will be adversely affected economically by an unfavorable judgment, it would be better to notify the China Securities Regulatory Commission in advance, so choose A.錯誤
An intermediary should:
(a) be able to comply with the capital requirements: for licensed corporations, the FRR; for registered institutions, the HKMA’s capital adequacy requirements; and
(b) not be subject to bankruptcy proceedings or have failed to meet a judgment debt.
In this case, if the Kaohsiung Securities will be adversely affected economically by an unfavorable judgment, it would be better to notify the China Securities Regulatory Commission in advance, so choose A.提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.7
-
561/567問題
561. 問題
1 分QID1234:Which of the following descriptions about an intermediary’s ability to comply with the capital requirements are accurate?
I. Registered institutions should comply with HKMA’s capital adequacy requirements.
II. Licensed corporation should comply with SFC’s FRR.
III. Licensed corporation should comply with HKMA’s capital adequacy requirements.
IV. Registered Institutions should comply with SFC’s FRR.正確
An intermediary should:
(a) be able to comply with the capital requirements: for licensed corporations the FRR, and for registered institutions the HKMA’s capital adequacy requirements.錯誤
An intermediary should:
(a) be able to comply with the capital requirements: for licensed corporations the FRR, and for registered institutions the HKMA’s capital adequacy requirements.提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.7
-
562/567問題
562. 問題
1 分QID3117:In assessing the competence of a corporation, which of the following factors would the SFC consider as part of the corporation’s corporate governance and internal controls?
I. The presence of a board of directors with defined roles and responsibilities. II. The establishment of a marketing department to promote services.
III. The implementation of proper compliance policies and procedures.
IV. The qualification of employees and supervisory staff.正確
The SFC considers proper organizational structure based on good corporate governance principles, proper compliance policies and procedures, and appropriately qualified employees with supervisory staff having at least three years’ relevant experience and appropriate qualifications as part of a corporation’s competence assessment. The establishment of a marketing department is not mentioned as a factor in corporate governance and internal controls.
錯誤
The SFC considers proper organizational structure based on good corporate governance principles, proper compliance policies and procedures, and appropriately qualified employees with supervisory staff having at least three years’ relevant experience and appropriate qualifications as part of a corporation’s competence assessment. The establishment of a marketing department is not mentioned as a factor in corporate governance and internal controls.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.8
-
563/567問題
563. 問題
1 分QID3112:What is a key element the SFC considers when determining the competence of a corporation?
正確
The SFC considers various key elements, including the combined competence of senior management and other staff members, when determining whether a corporation is competent. Options A, C, and D are not mentioned as key elements.
錯誤
The SFC considers various key elements, including the combined competence of senior management and other staff members, when determining whether a corporation is competent. Options A, C, and D are not mentioned as key elements.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.8
-
564/567問題
564. 問題
1 分QID3113:Which of the following are considered by the SFC when assessing the competence of a corporation?
I. Proper organizational structure based on good corporate governance principles. II. Presence of a competent risk manager or MIC of the risk management function. III. Adequate and effective internal control systems.
IV. The corporation’s financial performance in the last fiscal year.正確
The SFC considers proper organizational structure, presence of a competent risk manager or MIC, and adequate and effective internal control systems as key elements of a corporation’s competence. The corporation’s financial performance in the last fiscal year, while relevant to corporate competence, is not as a key element, making option IV incorrect.
錯誤
The SFC considers proper organizational structure, presence of a competent risk manager or MIC, and adequate and effective internal control systems as key elements of a corporation’s competence. The corporation’s financial performance in the last fiscal year, while relevant to corporate competence, is not as a key element, making option IV incorrect.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.8
-
565/567問題
565. 問題
1 分QID3114:Who must have at least three years’ relevant experience and appropriate qualifications as part of a corporation’s competence assessment?
正確
The SFC requires that supervisory staff have at least three years’ relevant experience and appropriate qualifications as part of the corporation’s competence assessment. Options A, B, and C are not specified regarding this requirement.
錯誤
The SFC requires that supervisory staff have at least three years’ relevant experience and appropriate qualifications as part of the corporation’s competence assessment. Options A, B, and C are not specified regarding this requirement.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.8
-
566/567問題
566. 問題
1 分QID3116:A corporation under review by the SFC has established risk management policies under the direct supervision of the CEO, who also handles other executive functions. Is this arrangement compliant with the SFC’s expectations for an independent risk management function?
正確
The SFC expects risk management policies, controls, and procedures to be established as an independent function under a competent risk manager or MIC of the risk management function. Having them under the direct supervision of the CEO, who handles other executive functions, does not comply with the expectation of independence.
錯誤
The SFC expects risk management policies, controls, and procedures to be established as an independent function under a competent risk manager or MIC of the risk management function. Having them under the direct supervision of the CEO, who handles other executive functions, does not comply with the expectation of independence.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.8
-
567/567問題
567. 問題
1 分QID3115:Which of the following internal control elements are required by the SFC for a corporation to demonstrate competence?
I. Proper internal audit trails and documentation.
II. Independent and qualified operational review personnel.
III. Compliance policies to ensure adherence to internal policies only.
IV. Risk management policies established under the financial manager.正確
The SFC requires adequate and effective internal control systems with proper internal audit trails and documentation, as well as independent and qualified operational review personnel. Compliance policies must ensure adherence to all applicable legal and regulatory requirements, not just internal policies, making option III incorrect. Risk management policies should be established as an independent function, not necessarily under the financial manager, making option IV incorrect.
錯誤
The SFC requires adequate and effective internal control systems with proper internal audit trails and documentation, as well as independent and qualified operational review personnel. Compliance policies must ensure adherence to all applicable legal and regulatory requirements, not just internal policies, making option III incorrect. Risk management policies should be established as an independent function, not necessarily under the financial manager, making option IV incorrect.
提示
Reference Chapter:1.9.8
✎ 操作方法 Tutorial